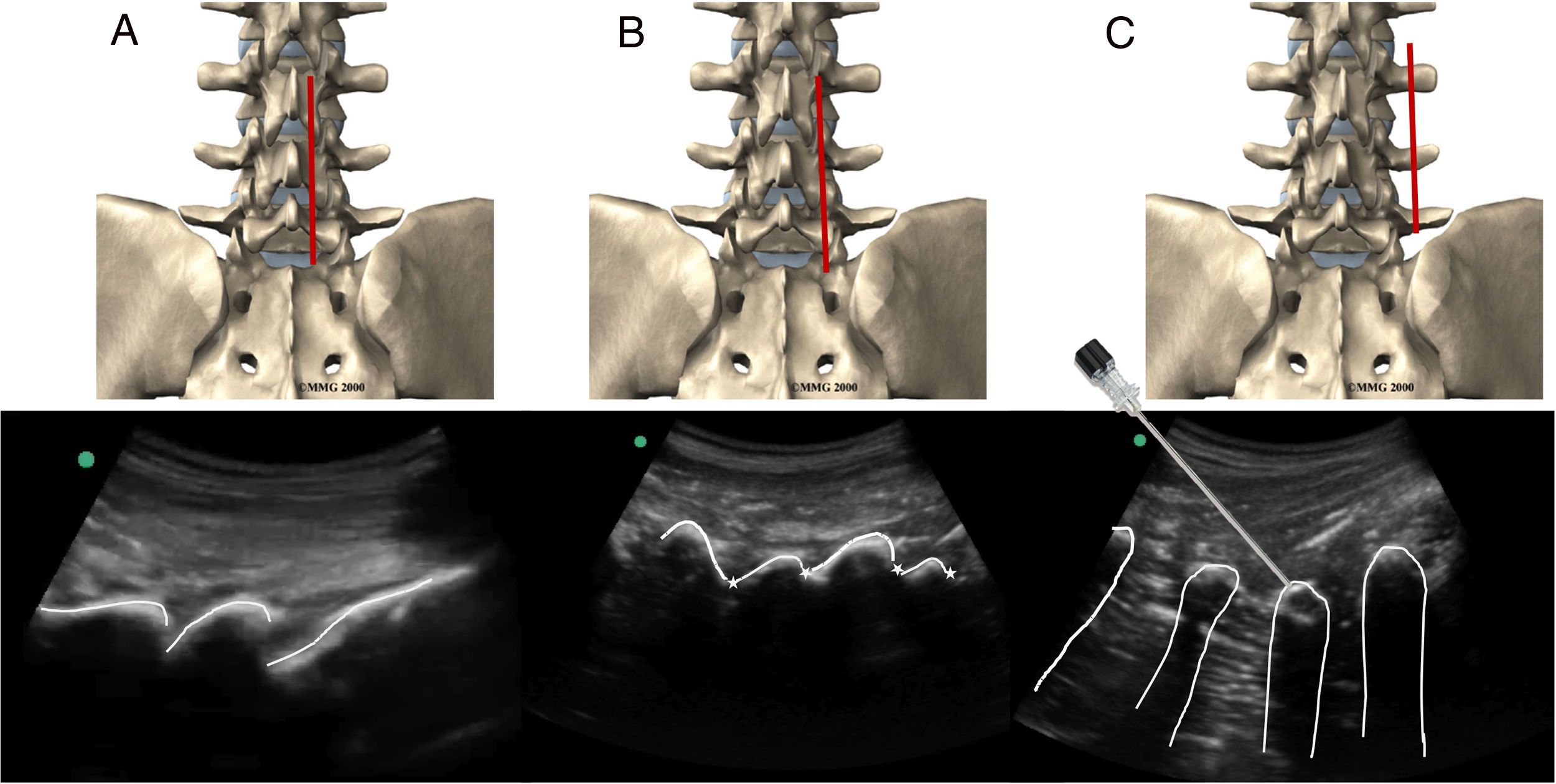
Thoracic erector spinae plane (ESP) block is now used for postoperative analgesia. However, although reports of lumbar ESP have been published, the anesthetic spread and mechanism of action of this technique remains unclear. We describe the lumbar ESP block technique and evaluate the spread of 20 ml of solution administered at the level of the transverse process of L4 in a cadaver model.
