Lingual tonsils are normal components of the oropharynx localized at the base of the tongue, which sometimes can become enlarged by inflammation. This may be a cause of unexpected difficult airway, considering most patients are asymptomatic and this supraglottic mass is not usually detected during a routine preoperative airway assessment. Commonly described in adults, there are limited reports in paediatric patients.
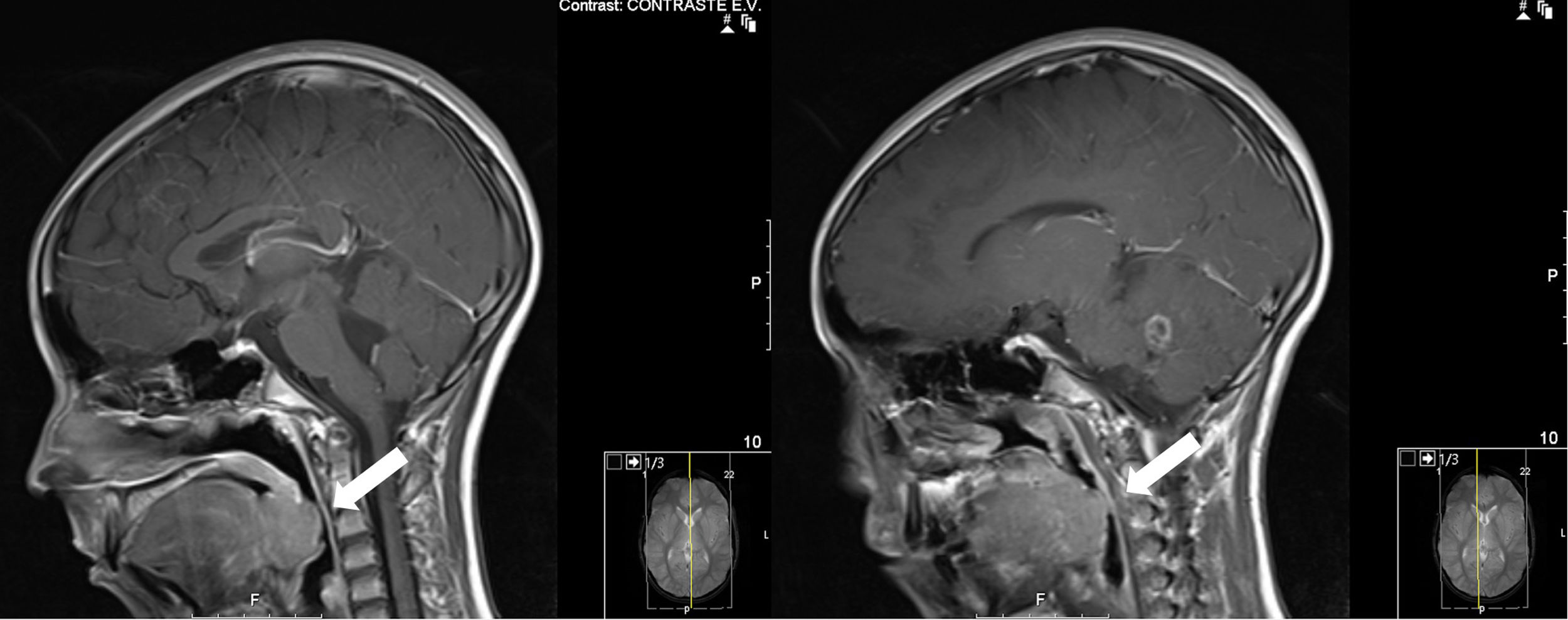
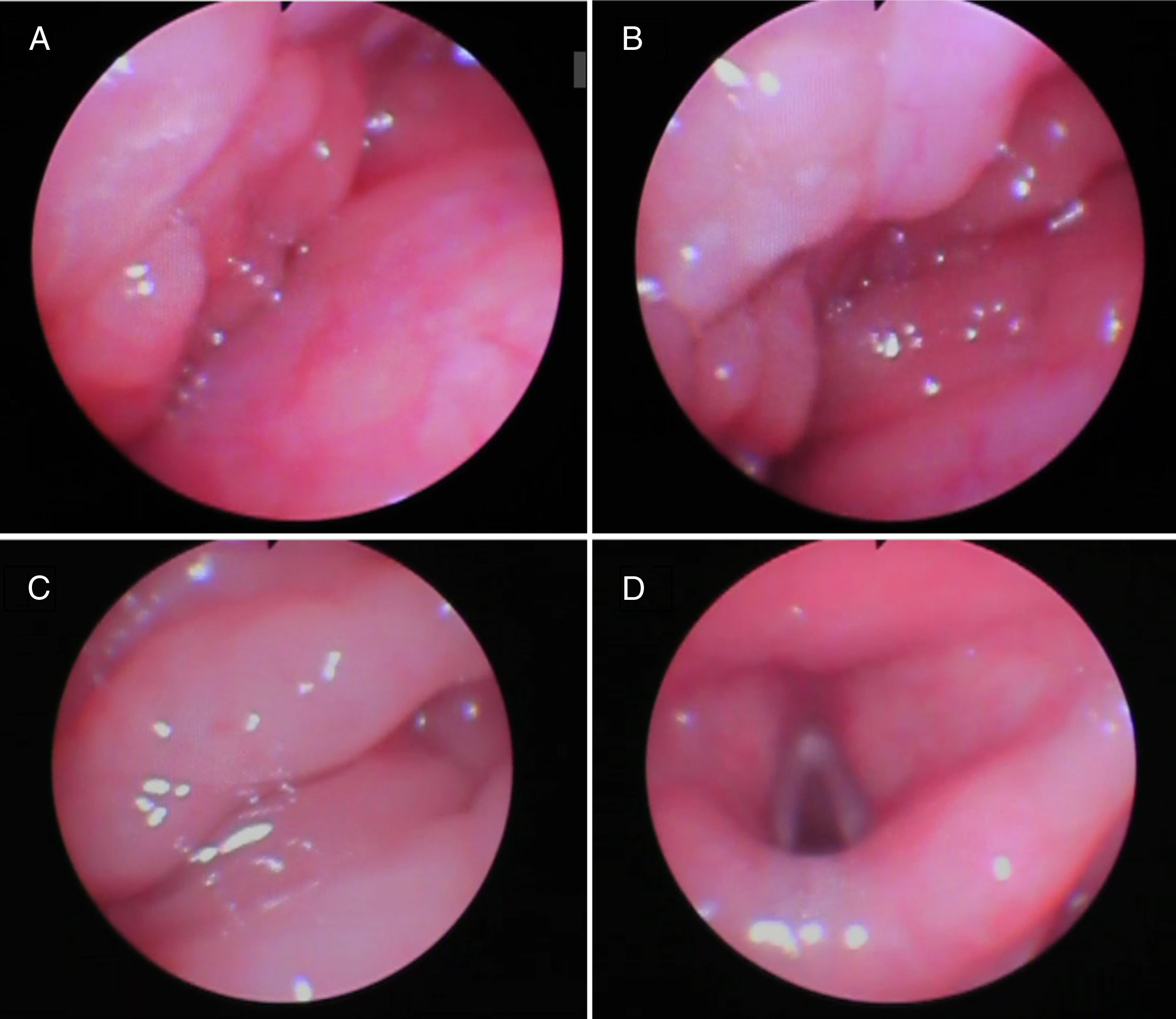
We describe a case of a 12 years old boy diagnosed with a cerebellar brain tumour that was scheduled for a resection. The first surgery was postponed because of respiratory complications as a result of unexpected difficult airway due to lingual tonsil hypertrophy. His surgery was rescheduled and a plan for airway management was laid out: fibroscopic intubation with spontaneous ventilation.
Considering this is a problem that cannot be identified by regular airway examination, we should be aware of the most effective ways to manage the situation as it arises.
Las amígdalas linguales son componentes normales de la orofaringe, situadas en la base de la lengua, que a veces pueden agrandarse debido a inflamación. Esto puede ser causa de vía aérea difícil no prevista, considerando que muchos pacientes son asintomáticos y que esta masa supra-glótica no es detectada habitualmente durante la valoración rutinaria preoperatoria de la vía aérea. Se describe de manera común en adultos, pero existen pocos informes sobre pacientes pediátricos.
Describimos el caso de un niño de 12 años, con diagnóstico de tumor cerebral cerebeloso, programado para resección quirúrgica. La primera cirugía se pospuso debido a complicaciones respiratorias como resultado de vía aérea difícil a causa de hipertrofia de la amígdala lingual. Se reprogramó la cirugía, estableciéndose un plan para el tratamiento de la vía aérea: intubación con fibra óptica con ventilación espontánea.
Considerando que se trata de un problema que no puede identificarse mediante una exploración regular de la vía aérea, debemos tomar conciencia acerca de los modos más efectivos de manejar esta situación, cuando surja.