To determine the inter-rater reliability in the ultrasonographic (US) measurement of the diaphragmatic excursion (DE) and the diaphragm thickness fraction (DTF) performed by non-medical health professionals in healthy people.
Participants and methodsProspective observational study in a third level hospital in Cali, Colombia. Measurements were made to 30 healthy volunteers chosen by convenience sampling, without a history of lung diseases, with ages between 18–60 years. A pilot test was previously carried out with 8 healthy volunteers. US measurements of DE, and DTF were based on previously published protocols. Each assessor independently observed several cycles of normal quiet breathing for 3min to establish a baseline. The Intraclass Correlation Index (ICC) was used to evaluate the inter-rater reliability in the measurements of DE and DTF, with 95% confidence intervals and a p<0.05.
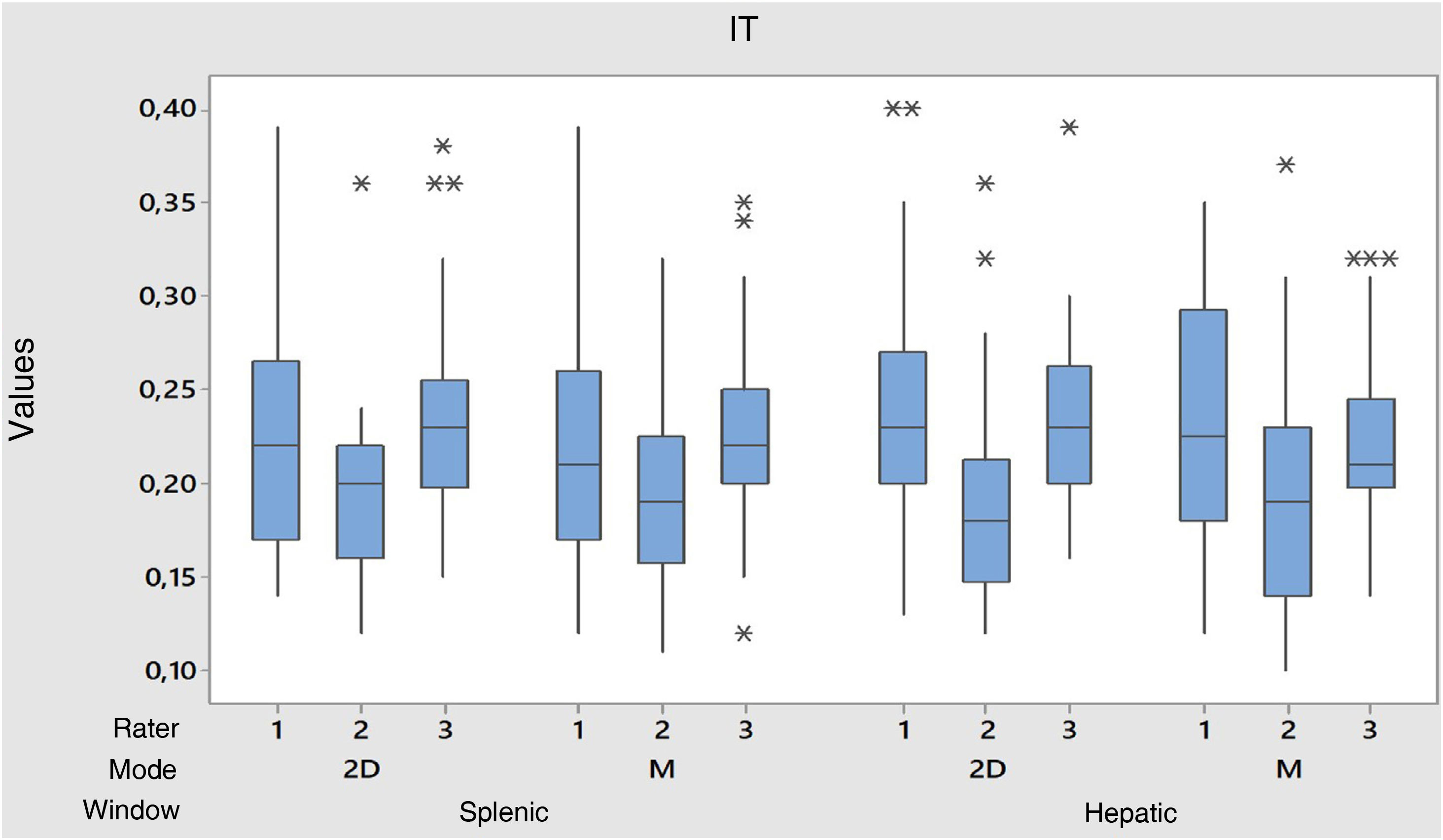
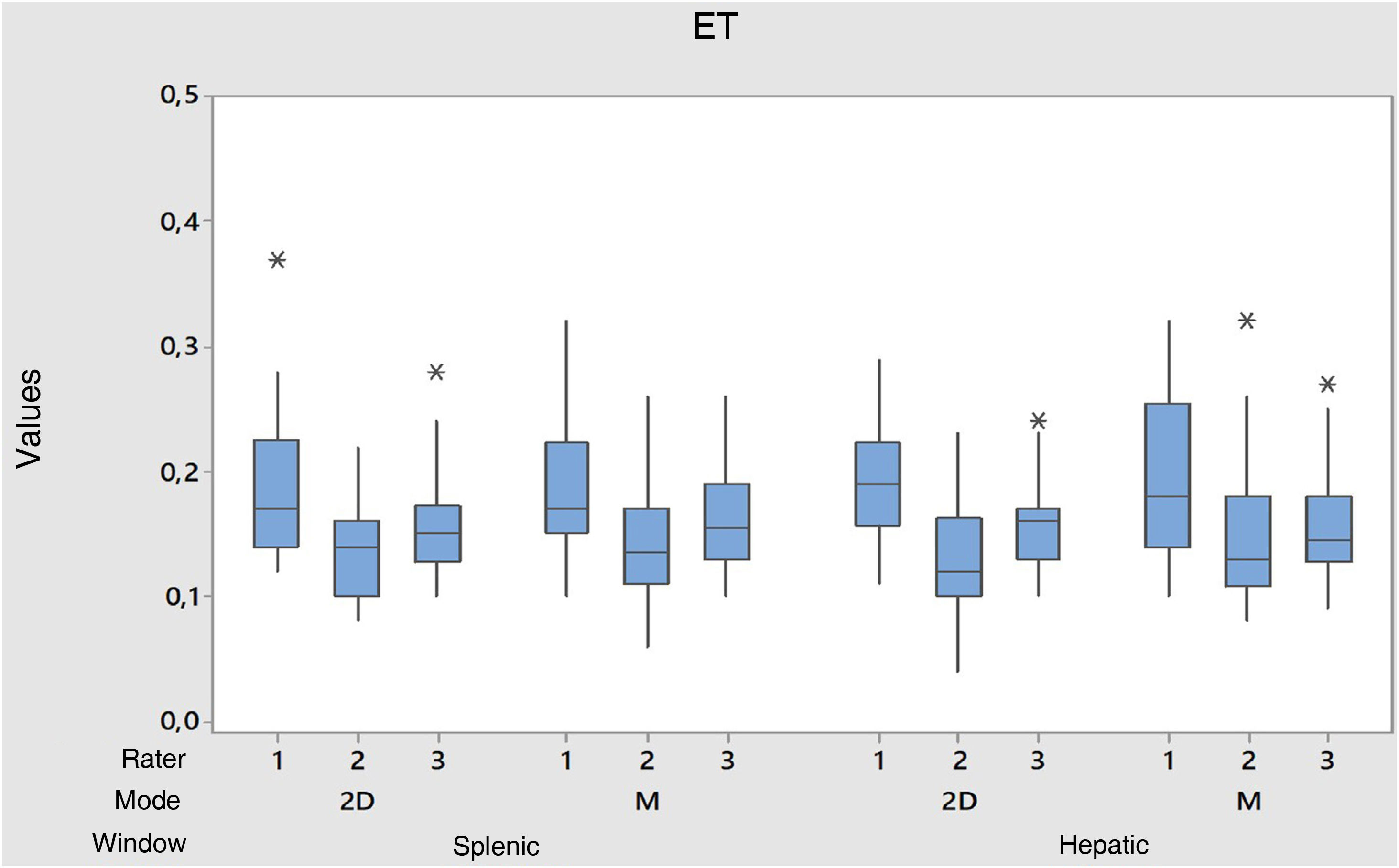
ResultsSubstantial agreement was identified in the measurement of DE in the splenic and hepatic windows because the ICC was greater than 0.6 (p<0.05). The measurement of the DTF in the hepatic window showed slight agreement in both 2D and M modes (p>0.05). In the splenic window, the measurement of the DTF in the 2D mode was found to be moderate agreement and for the M mode a slight agreement was found (p>0.05).
ConclusionsThe diaphragmatic US constitutes a reproducible method with acceptable inter-rater reliability for the measurement of inspiratory/expiratory thickness, and with little reliability for the measurement of DTF.
