Mutations in the exon 4 of the COMT gene are associated with chronic persistent surgical pain (CPSP). Especially COMT mutated allele G472A (Val158Met) associated with CPSP patients is reported in different ethnic population. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of genetic mutations and structural variations in exon 4 of COMT that can be related to the appearance of CPSP in patients under sternotomy.
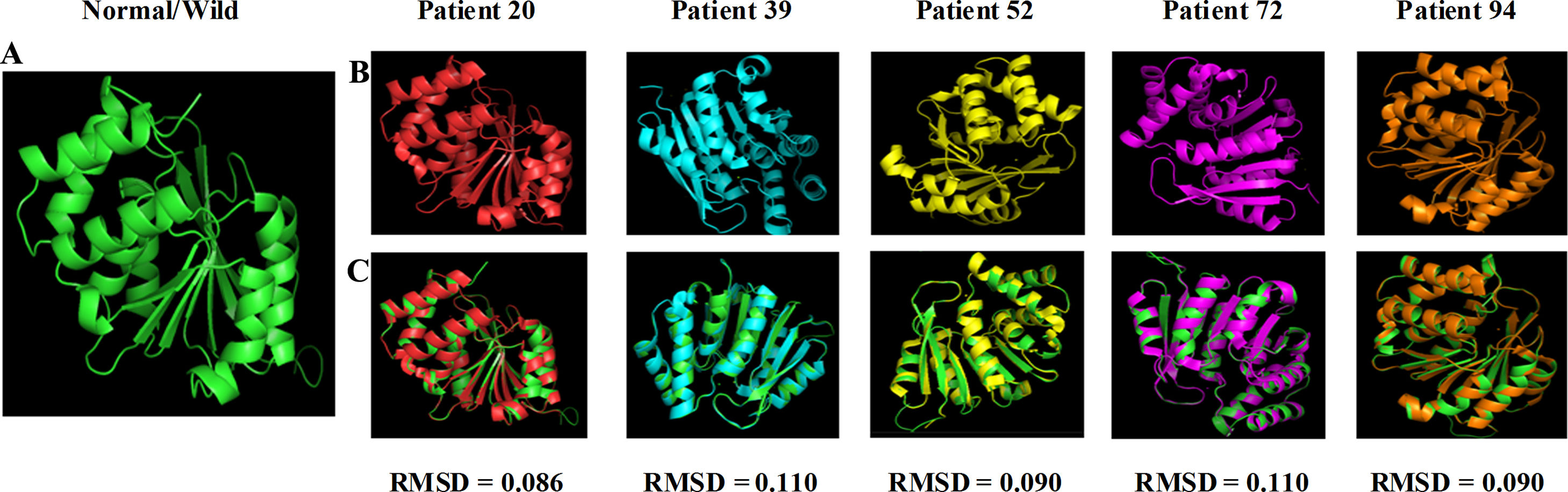
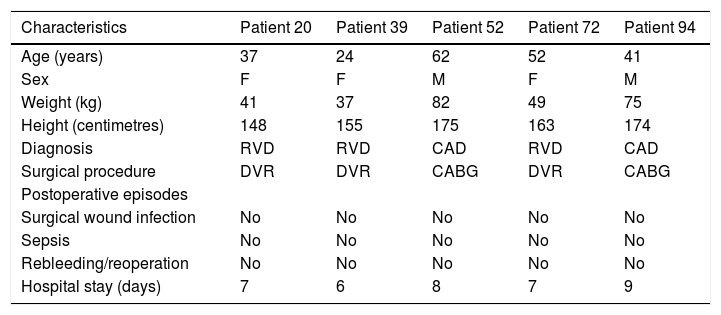
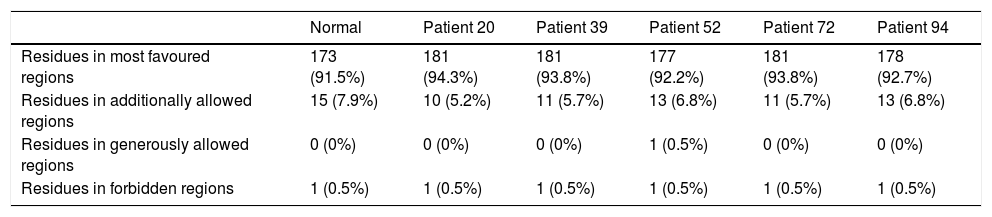
Materials and methodsOne hundred patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status grades I, II and III, who underwent sternotomy procedures, were selected to assess the development and magnitude of the CPSP evaluated with pain questionaries’ at the end of three months after surgery. This was correlated with COMT allele presence. The exon 4 of COMT gene (that contains the G472A allele) was studied. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were sequenced and mutated sequences were deposited in GenBank®. The structural analysis of COMT was performed using ProCheck® and distortions of three-dimensional tertiary structural orientation was evaluated with root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) score.
