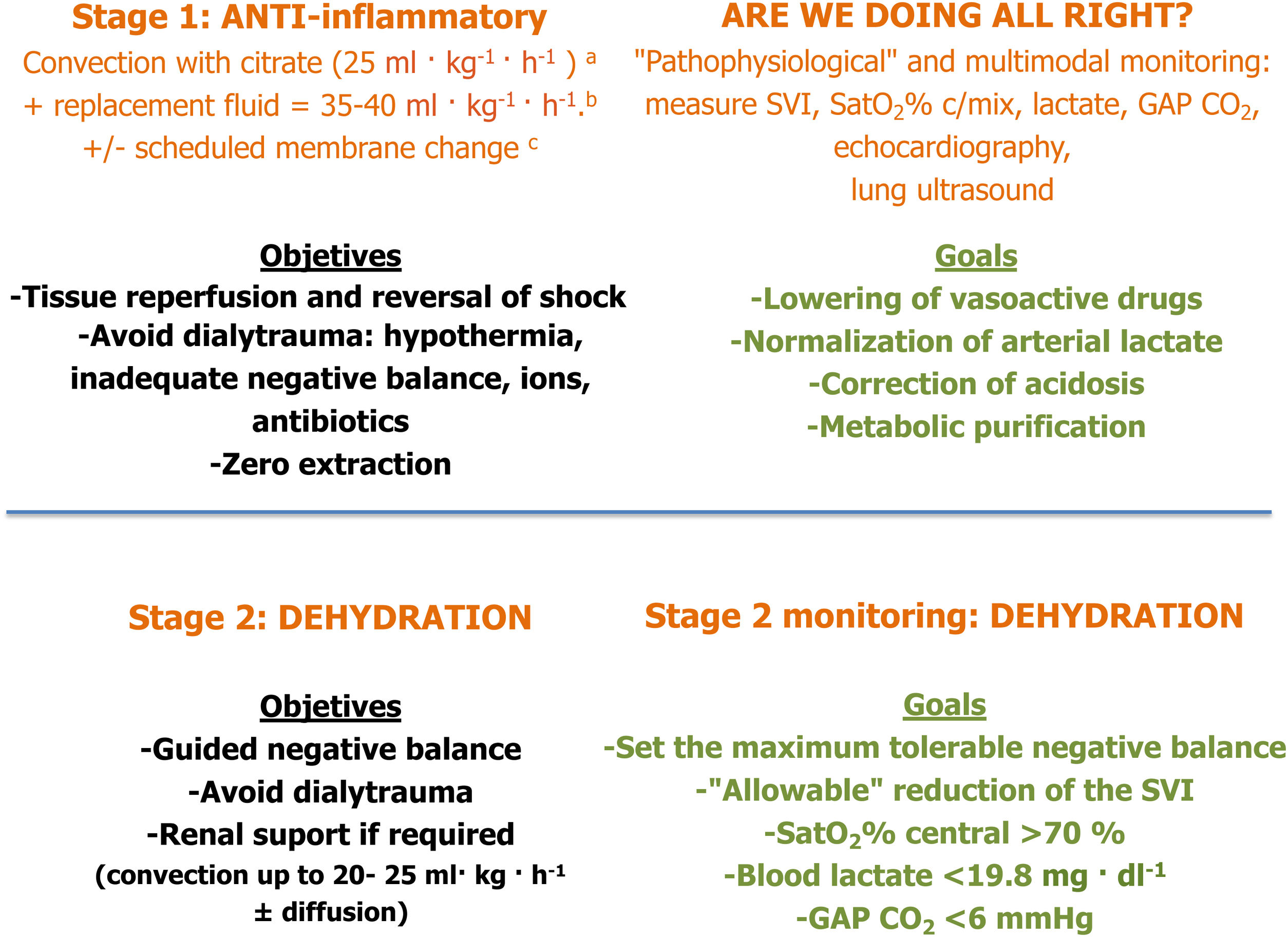
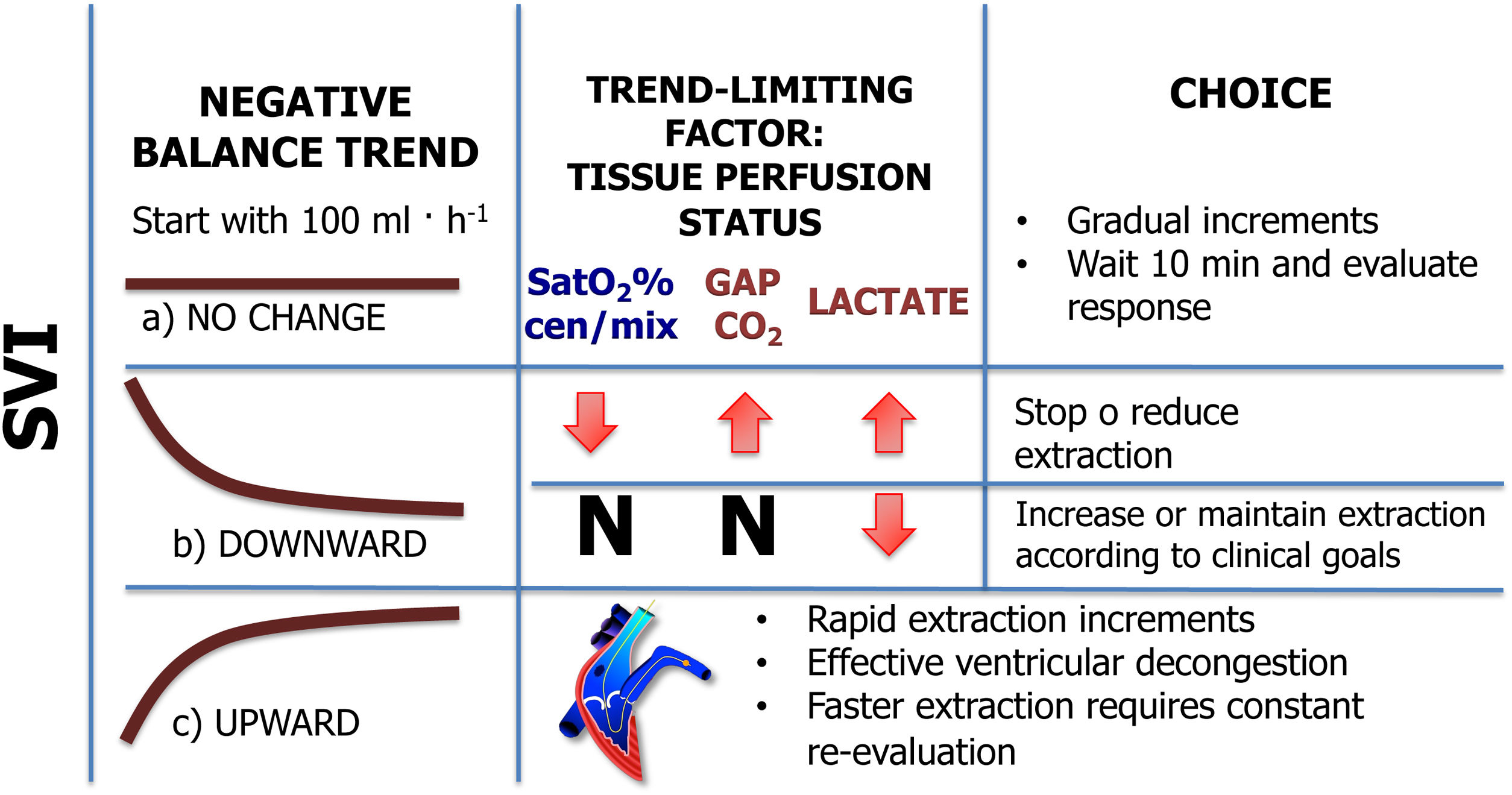
Haemofiltration paradigms used to manage critically ill patients with a dysregulated inflammatory response (DIR) assess kidney function to monitor its onset, adaptation, and completion. A Continuous Venous Hyperfiltration (CONVEHY) protocol is presented, in which a non-specific adsorption membrane (AN69-ST-Heparin Grafted) is used with citrate as an anticoagulant and substitution fluid. CONVEHY uses tools readily available to achieve kidney related and non-related objectives, and it is guided by the monitoring of pathophysiological responses.
ObjectivesTo compare the response to an AN69-ST-HG membrane when heparin (He, n=5: standard protocol) or citrate (Ci, n=6: CONVEHY protocol) was used to evaluate whether a larger study into the benefits of this protocol would be feasible.
