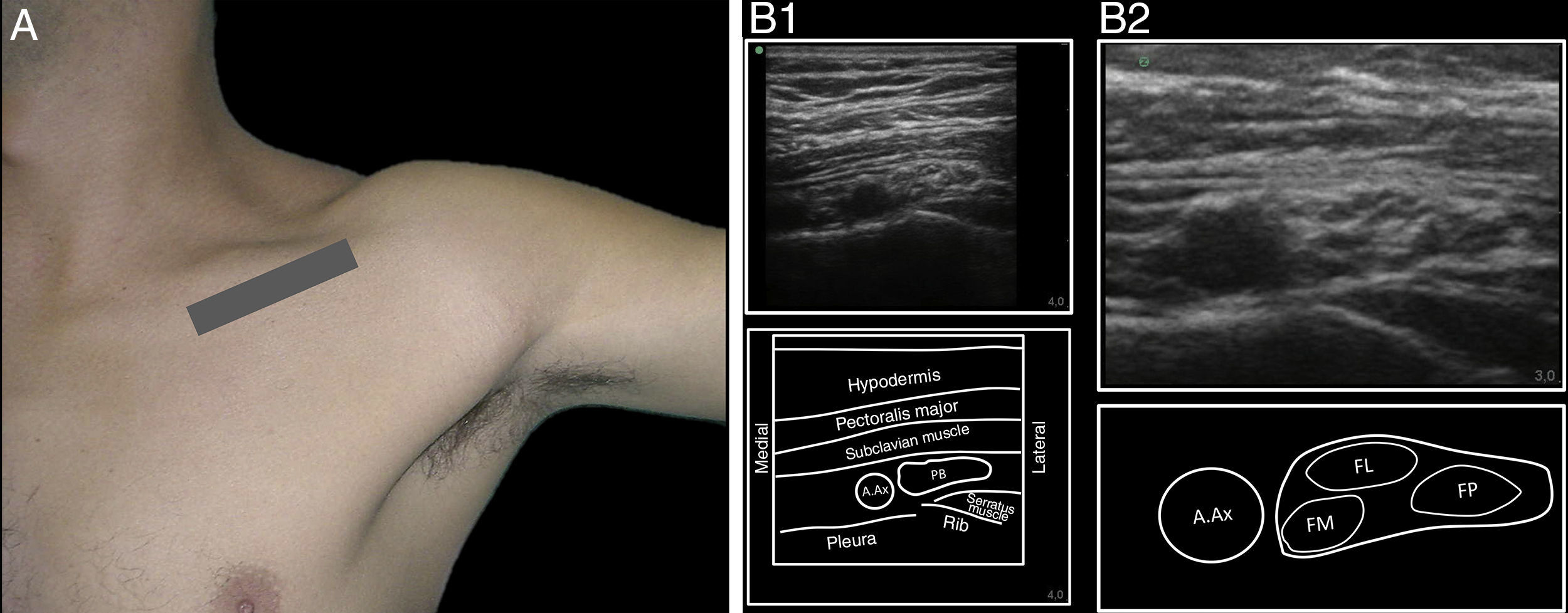
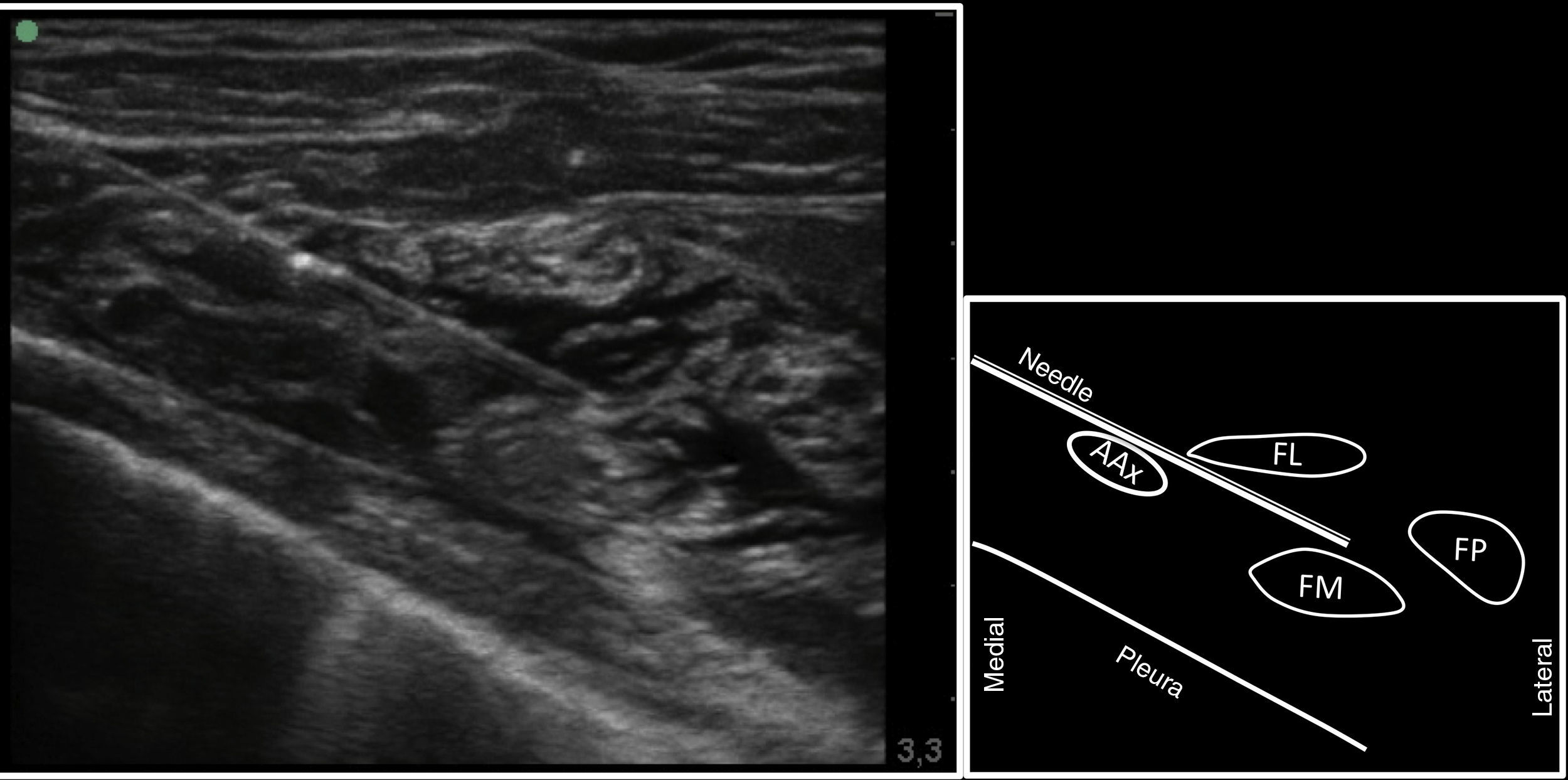
Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular block in the costoclavicular space located between the clavicle and the first rib, reaches the secondary trunks when they are clustered together and lateral to the axillary artery. This block is most often performed through a lateral approach, the difficulty being finding the coracoid process an obstacle and guiding the needle towards the vessels and pleura. A medial approach, meaning from inside to outside, will avoid these structures. Traditionally the assessment of a successful block is through motor or sensitive responses but a sympathetic fibre block can also be evaluated measuring the changes in humeral artery blood flow, skin temperature and/or perfusion index.
ObjectiveTo describe the medial approach of the ultrasound-guided costoclavicular block evaluating its development by motor and sensitive response and measurement of sympathetic changes.
