Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) causes a systemic inflammatory response in tissues, with an increase in IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α in blood and tissues. Cytoprotective effects of sevoflurane in different experimental models are well known, and this protective effect can also be observed in VILI. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of sevoflurane in VILI.
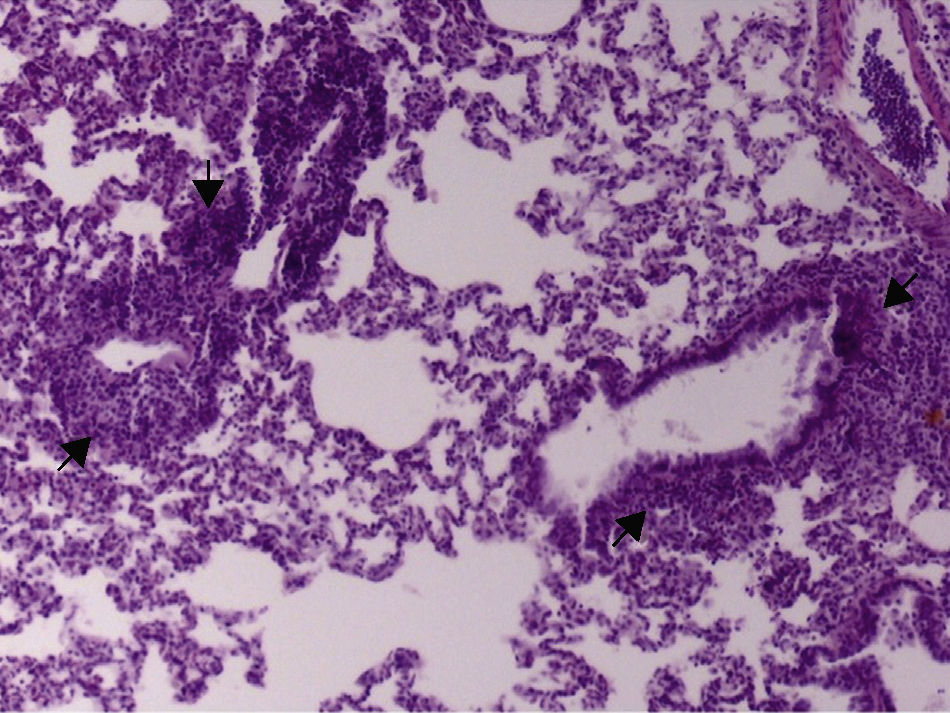
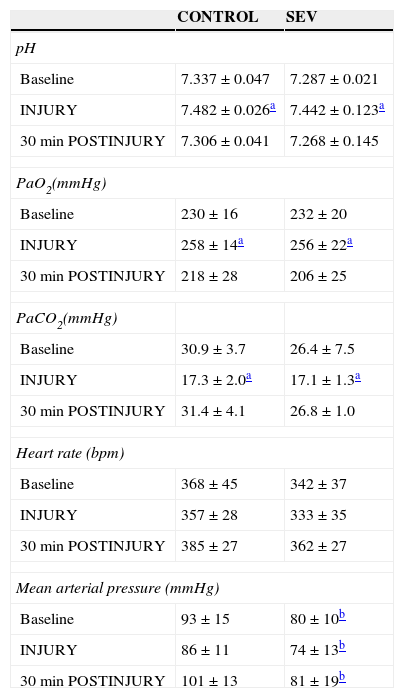
Material and methodsA prospective, randomized, controlled study was designed. Twenty female rats were studied. The animals were mechanically ventilated, without sevoflurane in the control group and sevoflurane 3% in the treated group (SEV group). VILI was induced applying a maximal inspiratory pressure of 35cmH2O for 20min without any positive end-expiratory pressure for 20min (INJURY time). The animals were then ventilated 30min with a maximal inspiratory pressure of 12cmH2O and 3cmH2O positive end-expiratory pressure (time 30min POST-INJURY), at which time the animals were euthanized and pathological and biomarkers studies were performed. Heart rate, invasive blood pressure, pH, PaO2, and PaCO2 were recorded. The lung wet-to-dry weight ratio was used as an index of lung edema.