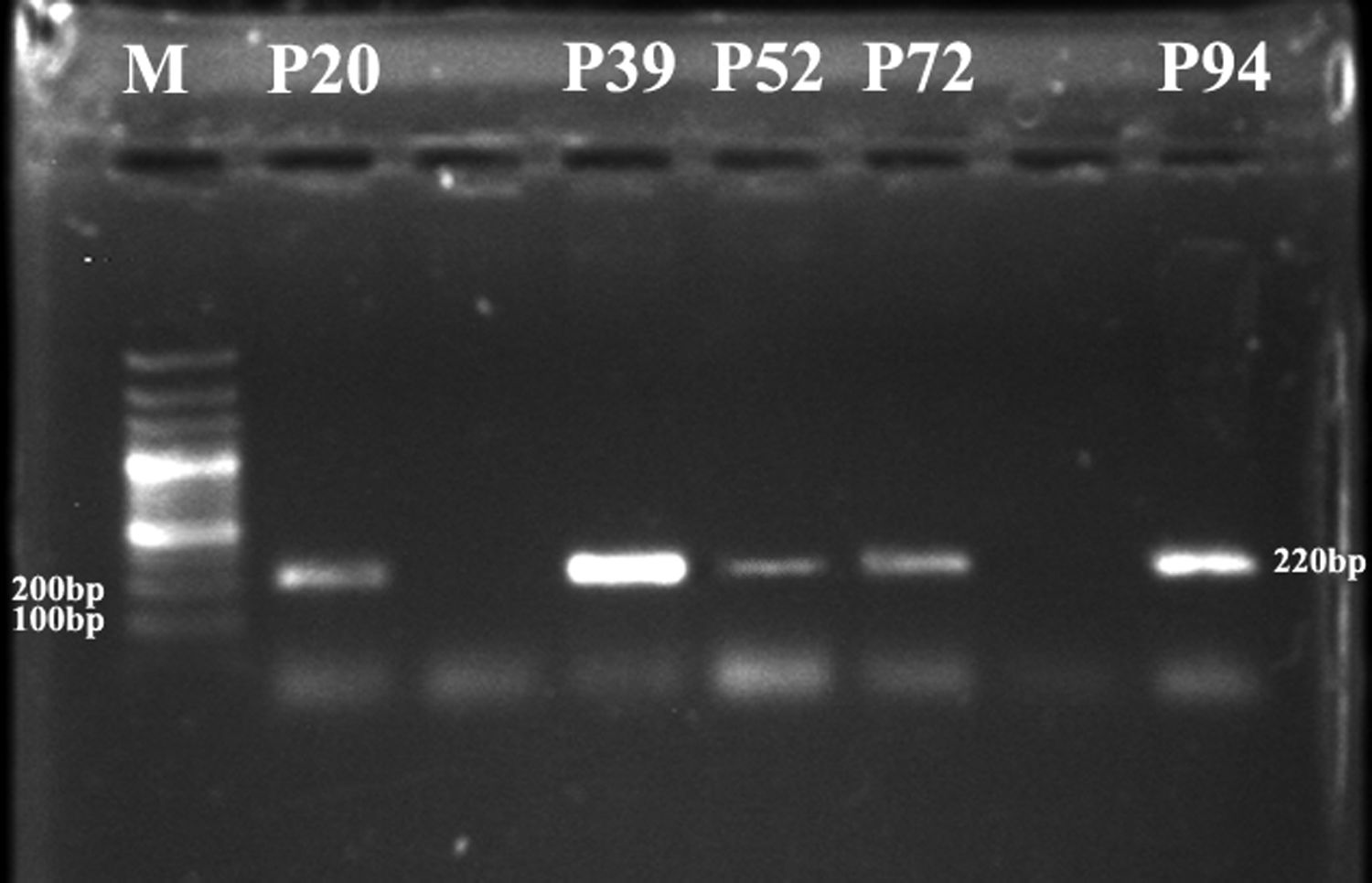
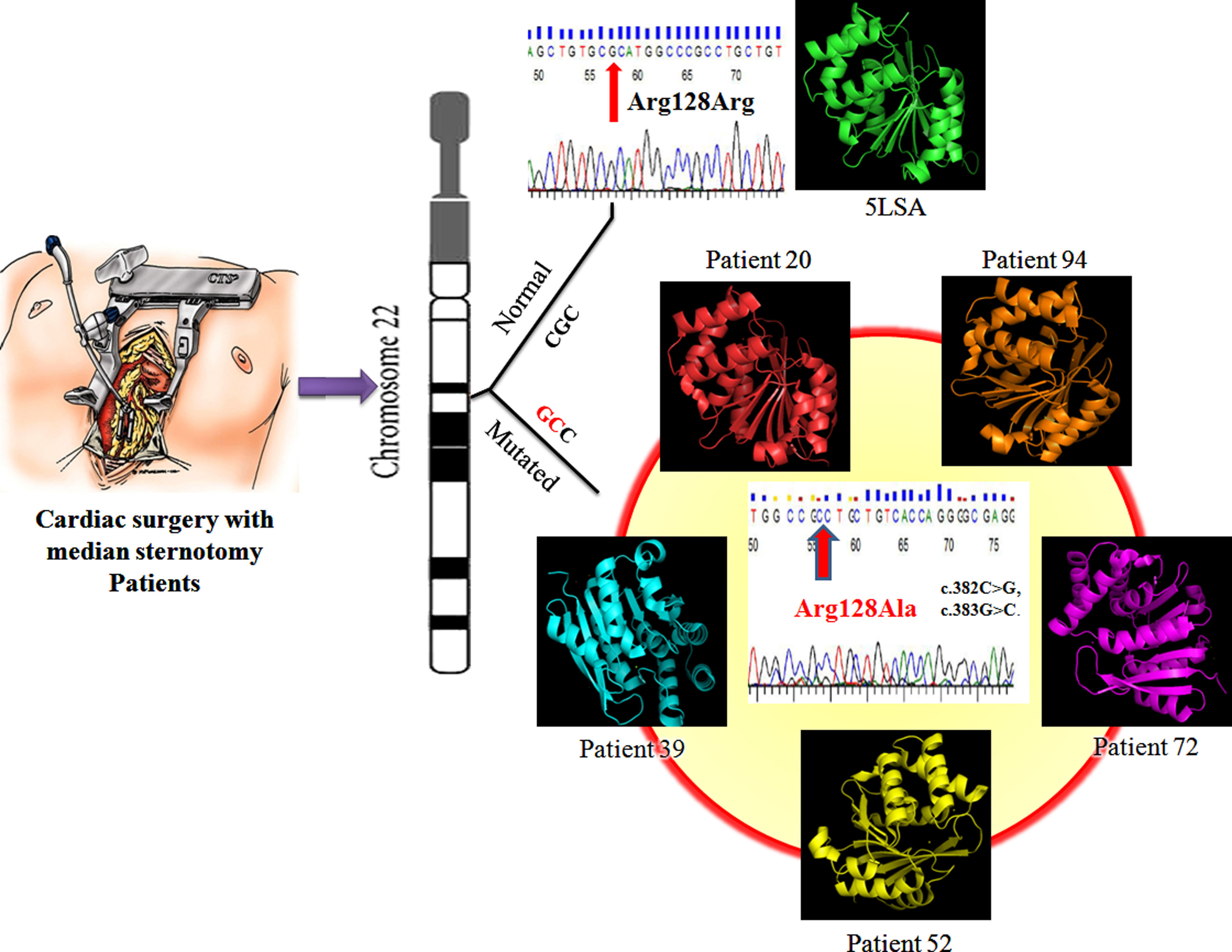
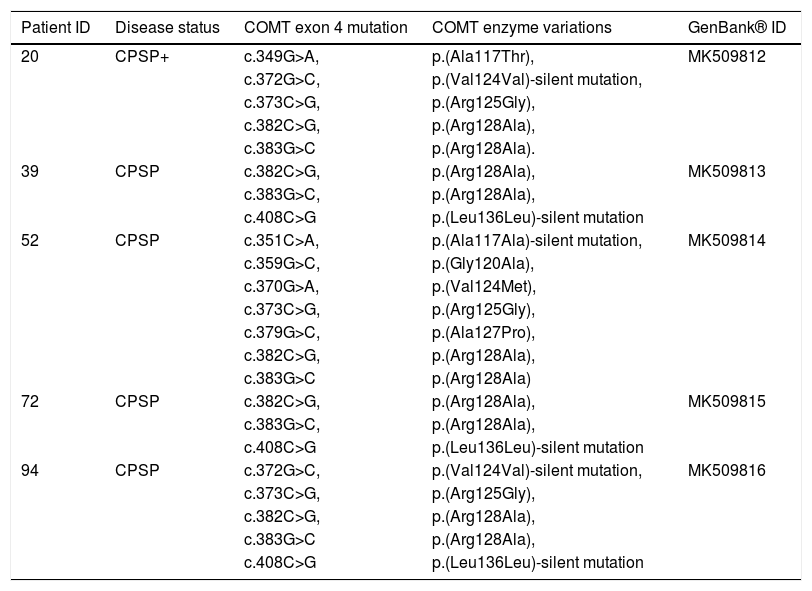
ResultsGenetic analysis carried out through PCR showed 220 bp amplicons. The 25% of patients with CPSP showed a Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) >4 pain score. 20% of these patients have known Val158Met mutation, 5% of patients showed novel mutations c.382C>G, c.383G>C; p. (Arg128Ala). The mutations in COMT gene contributed major structural variations in COMT leading to the formation of inactive COMT that correlates with CPSP.
ConclusionThe results of the present study showed that both novel and previously reported mutations in COMT gene has strong association with CPSP.
Las mutaciones en el exón 4 del gen COMT están asociadas a dolor quirúrgico persistente crónico (CPSP). En especial G472A (Val158Met), el alelo mutado de COMT, asociado a los pacientes de CPSP, se reporta en diferentes poblaciones étnicas. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la prevalencia de las mutaciones genéticas y las variaciones estructurales en el exón 4 de COMT, que puede guardar relación con la aparición de CPSP en pacientes sometidos a estenotomía.
Materiales y métodosSe seleccionaron 100 pacientes con estatus físico i, ii y iii de ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) sometidos a esternotomía, para evaluar el desarrollo y magnitud de CPSP mediante cuestionarios de dolor, transcurridos tres meses de la cirugía. Esto guardó relación con la presencia alélica de COMT. Se estudió el exón 4 del gen COMT (que contiene el alelo G472A). Se secuenciaron los productos de la reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR), depositándose las secuencias mutadas en GenBank®. Se realizó el análisis estructural de COMT utilizando ProCheck®, evaluándose las distorsiones de la orientación estructural terciaria tridimensional con la escala RMSD (raíz de la desviación cuadrática media).
ResultadosEl análisis genético realizado con PCR reflejó amplicones de 220 bp. El 25% de los pacientes con CPSP reflejó una puntuación de dolor <4 en la escala NRS. El 20% de estos pacientes tenía mutación Val158Met conocida, el 5% de los pacientes reflejó mutaciones nuevas c.382C>G, c.383G>C; p. (Arg128Ala). Las mutaciones del gen COMT contribuyeron a variaciones estructurales mayores de COMT, conducentes a la formación de COMT inactiva que se correlaciona con CPSP.
ConclusiónLos resultados del presente estudio mostraron que tanto las nuevas mutaciones como las previamente reportadas del gen COMT tienen una fuerte asociación con CPSP.