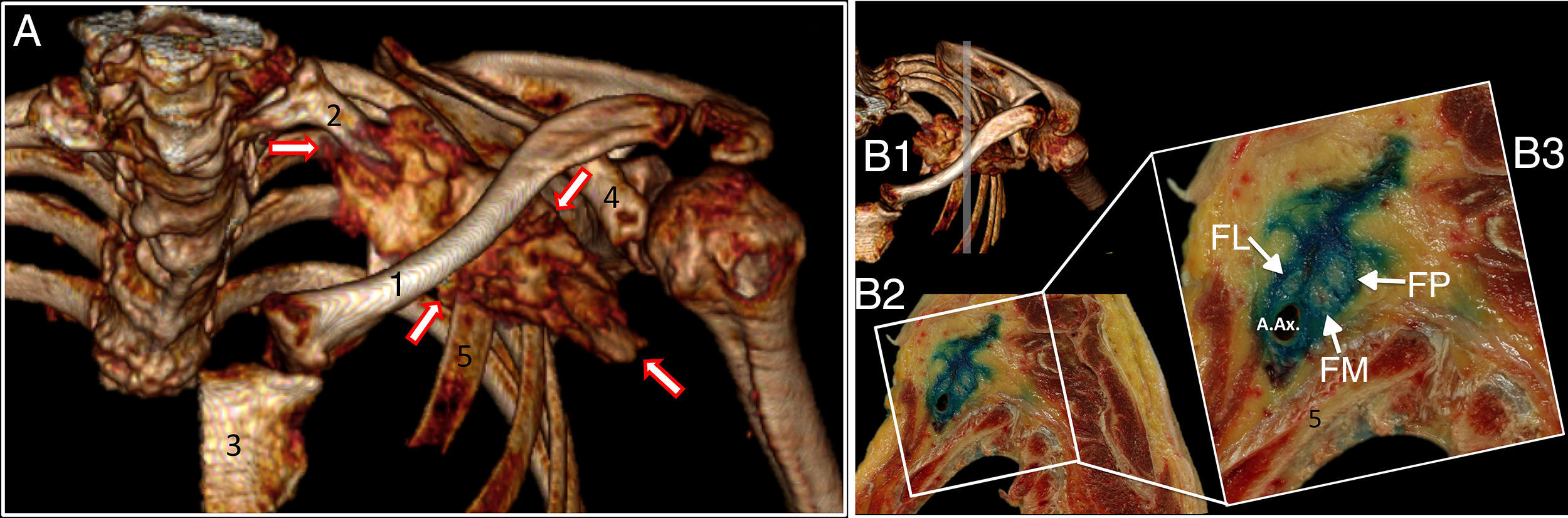
Materials and methodsDescription of the technique and administration of 20ml of contrast in a fresh cadaver model, evaluating the distribution with CT-scan and sagittal sections of the anatomic piece. Subsequently in a clinical phase, including 11 patients, we evaluated the establishment of motor, sensitive and sympathetic blocks. We evaluated the sympathetic changes reflected by humeral artery blood flow, skin temperature and distal perfusion index.
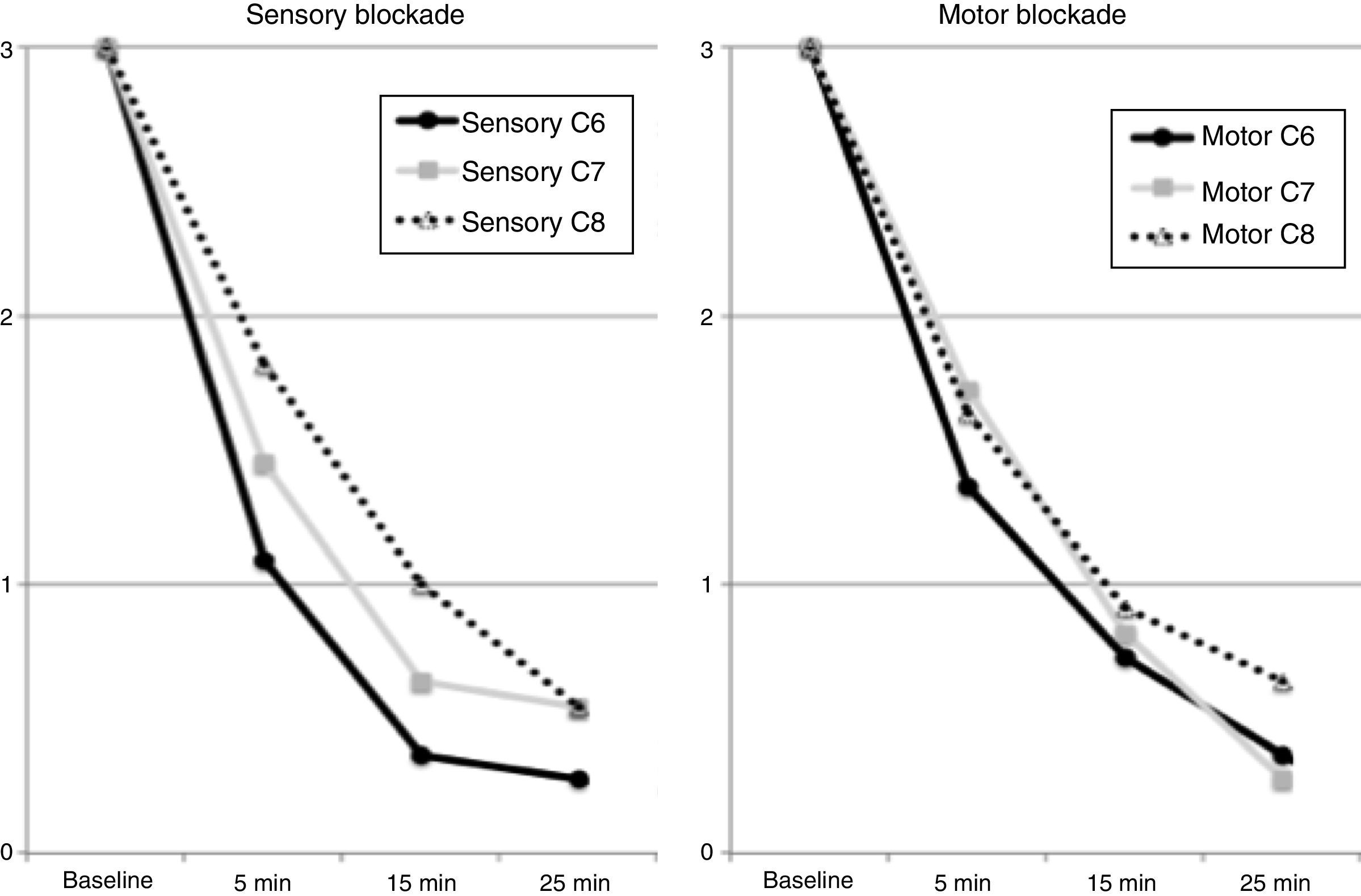
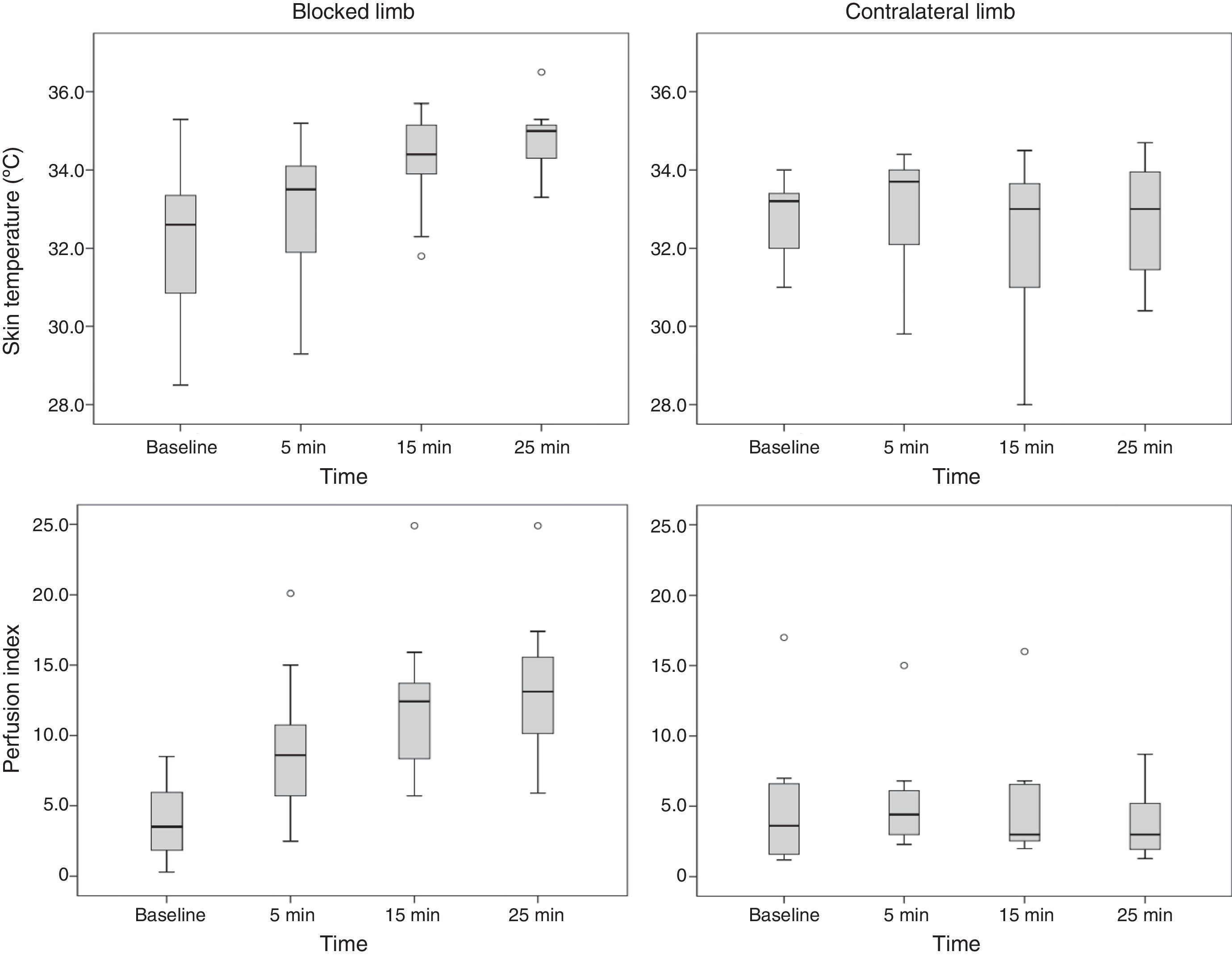
ResultsIn the anatomical model the block was conducted without difficulties, showing an adequate periclavicular distribution of the contrast in the CT-scan and in sagittal sections, reaching the interscalenic space as far as the secondary trunks. Successful blocks were observed in 91% of patients after 25min. All the parameters reflecting sympathetic block increased significantly. The humeral artery blood flow showed an increase from 108±86 to 188±141ml/min (p=0.05), skin temperature from 32.1±2 to 32.8±9°C (p=0.03) and perfusion index from 4±3 to 9±5 (p=0.003).