Determinar la confiabilidad inter-evaluador en la medición ultrasonográfica (US) de la excursión diafragmática (ED) y la fracción de engrosamiento diafragmático (FED) realizada por profesionales de salud no médicos en voluntarios sanos.
Participantes y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo en un Hospital de tercer nivel en Cali, Colombia. Se realizaron mediciones a 30 voluntarios sanos escogidos mediante muestreo a conveniencia, sin antecedentes de enfermedades pulmonares, con edades entre los 18–60 años. Previamente se realizó una prueba piloto con 8 voluntarios sanos. Las mediciones US de ED, y FED se basaron en protocolos publicados anteriormente. Cada evaluador observaba independientemente varios ciclos de respiración tranquila normal durante 3 minutos para establecer una línea de base. Para evaluar la confiabilidad inter-evaluador en las mediciones de ED y FED se utilizó el Índice de Correlación Intraclase (ICC), con intervalos de confianza del 95% y un p<0,05.
ResultadosSe identificó concordancia sustancial en la medición de la ED en las ventanas esplénica y hepática debido a que el ICC fueron mayores a 0,6 (p<0,05). La medición de la FED en la ventana hepática mostró concordancia leve tanto en el modo 2D como en el modo M (p>0,05). En la ventana esplénica, la medición de la FED en el modo 2D se identificó concordancia regular y para el modo M se encontró una concordancia leve (p>0,05).
ConclusionesLa US diafragmática constituye un método reproducible con aceptable confiabilidad inter-evaluador, para la medición del grosor inspiratorio/espiratorio, y con confiabilidad pobre para la medición de FED.