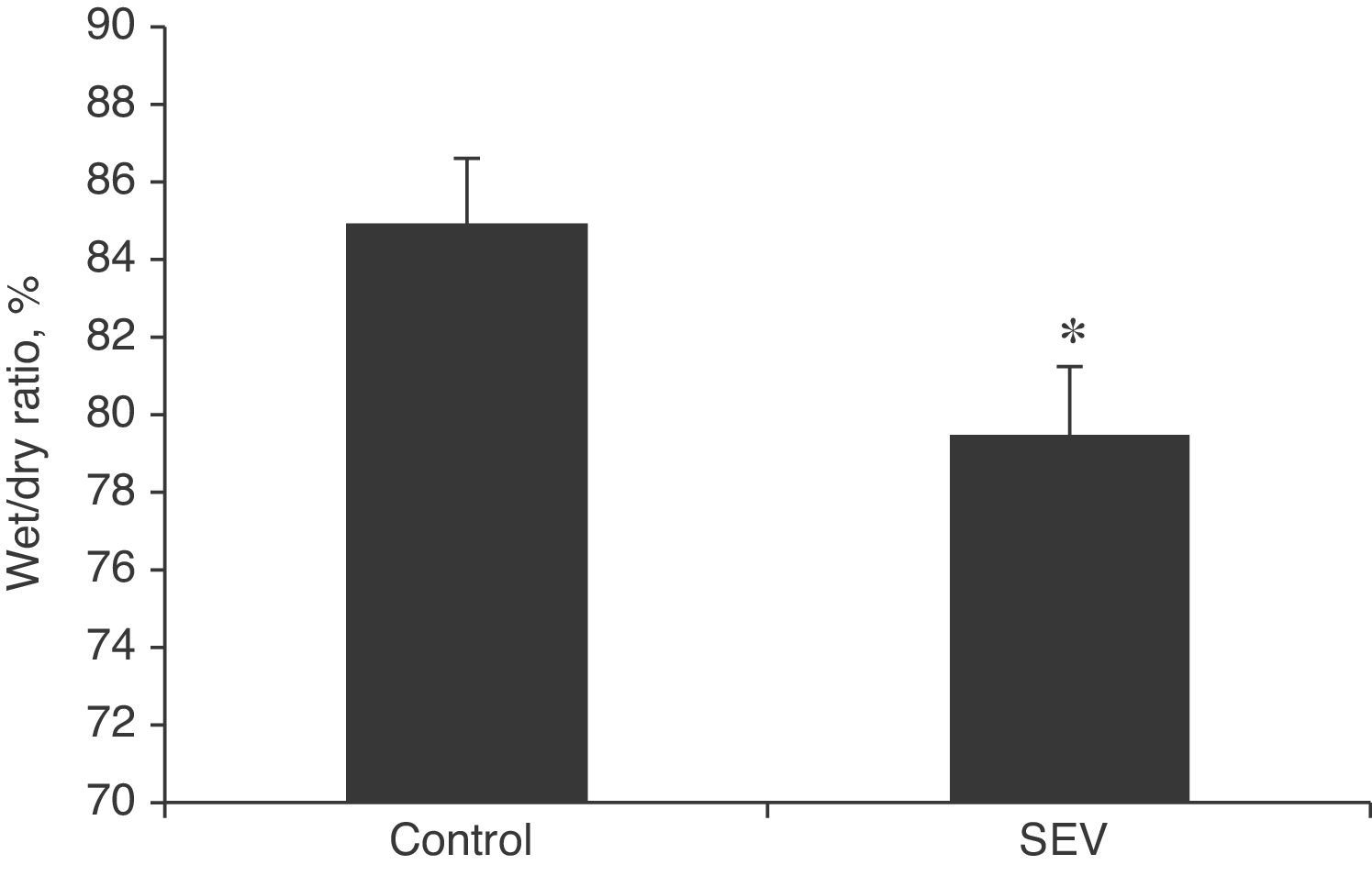
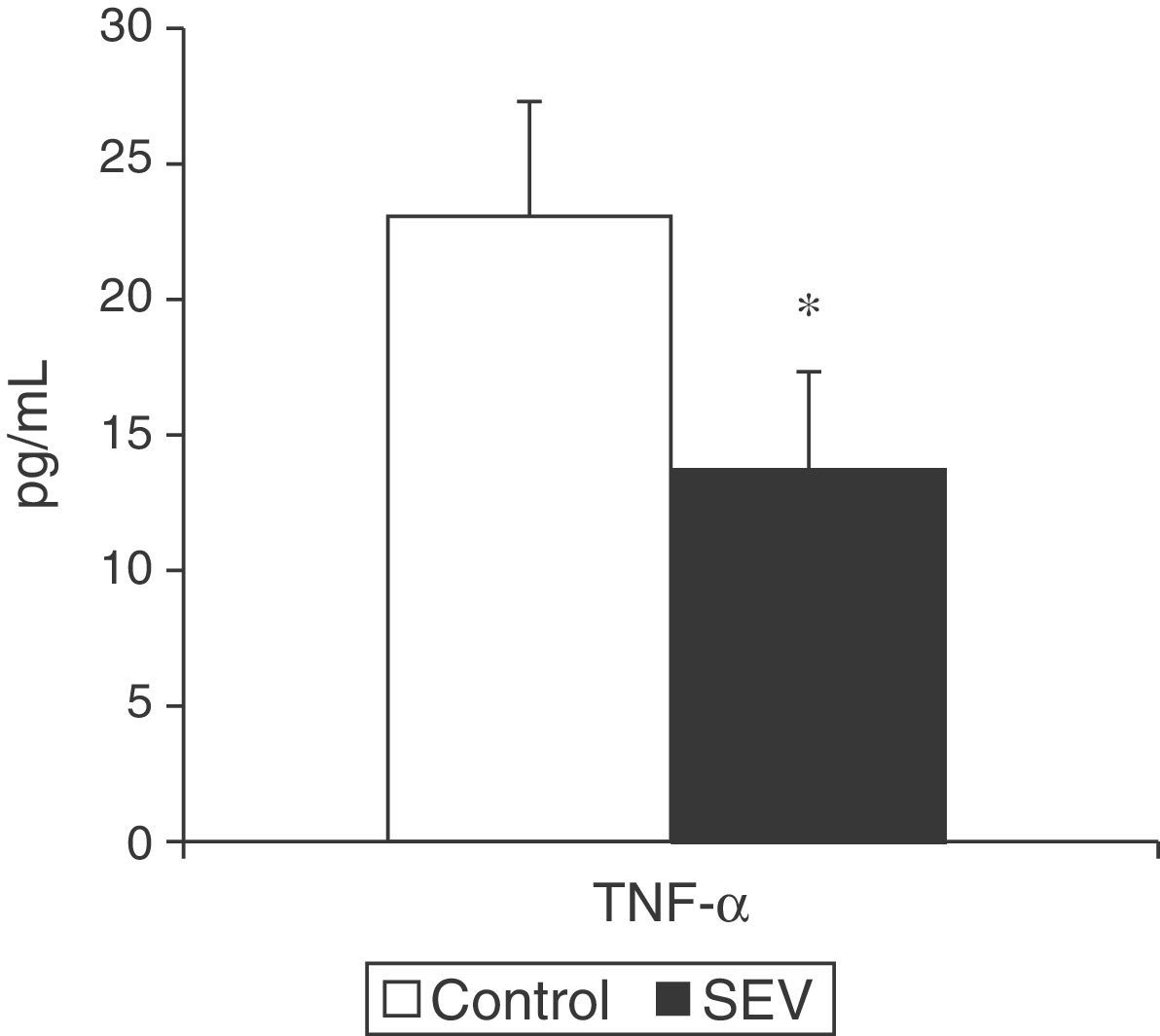
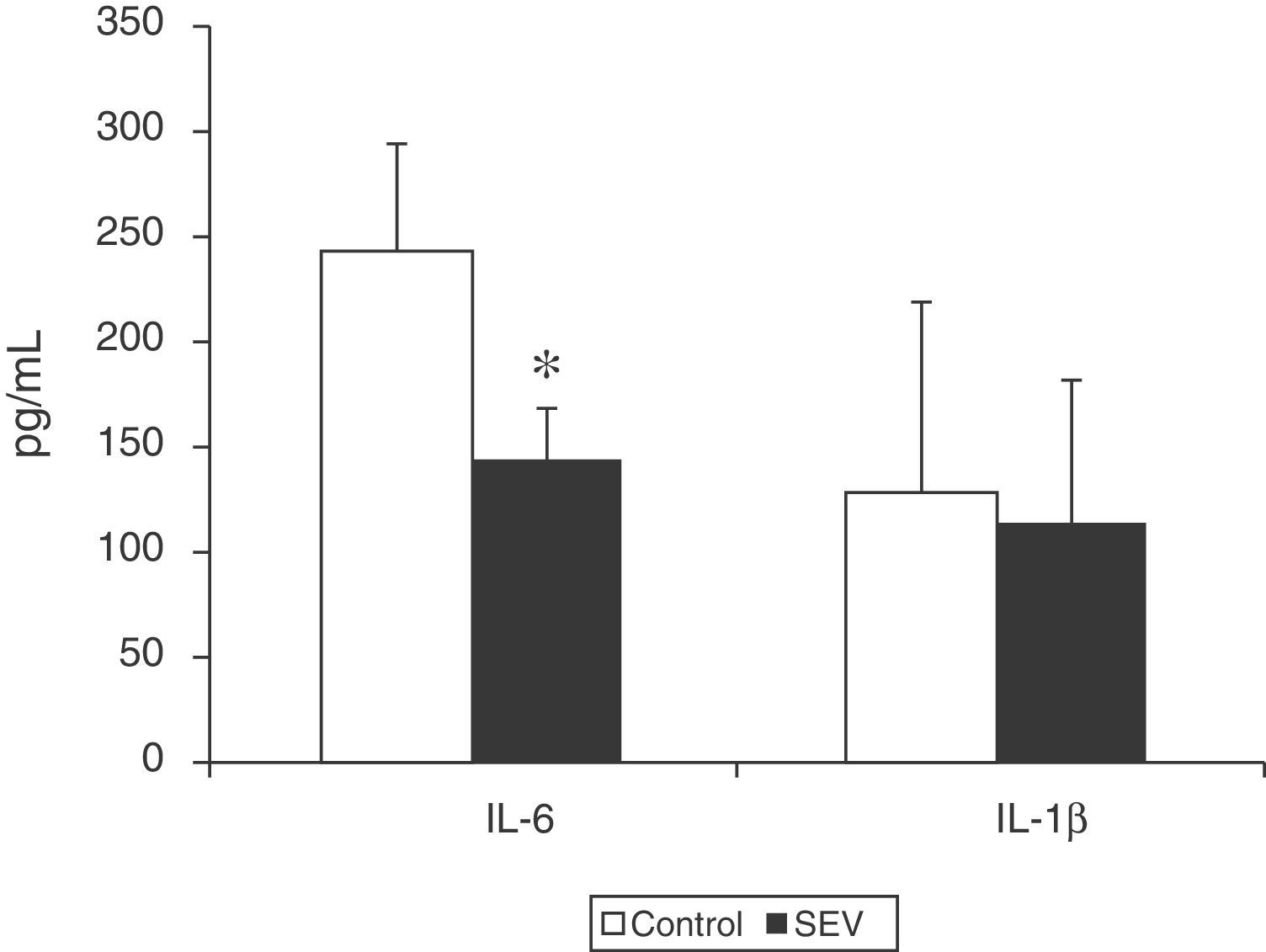
ResultsNo differences were found in the blood gas analysis parameters or heart rate between the 2 groups. Blood pressure was statistically higher in the control group, but still within the normal clinical range. The percentage of pulmonary edema and concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 in lung tissue in the SEV group were lower than in the control group.
ConclusionsSevoflurane attenuates VILI in a previous healthy lung in an experimental subclinical model in rats.
El daño pulmonar inducido por la ventilación mecánica (VILI) provoca una respuesta inflamatoria sistémica, con elevación en sangre y tejidos de IL-1, IL-6 y