The quality of postoperative recovery is one of the most important among all the quality indicators used in clinical situations. This is even more important after cancer surgery. Our aim was to evaluate this after non-reconstructive breast surgery under general anaesthesia and paravertebral blockade or serratus–intercostal plane blockade, in the early and late post-operative period.
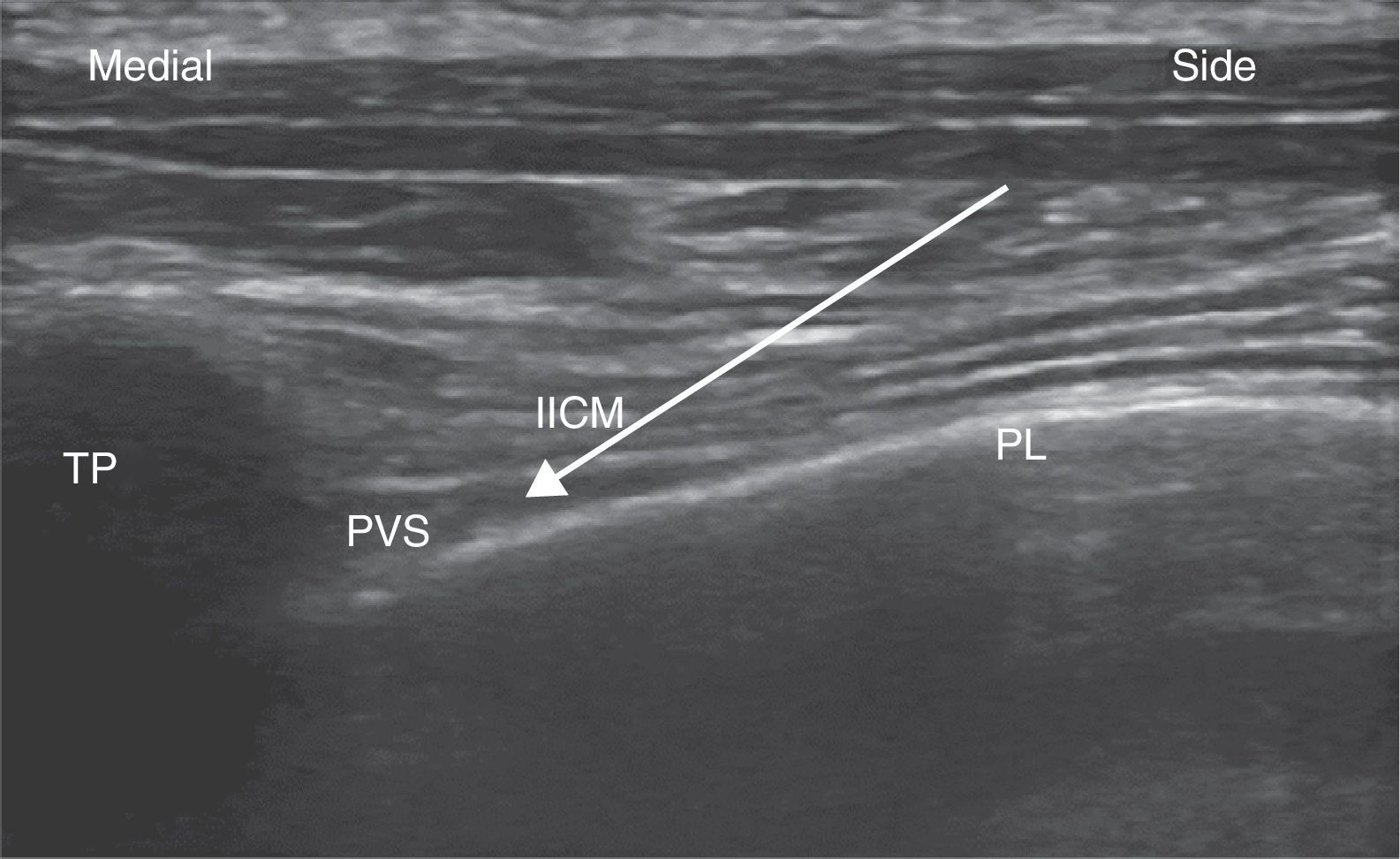