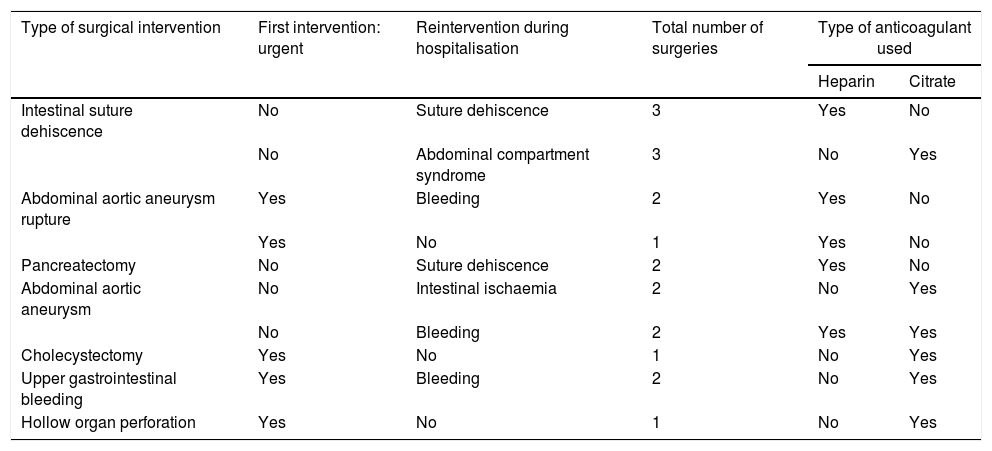
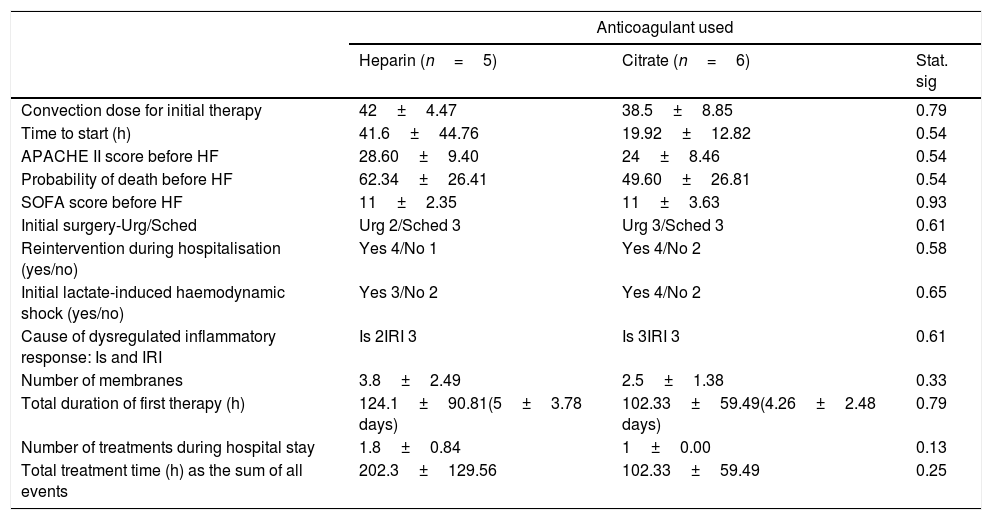
Materials and methodsIn a retrospective pilot study, the benefits of the CONVEHY protocol to manage patients with a DIR in a surgical critical care unit (CCUs) were assessed by evaluating the SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) (He 11±2.35; Ci 11±3.63: p = 0.54) and APACHE II (He 28.60±9.40; Ci 24±8.46: p = 0.93) scores.
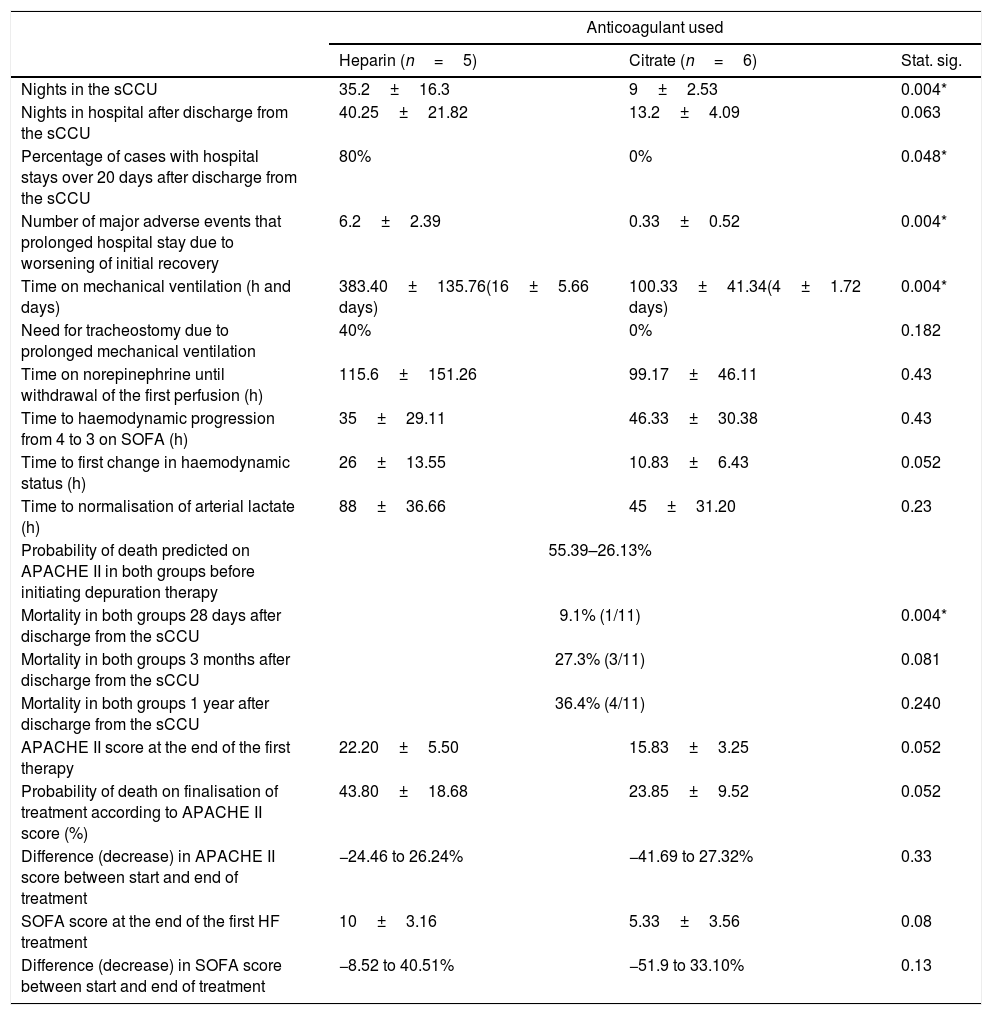
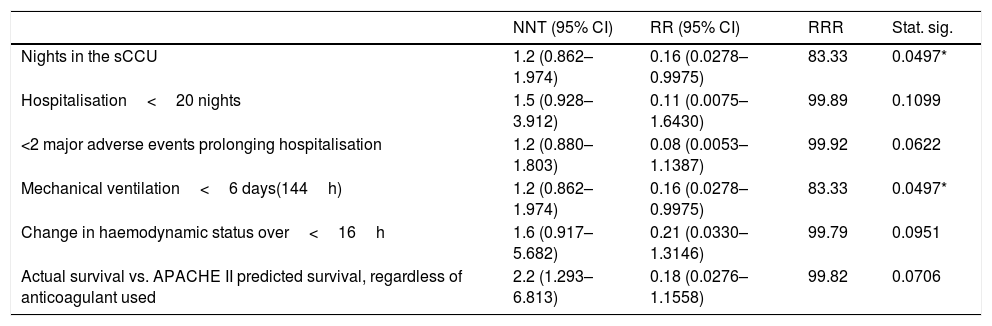
ResultsNights in hospital (He 35.2±16.3 nights; Ci 9±2.53: p = 0.004), hospital admission after discharge from the CCUs (He 40.25±21.82; Ci 13.2±4.09: p = 0.063), patients hospitalised >20 days (He 80%; Ci 0%: p = 0.048), days requiring mechanical ventilation (He 16±5.66; Ci 4±1.72: p = 0.004), and the predicted (55.39±26.13%) versus real mortality in both groups (9.1%: p = 0.004).
ConclusionsThe CONVEHY protocol improves the clinical responses of patients with DIR, highlighting the potential value of performing larger and confirmatory studies.
Los paradigmas de la hemofiltración para manejar pacientes críticos con una respuesta inflamatoria desregulada (RID) evalúan la función renal para su inicio, adaptación y finalización. Presentamos la Hiperfiltración Venosa Continua (Protocolo CONVEHY), en el cual una membrana de adsorción