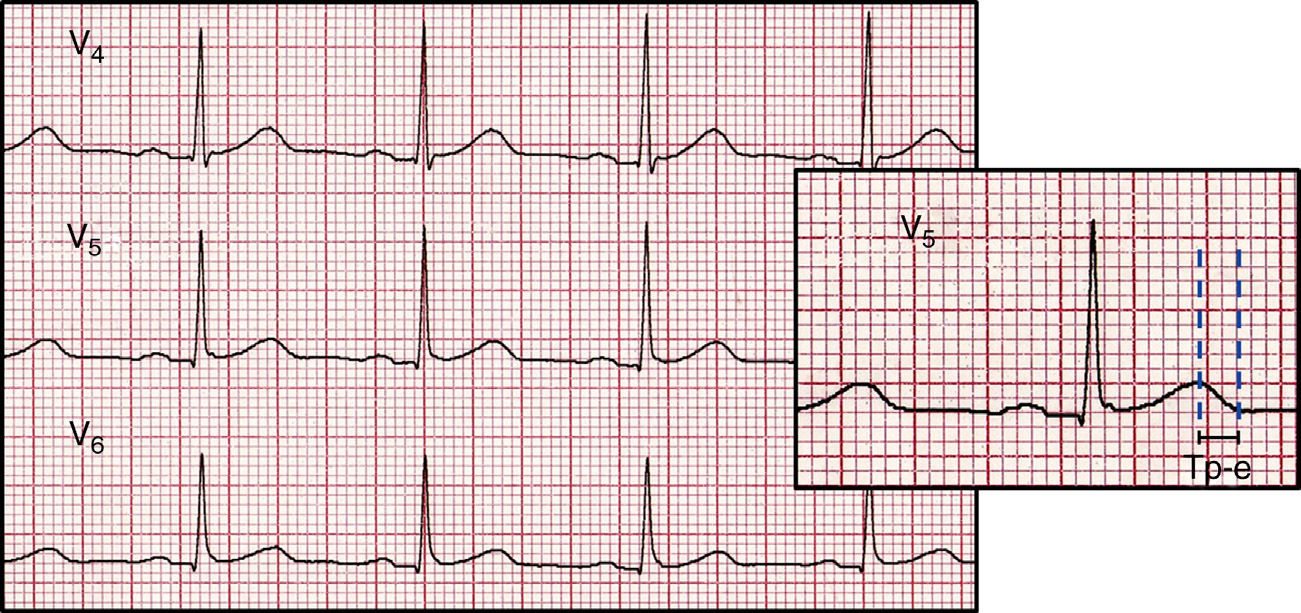
Droperidol and ondansetron prolong QT interval, a circumstance that has raised some concerns regarding the possibility of inducing torsades de pointes (TdP). However drug-induced spatial dispersion of ventricular repolarization has been shown to be the principal arrhythmogenic substrate for TdP. The aim of this study is to explore the effects of droperidol and ondansetron on the dispersion of repolarization, measured using the T peak-to-end interval (Tp-e) and Tp-e/QT and Tp-e/RR1/2 ratios in surgical anesthetized patients.