ConclusionsThe medial approach of the ultrasound-guided costoclavicular block is anatomically feasible, with high clinical effectiveness using 20ml of 1.5% mepivacaine. The sympathetic block can be evaluated with all three parameters studied.
El bloqueo infraclavicular ecoguiado en el espacio costoclavicular, situado entre la clavícula y la segunda costilla, pretende acceder a los troncos secundarios del plexo braquial cuando se hallan agrupados y laterales a la arteria axilar. Habitualmente se realiza mediante abordaje lateral, con la dificultad de la interposición de la apófisis coracoides y la dirección de la aguja hacia los vasos y la pleura. Un abordaje medial, es decir de interno a externo, evita estas estructuras. Tradicionalmente evaluamos el resultado del bloqueo infraclavicular mediante la valoración sensitiva y motora; no obstante, el bloqueo de las fibras simpáticas podría evaluarse objetivamente a través de los cambios en el flujo arterial, la temperatura cutánea y/o el índice de perfusión de la extremidad.
ObjetivoDescribir el bloqueo costoclavicular ecoguiado con acceso medial, evaluando su desarrollo mediante la evaluación motora, sensitiva y simpática.
Materiales y métodosDescripción inicial de la técnica y punción ecoguiada con contraste en cadáver, evaluando la distribución de un volumen de 20ml mediante tomografía computarizada (TC) y secciones sagitales de la pieza anatómica. Posteriormente, una fase clínica con inclusión de 11 pacientes a quienes se evaluó la instauración del bloqueo motor, sensitivo y simpático. Este último a través de la medición del flujo humeral, el índice de perfusión digital y la temperatura cutánea distal.
ResultadosEn el cadáver se realizó el acceso sin dificultades y se evidenció una adecuada distribución periclavicular de medio de contraste en la TC y en las secciones, alcanzando desde el espacio interescalénico hasta los troncos secundarios. El 91% de los pacientes presentó bloqueo quirúrgico a los 25min. Todos los parámetros de bloqueo simpático evaluados aumentaron significativamente. El flujo arterial humeral aumentó de 108±86 a 188±141ml/min (p=0,05). La temperatura cutánea de 32,1±2 a 32,8±9°C (p=0,03) y el índice de perfusión de 4±3 a 9±5 (p=0,003).
ConclusionesEl abordaje medial del bloqueo costoclavicular ecoguiado fue anatómicamente factible y con elevada eficacia clínica tras 20ml de mepivacaína al 1,5%. El bloqueo simpático obtenido puede evaluarse mediante los 3 parámetros estudiados.