inespecífica (AN69-ST-heparina anclada) se utiliza con citrato como líquido anticoagulante y de sustitución. El protocolo CONVEHY utiliza herramientas fácilmente disponibles para lograr objetivos renales y no renales, guiándose por las respuestas fisiopatológicas.
ObjetivosComparar la respuesta a la membrana AN69-ST-HA cuando se utilizó heparina (He, n = 5: protocolo estándar) o citrato (Ci, n = 6: protocolo CONVEHY) para evaluar si fuera factible un estudio mayor sobre los beneficios de este protocolo.
Materiales y métodosEn un estudio retrospectivo, se evaluaron los beneficios del protocolo CONVEHY en pacientes con RID en una unidad de cuidados críticos quirúrgicos (UCCq), evaluando las puntuaciones SOFA (He 11±2,35; Ci 11±3,63; p = 0,54) y APACHE II (He 28,60±9,40; Ci 24±8,46; p = 0,93).
ResultadosHospitalización (He 35,2±16,3 noches; Ci 9±2,53; p = 0,004), hospitalización tras el alta de UCCq (He 40,25±21,82; Ci 13,2±4,09; p = 0,063), pacientes hospitalizados > 20 días (He 80%; Ci 0%; p = 0,048), días con ventilación mecánica (He 16±5,66; Ci 4±1,72; p = 0,004) y la mortalidad predicha (55,39±26,13%) frente a la real en ambos grupos (9,1%; p = 0,004).
ConclusionesEl protocolo CONVEHY mejora las respuestas clínicas de los pacientes con una RID, destacando el valor potencial de realizar estudios más grandes y confirmatorios.