TNF-α. Conocidos los efectos citoprotectores de sevoflurano en diferentes modelos experimentales, este podría tener un comportamiento similar ante el VILI. El objetivo de este estudio es valorar el efecto de sevoflurano en el VILI.
Material y métodosEstudio experimental, prospectivo, controlado y aleatorizado. Se utilizaron 20 ratas hembra. Los animales fueron ventilados mecánicamente sin sevoflurano en el grupo control y con sevoflurano al 3% en el grupo tratado (grupo SEV). Se provocó el VILI mediante una presión inspiratoria máxima de 35cmH2O sin presión positiva al final de la expiración durante 20min (tiempo LESIÓN). Después, los animales fueron ventilados 30min con una presión inspiratoria máxima de 12cmH2O y 3cmH2O de presión positiva al final de la expiración (tiempo 30min POSLESIÓN). Se registraron la frecuencia cardiaca, las presiones arteriales sistólica, diastólica y media, el pH, la PaO2 y la PaCO2. Se analizó la ratio peso húmedo/seco del tejido pulmonar.
ResultadosNo existieron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en los parámetros gasométricos ni en la frecuencia cardiaca entre los 2 grupos en estudio. La PAM fue significativamente mayor en el grupo control, pero dentro de límites clínicos normales. El porcentaje de edema pulmonar y las concentraciones de TNF-α e IL-6 en tejido pulmonar en el grupo de animales ventilados con sevoflurano fueron menores que en el grupo control.
ConclusionesSevoflurano atenúa el VILI en pulmón previamente sano, en un modelo experimental de VILI subclínico en ratas.