Neuromuscular blockade enables airway management, ventilation and surgical procedures. However there is no national consensus on its routine clinical use. The objective was to establish the degree of agreement among anaesthesiologists and general surgeons on the clinical use of neuromuscular blockade in order to make recommendations to improve its use during surgical procedures.
MethodsMultidisciplinary consensus study in Spain. Anaesthesiologists experts in neuromuscular blockade management (n=65) and general surgeons (n=36) were included. Delphi methodology was selected. A survey with 17 final questions developed by a dedicated scientific committee was designed. The experts answered the successive questions in two waves. The survey included questions on: type of surgery, type of patient, benefits/harm during and after surgery, impact of objective neuromuscular monitoring and use of reversal drugs, viability of a multidisciplinary and efficient approach to the whole surgical procedure, focusing on the level of neuromuscular blockade.
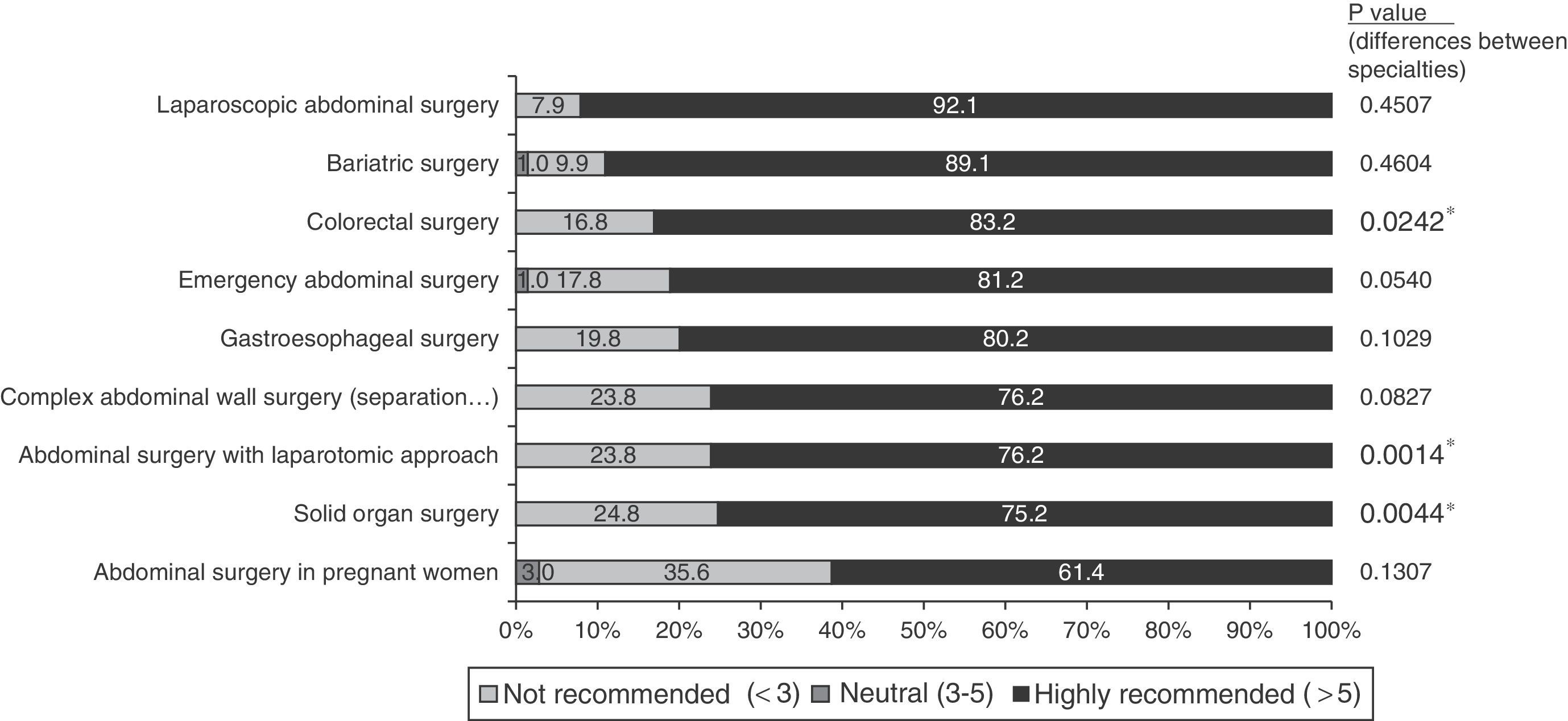
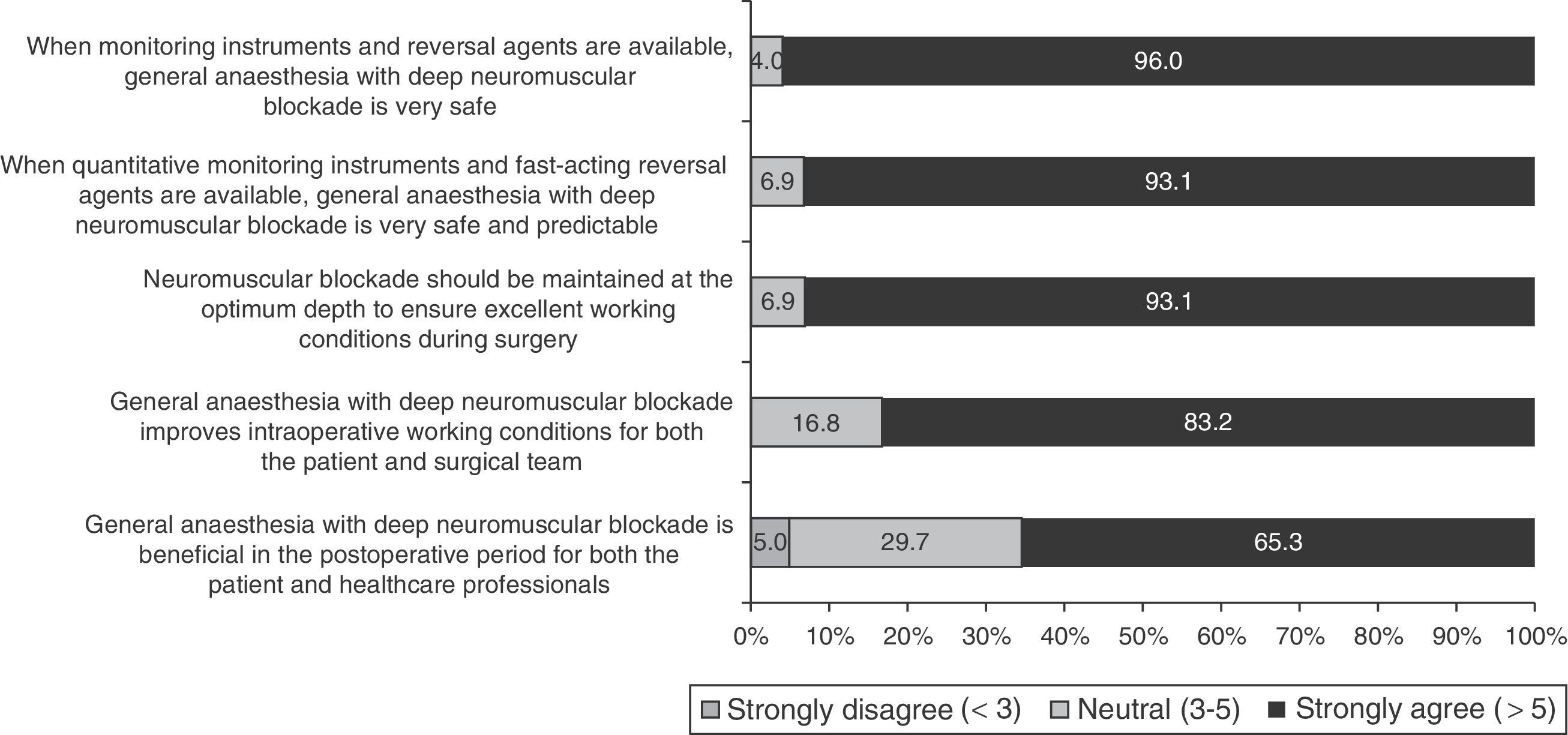
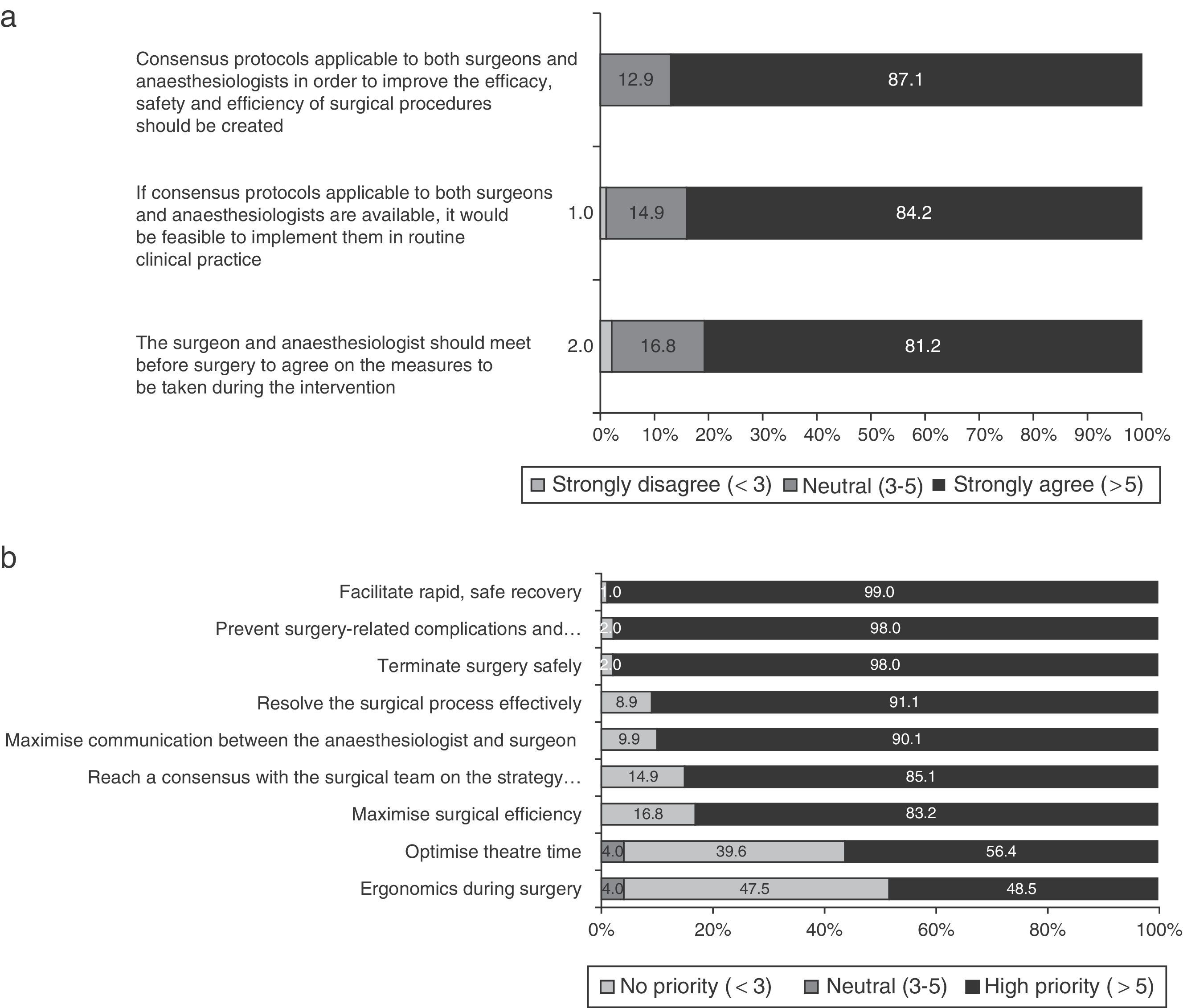
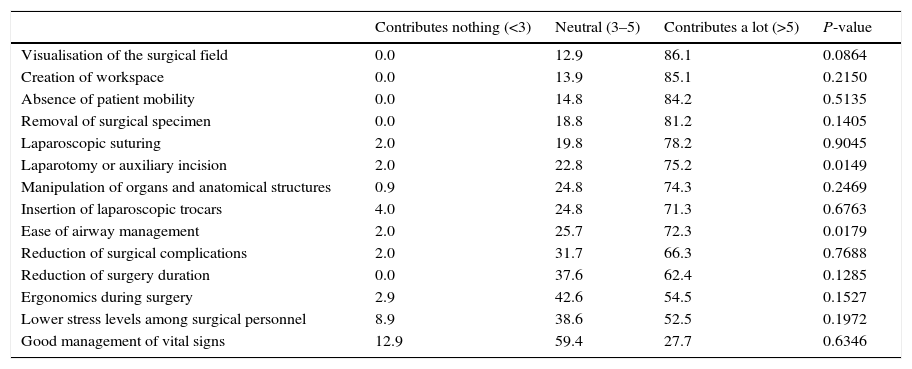
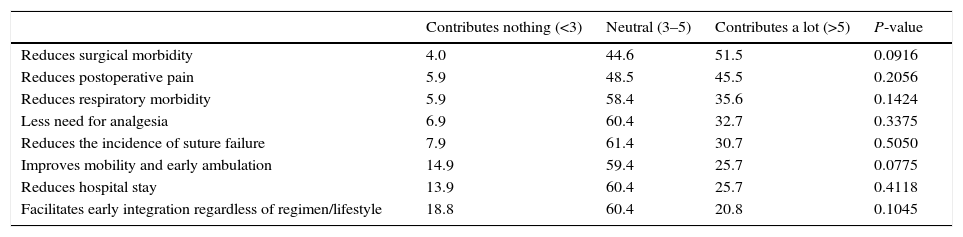
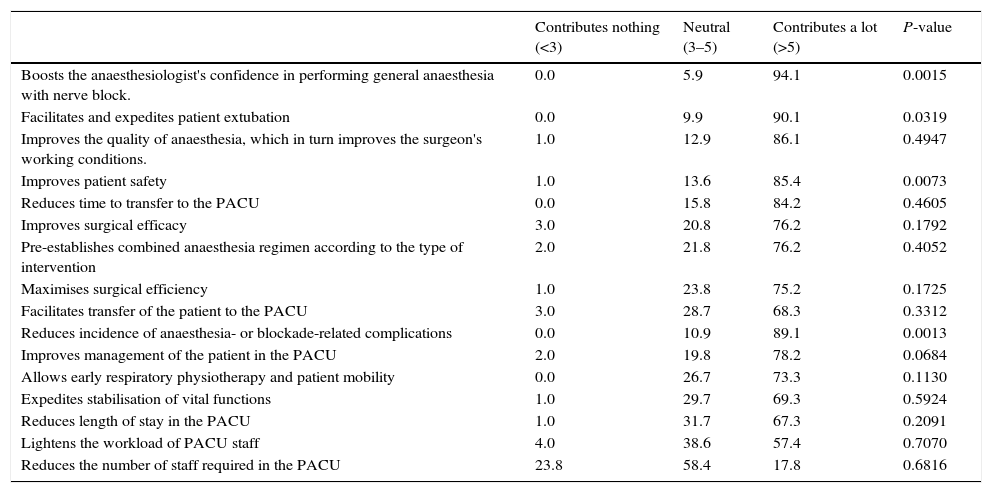
ResultsFive recommendations were agreed: (1) deep neuromuscular blockade is very appropriate for abdominal surgery (degree of agreement 94.1%), (2) and in obese patients (76.2%); (3) deep neuromuscular blockade maintenance until end of surgery might be beneficial in terms of clinical aspects, such as immobility or better surgical access (86.1–72.3%); (4) quantitative monitoring and reversal drugs availability is recommended (89.1%); finally (5) anaesthesiologists/surgeons joint protocols are recommended.
ConclusionsCollaboration among anaesthesiologists and surgeons has enabled some general recommendations to be established on deep neuromuscular blockade use during abdominal surgery.