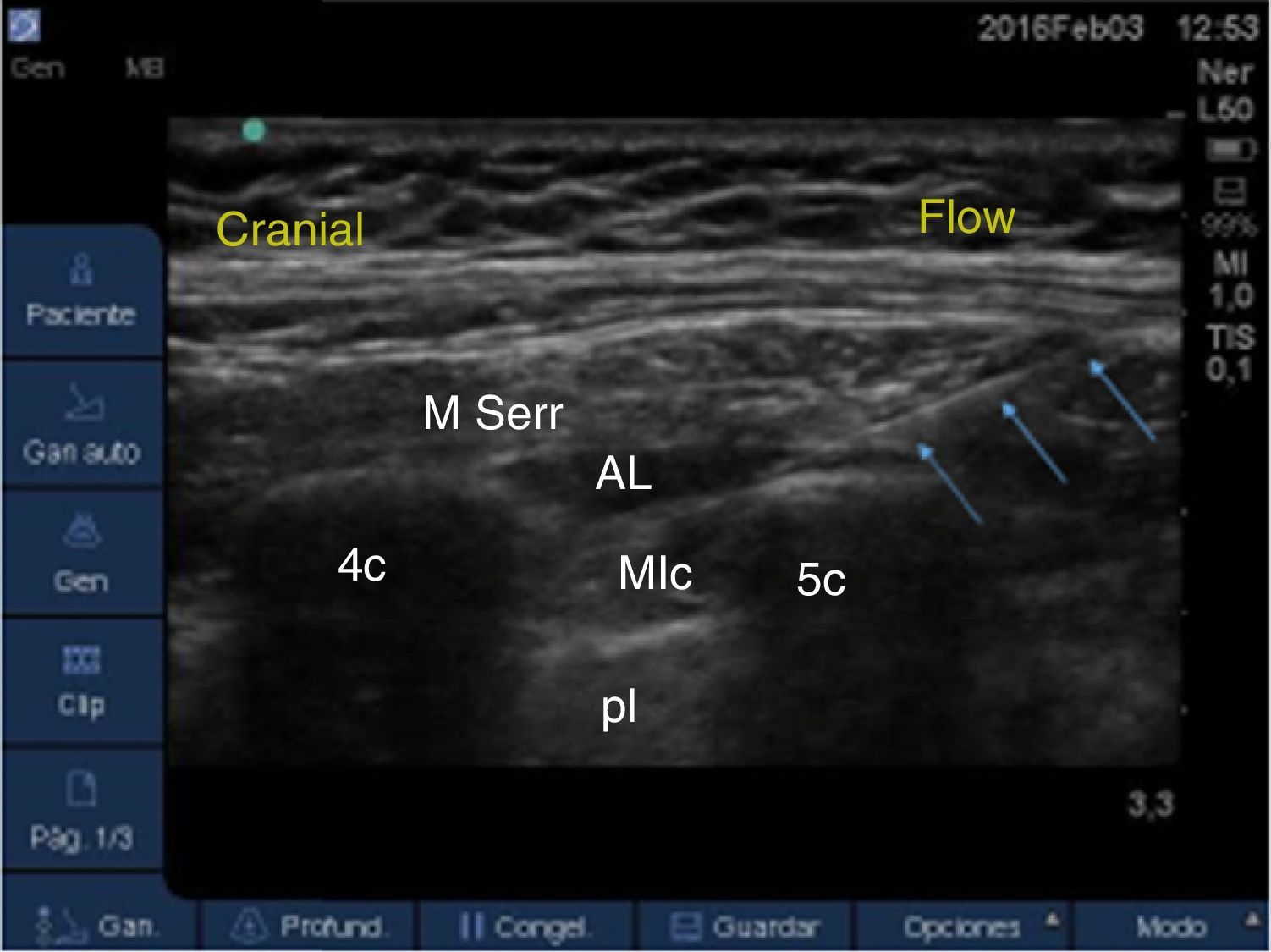
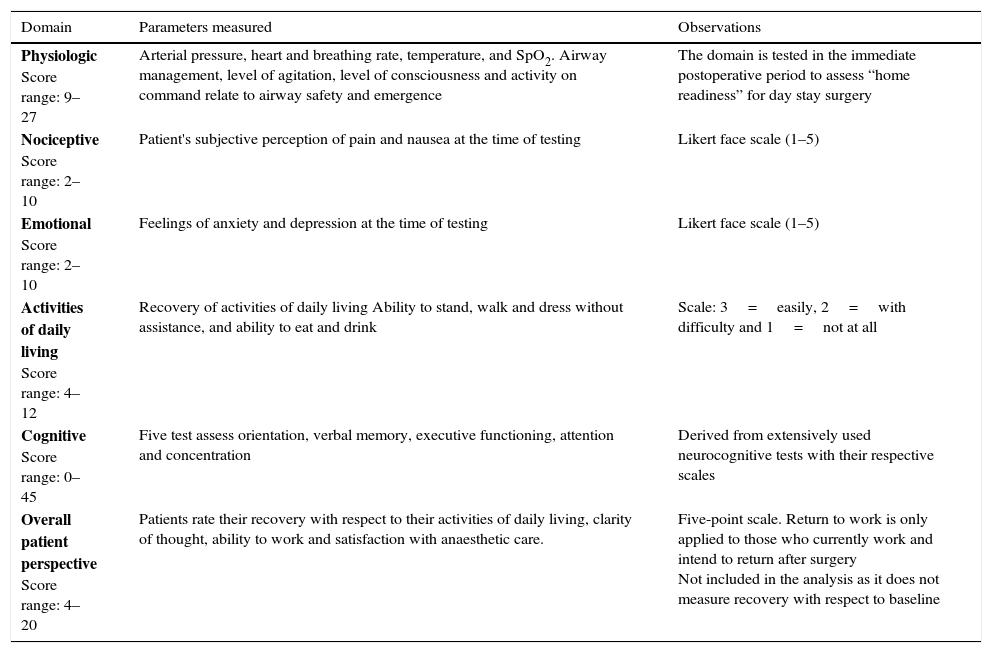
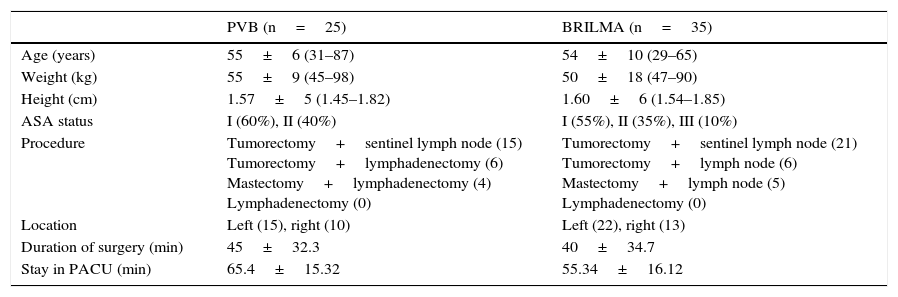
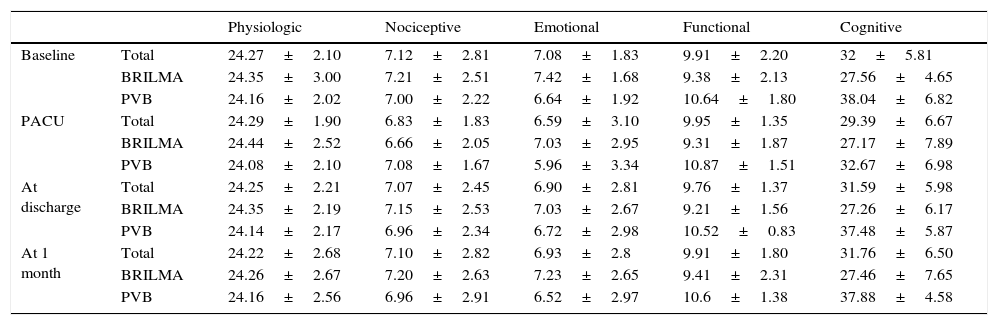
Material and methodsA prospective observational study was conducted on 60 patients (25 paravertebral blockade group and 35 serratus–intercostal plane blockade group) scheduled for non-reconstructive breast surgery during a 6 month period. Every patient received general anaesthesia and were randomised to receive either paravertebral blockade or serratus–intercostal plane blockade. The quality of post-anaesthetic recovery was quantified by Postoperative Quality Recovery Scale, which is used to assess physiological, nociceptive, emotional, autonomy, cognitive and general state domains at different times: baseline (before surgery), 15min after the end of surgery, at discharge to home, and one month after surgery.