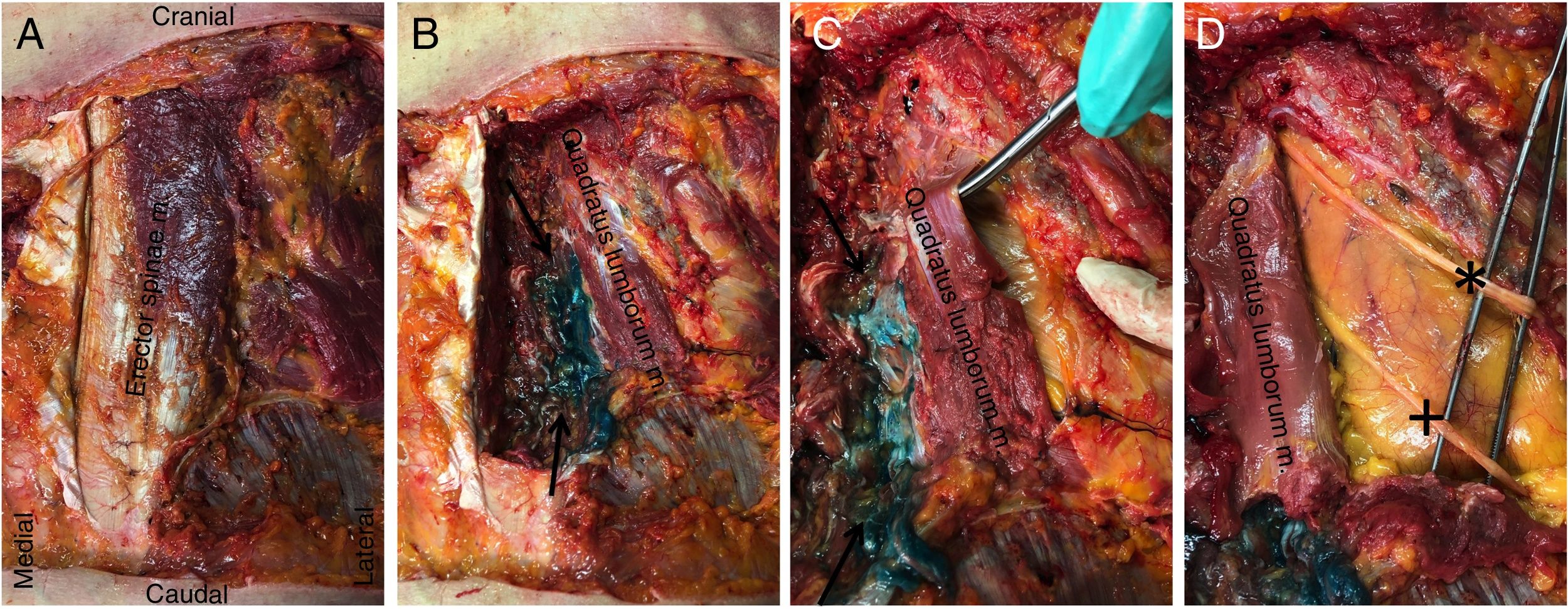
MethodsObservational study after 12 lumbar ESP blocks at L4 on a fresh cadaver model (6 bilaterally). The spread of 20 ml of injected contrast solution was assessed by computed tomography in all 6 samples. Four of the samples were evaluated by anatomical study, 2 by plane dissection, and 2 others were frozen and cut into 2–2.5 cm axial slices.
