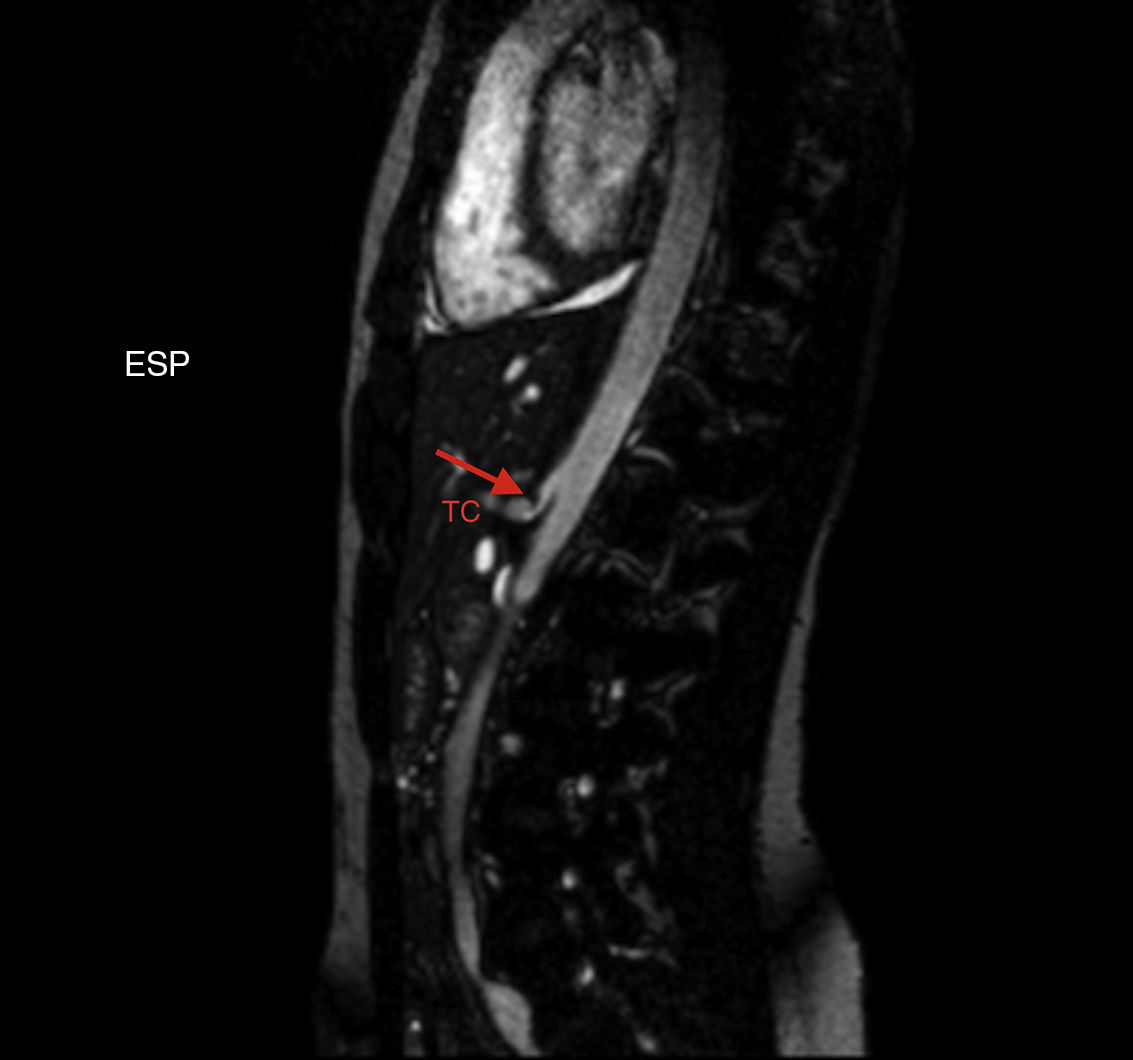
Median arcuate ligament syndrome, also known as celiac artery compression syndrome, is a rare and unusual clinical disorder. Its symptoms are non-specific, which complicates its diagnosis, and a multidisciplinary approach is required to treat the disorder. The ligament is circumferentially cleared by laparoscopy. Selective angiography and endovascular techniques may be used after laparoscopy. Vital organs and important vascular structures can be injured during the surgery. The combination of different procedures, as well as the high risk of damage, make this process a significant challenge for the anaesthetist. During corrective surgery for median arcuate ligament syndrome, general anaesthesia must be adapted to the various haemodynamic and ventilatory requirements, and strict control of pain established, as oral tolerance is a key factor in the post-operative recovery of these patients.
El síndrome del ligamento arcuato medio, o síndrome de compresión del tronco celíaco, es un cuadro clínico poco frecuente. La especificidad de sus síntomas hace difícil su diagnóstico. En el caso descrito la corrección quirúrgica del síndrome del ligamento arcuato medio precisó un abordaje multidisciplinar. Inicialmente se realizó una descompresión laparoscópica y, posteriormente, control angiográfico y procedimientos endovasculares. La combinación de diferentes técnicas intervencionistas, asociada al riesgo de lesión de órganos y estructuras vasculares importantes, convirtieron esta enfermedad en un reto para el anestesiólogo. Durante la cirugía de corrección del síndrome del ligamento arcuato medio, la anestesia general ha de adaptarse a los diferentes requerimientos hemodinámicos y ventilatorios, y se ha de establecer un estrecho control del dolor, ya que el inicio de la tolerancia oral es un factor clave en la recuperación postoperatoria de estos pacientes.