El bloqueo neuromuscular facilita la manipulación de la vía aérea, la ventilación y procedimientos quirúrgicos, pero no hay un consenso a nivel nacional que facilite la práctica clínica habitual. El objetivo fue conocer el grado de acuerdo entre anestesiólogos y cirujanos sobre el uso clínico del bloqueo neuromuscular, para establecer recomendaciones de mejora de su empleo durante un procedimiento anestésico-quirúrgico.
MétodosEstudio de consenso multidisciplinar en España, que incluyó anestesiólogos expertos en bloqueo neuromuscular (n=65) y cirujanos generales (n=36). Se utilizó metodología Delphi. Cuestionario con 17 preguntas consensuado por un comité científico, al que respondieron los expertos en dos olas. El cuestionario incluyó preguntas sobre: tipo de cirugía, tipo de paciente, beneficios/perjuicios durante y después de la cirugía, repercusión de la monitorización objetiva y del uso de fármacos reversores, la viabilidad de abordaje multidisciplinar y eficiente del procedimiento quirúrgico, enfocado en el grado de bloqueo neuromuscular.
ResultadosSe establecieron cinco recomendaciones: 1) el bloqueo neuromuscular profundo es muy adecuado en cirugía abdominal (grado de acuerdo 94,1%), y 2) en pacientes con obesidad (76,2%); 3) el mantenimiento del bloqueo neuromuscular profundo hasta el final de la cirugía puede ser beneficioso en aspectos clínicos, como inmovilidad del paciente o mejor acceso quirúrgico (86,1 y 72,3%); 4) la monitorización cuantitativa y la disponibilidad de reversores del bloqueo neuromuscular es recomendable (89,1%); 5) se recomiendan protocolos de actuación conjuntos entre anestesiólogos y cirujanos.
ConclusionesLa colaboración entre anestesiólogos y cirujanos generales, ha permitido establecer una serie de recomendaciones genéricas sobre el uso de bloqueo neuromuscular profundo en cirugía abdominal.