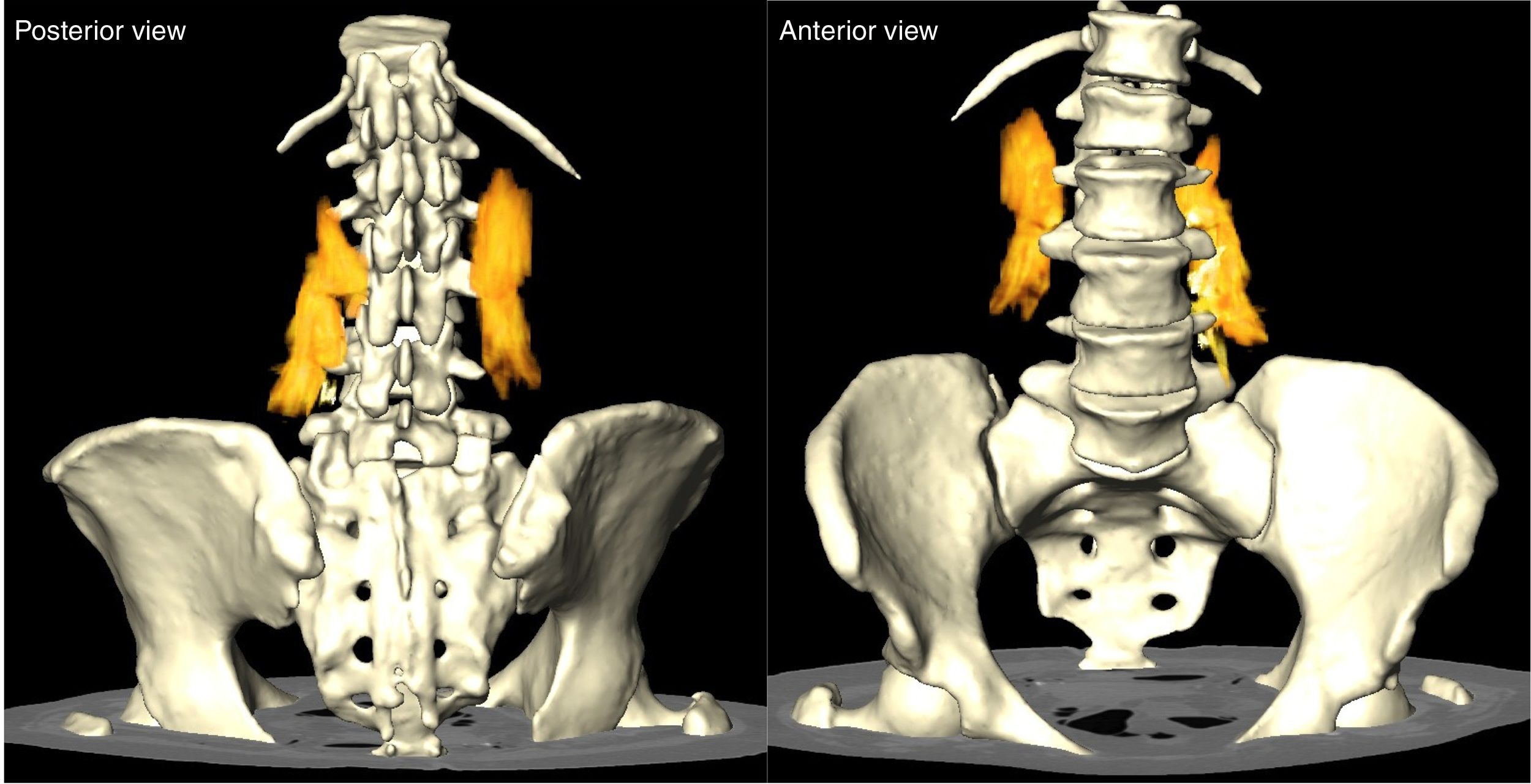
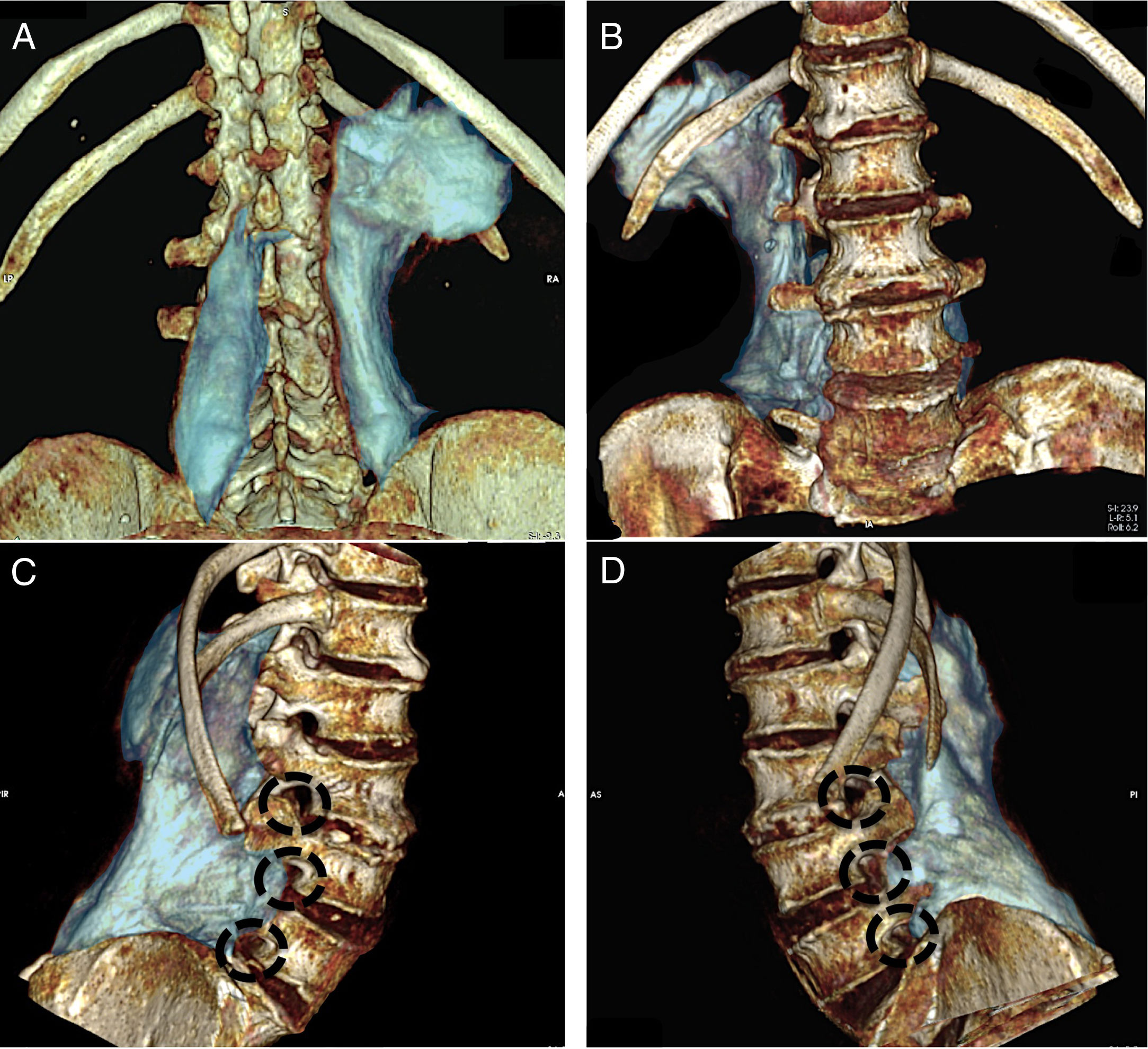
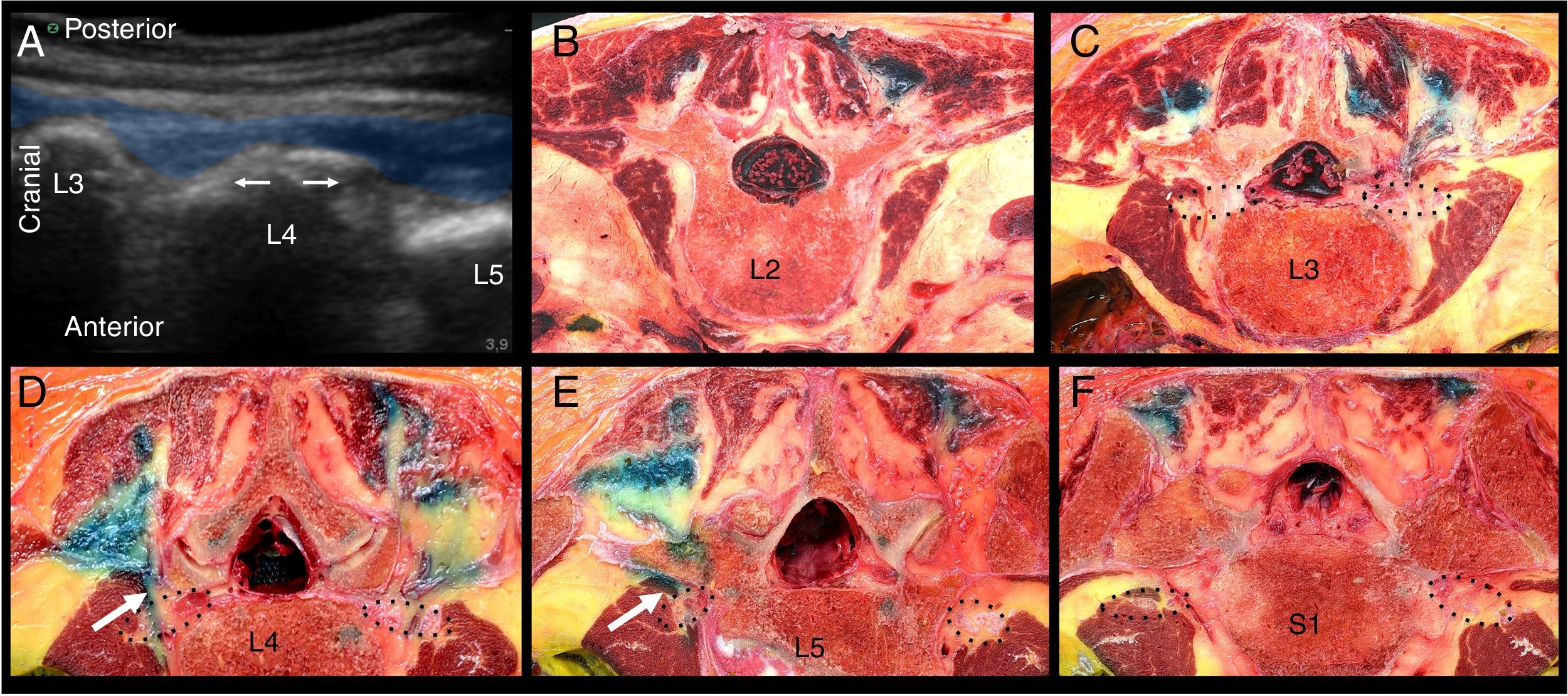
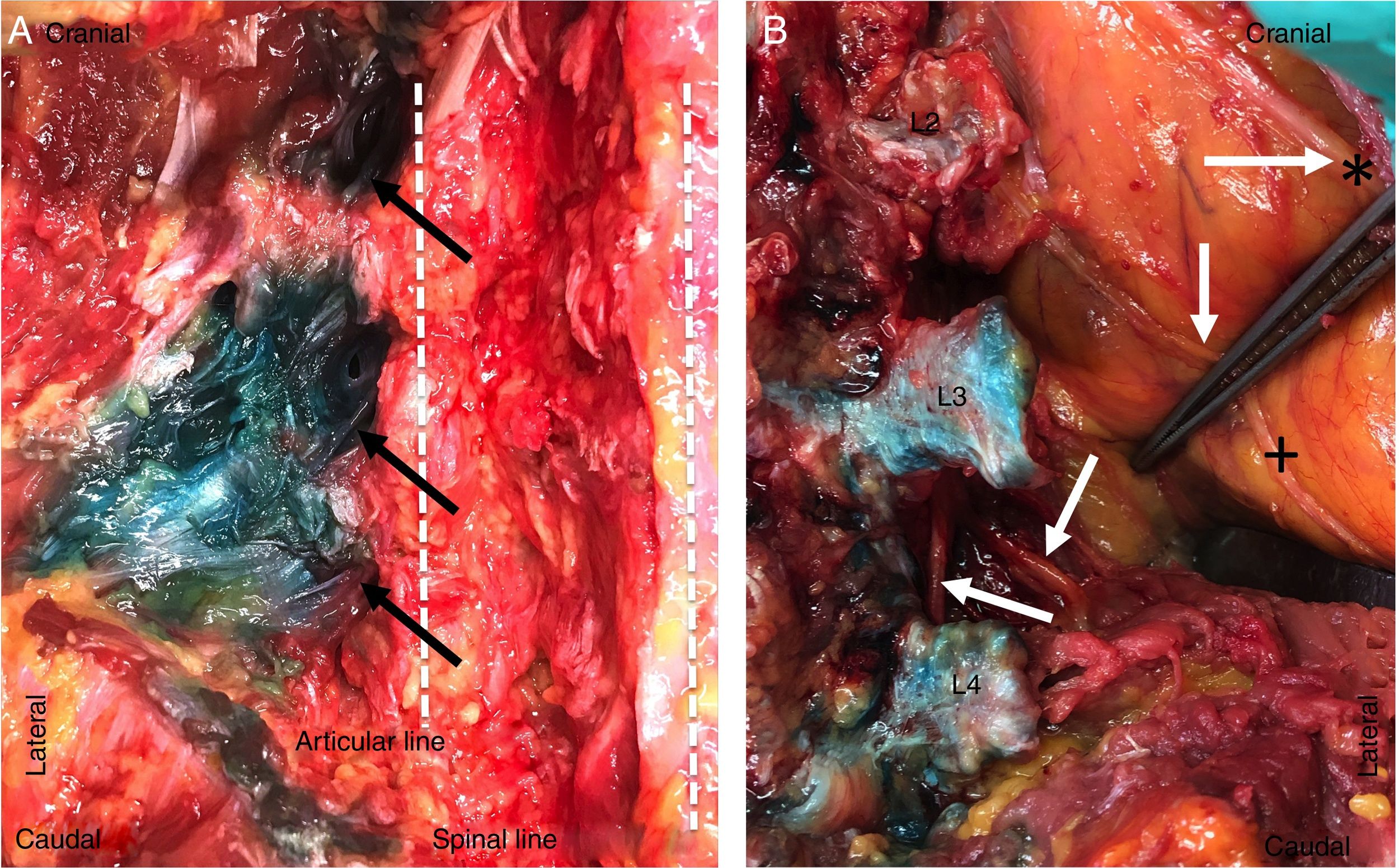
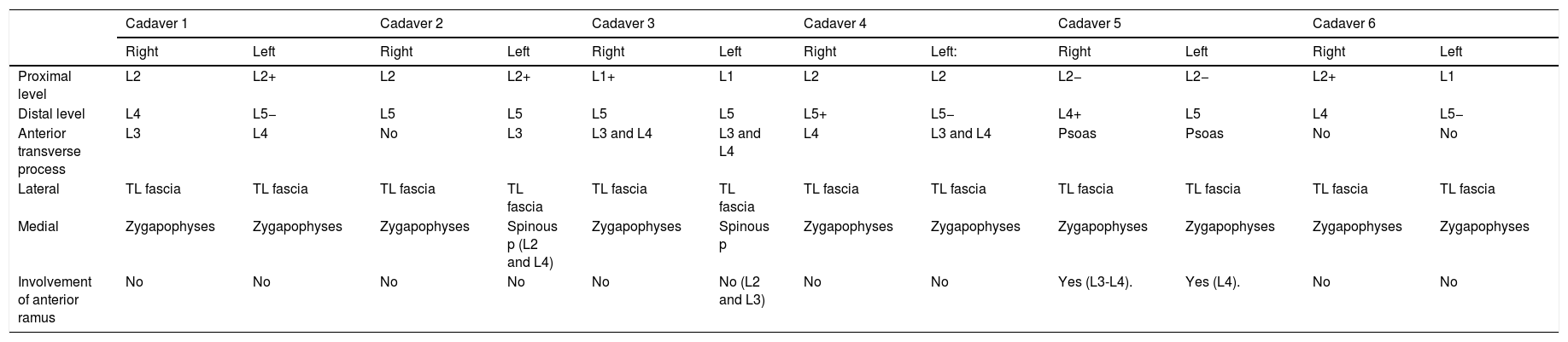
ResultsThe injected solution spread from L2 to L5 in a cranio-caudal direction in the erector spinae muscle, reaching the facet joints medially and the thoracolumbar fascia laterally. In 33% of cases the solution did not spread anterior to the transverse process; in 51%, spread was minimal and did not affect the corresponding spinal nerves, and in 2 samples (16%), spread was extensive and reached the corresponding spinal nerves.