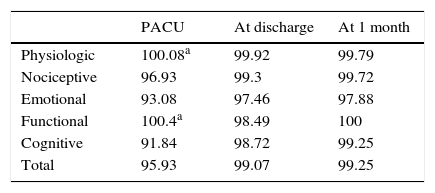
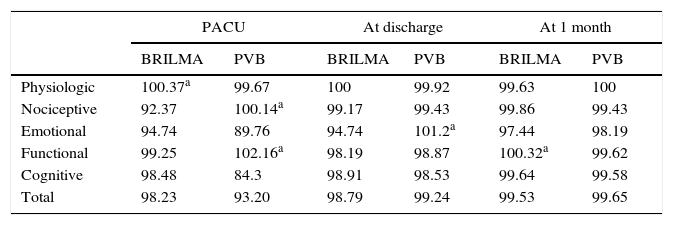
ResultsA total recovery of 95.93% was achieved in the early postoperative period (15min PACU), 99.07% at discharge to home, and 99.25% at one month after the intervention. No significant differences were found between groups in total score or in each evaluated area.
ConclusionsA progressive improvement was observed in the scores assessed with the Postoperative Quality Recovery Scale, reaching values that would allow the discharge to home and early return to usual active life from the immediate postoperative period, with no significant differences between the 2 analgesic techniques. Savings in opioid use and the excellent recovery were observed in all measured domains observed.
La cuantificación de la calidad de la recuperación posquirúrgica destaca entre los indicadores de calidad utilizados en clínica. Ello es más importante aún tras cirugía oncológica. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la calidad de la recuperación tras cirugía no reconstructiva de mama tras anestesia general combinada con bloqueo paravertebral versus bloqueo del espacio serrato-intercostal en el postoperatorio inmediato y tardío.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo en 60 pacientes programadas para cirugía no reconstructiva de mama en un periodo de 6 meses bajo anestesia combinada general y bloqueo paravertebral (25 pacientes) o bloqueo del espacio serrato-intercostal (35 pacientes). La calidad de la recuperación postanestésica se midió con la escala Postoperative Quality Recovery Scale, valorando los dominios fisiológico, nociceptivo, emocional, autonomía, cognitivo y estado general en diferentes momentos: basal (previo a cirugía), 15min tras finalizar la intervención, al alta hospitalaria y al mes postintervención.
ResultadosSe consiguió una recuperación total del 95,93% en el postoperatorio inmediato (15min unidad de recuperación postoperatoria [URPA]), del 99,07% al alta y del 99,25% al mes de la intervención. No se encontraron diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos ni en la puntuación total ni en las diversas áreas medidas por la escala.
ConclusionesCon la técnica descrita se ha objetivado una alta puntuación de recuperación con la Postoperative Quality Recovery Scale, que posibilitaría el alta en el postoperatorio inmediato y la vuelta precoz a la vida activa habitual. En ambos grupos se observó un ahorro de opioides y una recuperación excelente de todos los dominios evaluados, sin diferencias significativas.