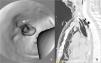
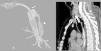
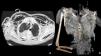
Iatrogenic tracheal rupture (ITR) is a serious complication secondary to procedures such as emergent orotracheal intubation or tracheostomy, among others. The management of ITR depends on the size, extension and location of the injury, along with the patient's respiratory status and comorbidities. The priority of treatment is to keep the airway permeable to ensure adequate ventilation. We present the case of a tracheal rupture after performing a percutaneous tracheostomy, in a patient diagnosed with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to bilateral interstitial pneumonia due to SARS-Cov-2. The issues are discussed, such as the management (conservative vs. surgical) depending on the features of the injury and the patient, in the extraordinary context that the COVID-19 pandemic has entailed.
La rotura traqueal iatrogénica (RTI) es una complicación grave secundaria a procedimientos como intubación orotraqueal emergente o realización de traqueostomía entre otros. El manejo de la RTI depende del tamaño, extensión y localización de la lesión, junto con el estado respiratorio y comorbilidades del paciente. La prioridad del tratamiento es mantener permeable la vía aérea para asegurar una adecuada ventilación. Presentamos el caso de una rotura traqueal tras la realización de traqueostomía percutánea, en un paciente diagnosticado de síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo grave secundario a neumonía intersticial bilateral por SARS-CoV-2, e intentamos arrojar luz sobre el manejo (conservador vs. quirúrgico) en función de las características de la lesión y del paciente, en el contexto tan particular que ha supuesto la pandemia COVID-19.