ConclusionsLumbar ESP at L4 always acts on the posterior branches of the spinal nerves, but seldom spreads to the paravertebral space to block the spinal nerve.
El bloqueo en el plano del erector espinal (erector spinae plane [ESP]) a nivel torácico se ha introducido cómo método analgésico postoperatorio. Sin embargo, a pesar de que su empleo a nivel lumbar ha sido publicada, su distribución y su mecanismo de acción no han sido esclarecidos. Nos propusimos describir la técnica de punción del bloqueo ESP a nivel lumbar y evaluar la distribución de 20 ml administrados a nivel de la transversa de L4 en un modelo cadavérico.
MétodosEstudio observacional tras 12 bloqueos del ESP lumbar en L4, sobre un modelo de cadáver fresco (6 bilaterales). Se valoró la distribución de 20 ml de solución inyectada contrastada mediante tomografía computarizada en las 6 muestras. Fueron evaluados mediante estudio anatómico 4 de las muestras, 2 mediante disección por planos y otros 2 fueron congelados y seccionados con cortes axiales de 2-2,5 cm de grosor.
ResultadosLa distribución de la solución inyectada se distribuyó en el interior de la musculatura erectora espinal cráneo-caudal desde L2 a L5, con límite medial en la articulares interapofisarias y lateral en la fascia toracolumbar. El paso anterior a la transversa no se observó en el 33% de los casos, fue mínimo y sin afectación de los nervios espinales correspondientes en el 51%, siendo extenso en 2 muestras (16%) y con afectación del nervio espinal correspondiente.
ConclusionesEl ESP lumbar a nivel de L4 tiene una acción constante sobre los ramos posteriores de los nervios espinales, siendo infrecuente su paso al espacio paravertebral y bloquear el nervio espinal.