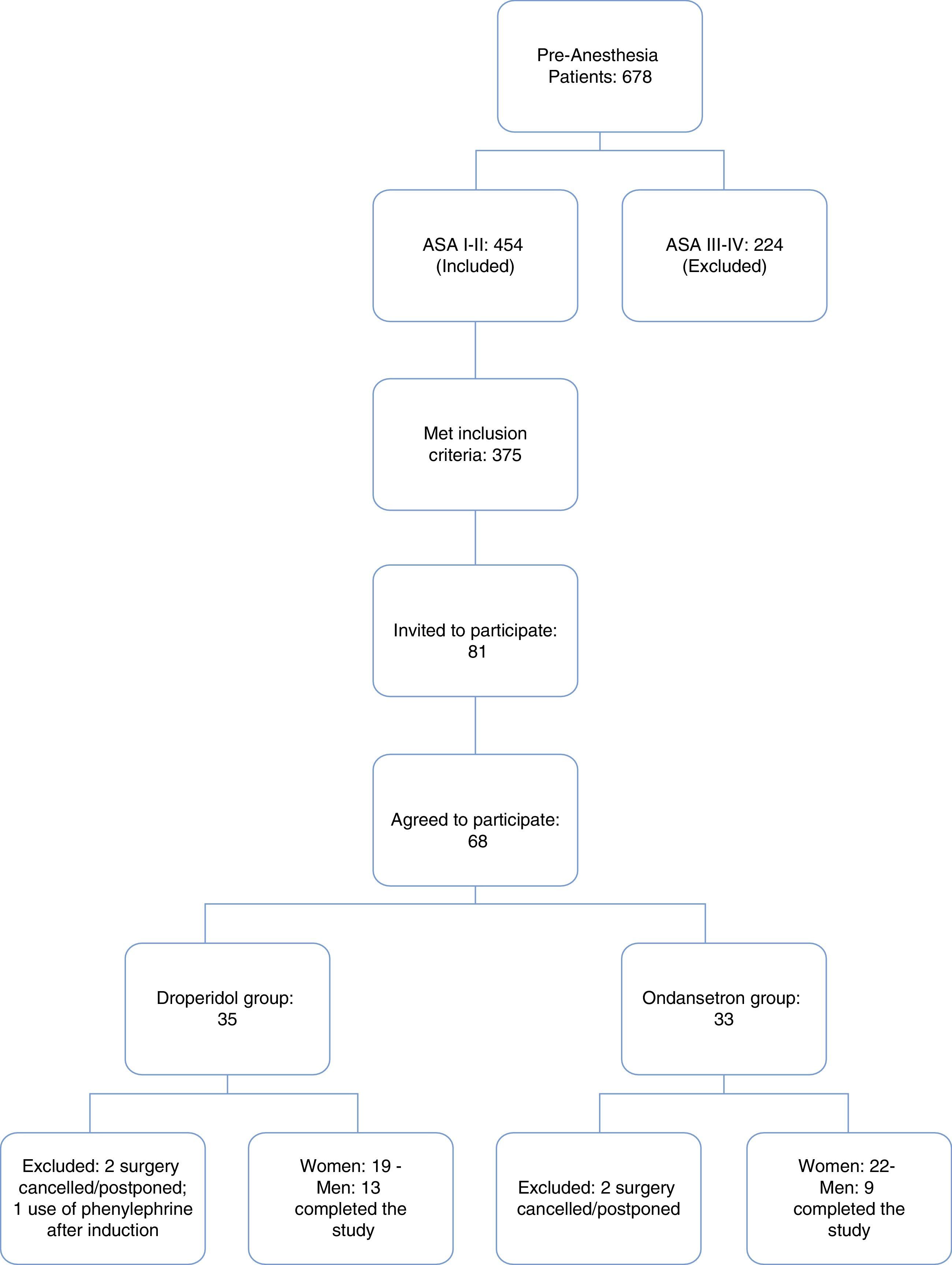
MethodsA randomized, double-blind study carried out on sixty-three adult patients without cardiac disease or factors favoring QT prolongation and undergoing non-cardiac surgery were randomly assigned to the droperidol or ondansetron group. Under propofol anesthesia, a 12-lead EKG was obtained, and 1.25mg droperidol or 4mg ondansetron was injected. Five minutes later, a new 12-lead EKG was recorded. EKG analyses were independently performed by two cardiologists blinded to the state of the traces or group allocation. QT, RR and Tp-e intervals were measured by averaging five successive beats in lead II (QT) or V5 (Tp-e). The mean value for each measurement was calculated for statistical analysis.
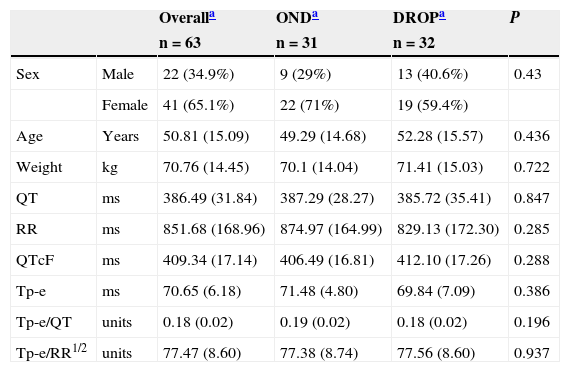
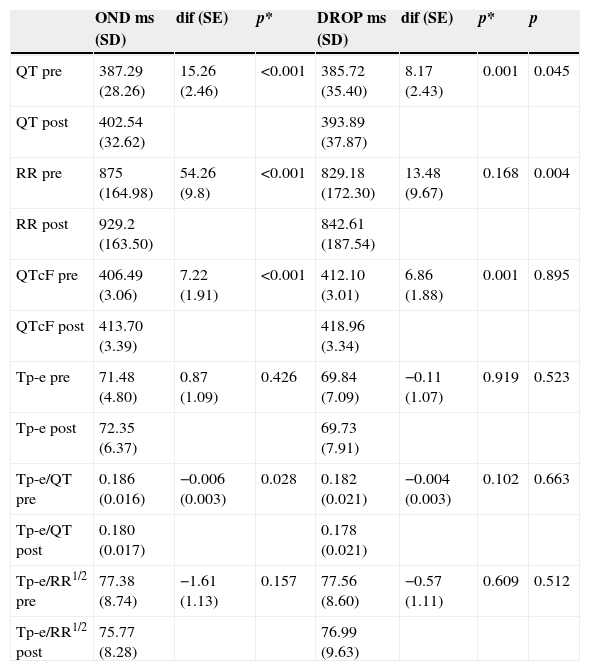
ResultsThirty-two patients (19 women) received droperidol, and 31 (22 women) ondansetron. Droperidol and ondansetron prolonged the QTcF interval (Fridericia formula) by 6.8 and 7.2ms (mean values) respectively, but neither droperidol nor ondansetron increased the Tp-e interval or Tp-e/QT and Tp-e/RR1/2 ratios.
ConclusionAt antiemetic doses, neither ondansetron (4mg) nor droperidol (1.25mg) increases the dispersion of ventricular repolarization in healthy adult patients anesthetized with propofol.
El droperidol y el ondansetrón prolongan el intervalo QT, lo que ha generado dudas sobre la posibilidad de que pudieran inducir arritmias como la torsades de pointes (TdP). Sin embargo, se ha demostrado que no es la prolongación del QT sino la dispersión espacial de la repolarización ventricular el principal sustrato arritmogénico para el desarrollo de TdP. El objetivo de este estudio es valorar los efectos del droperidol y el ondansetrón en la dispersión de la repolarización a través de la medida del intervalo T-peak-to-end (Tp-e) y los cocientes Tp-e/QT y Tp-e/RR1/2 en pacientes quirúrgicos anestesiados.
MétodosEstudio doble ciego en 63 adultos sin cardiopatía o factores que favorecen la prolongación del intervalo QT, sometidos a cirugía no cardiaca asignados aleatoriamente a 2 grupos: droperidol u ondansetrón. Durante la anestesia con propofol se realizó un ECG de 12 derivaciones, posteriormente se inyectaron 1,25mg de droperidol o 4mg de ondansetrón y 5min después se obtuvo un nuevo ECG. El análisis de los ECG fue realizado independientemente por 2 cardiólogos que desconocían el momento del registro y el fármaco administrado. Los intervalos QT, RR y Tp-e se midieron como promedio de 5latidos sucesivos en la derivaciónII (QT) o V5 (Tp-e). Se calculó el valor medio para cada medida en el análisis estadístico.
ResultadosRecibieron droperidol 32 pacientes (19 mujeres) y ondansetrón 31 (22 mujeres). Ambos fármacos prolongaron el intervalo QTcF (fórmula Fridericia) un promedio 6,8 y 7,2ms, respectivamente, pero ninguno aumentó el intervalo Tp-e o los cocientes Tp-e/QT y Tp-e/RR1/2.
ConclusiónA dosis antieméticas, ni el ondansetrón ni el droperidol aumentan la dispersión de la repolarización ventricular en pacientes adultos sanos anestesiados con propofol.