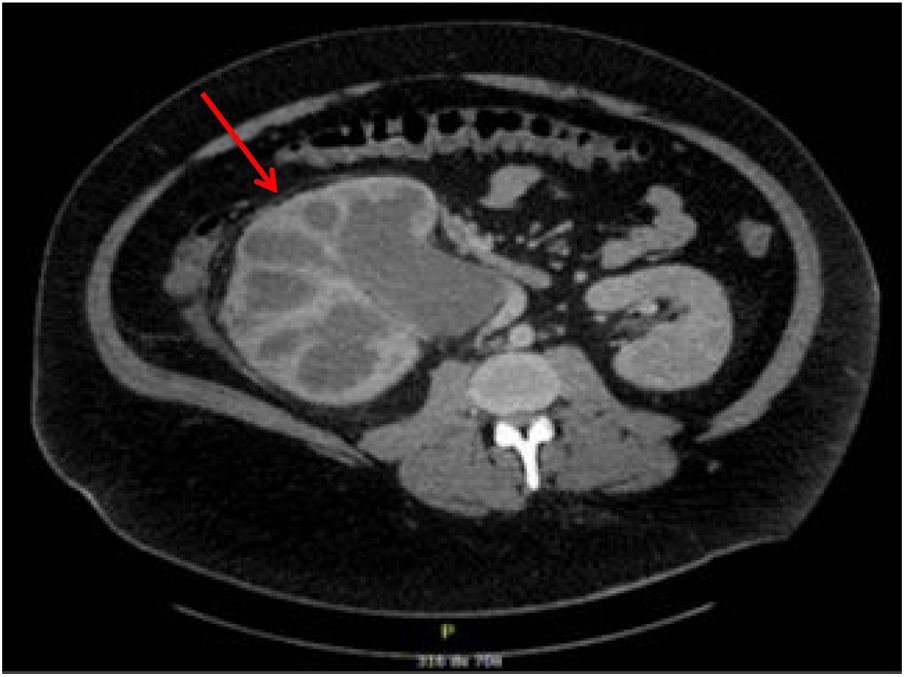
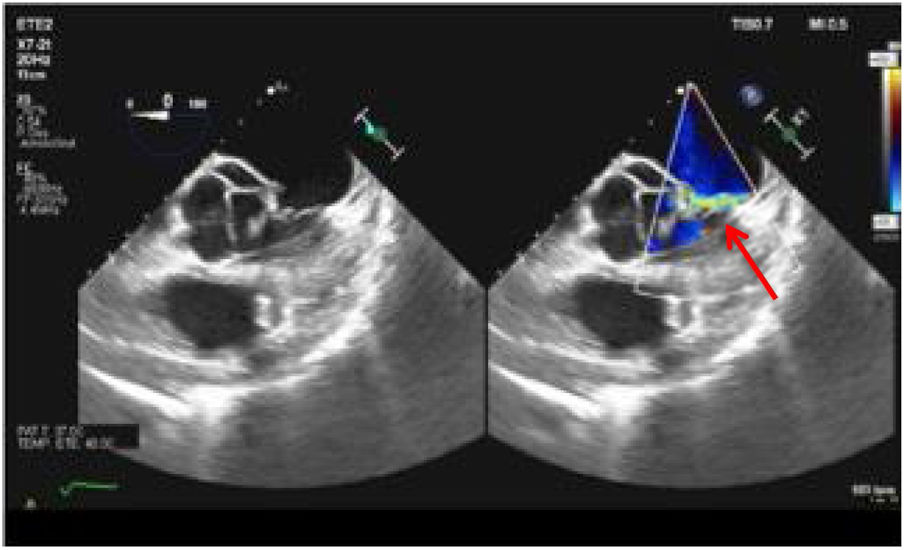
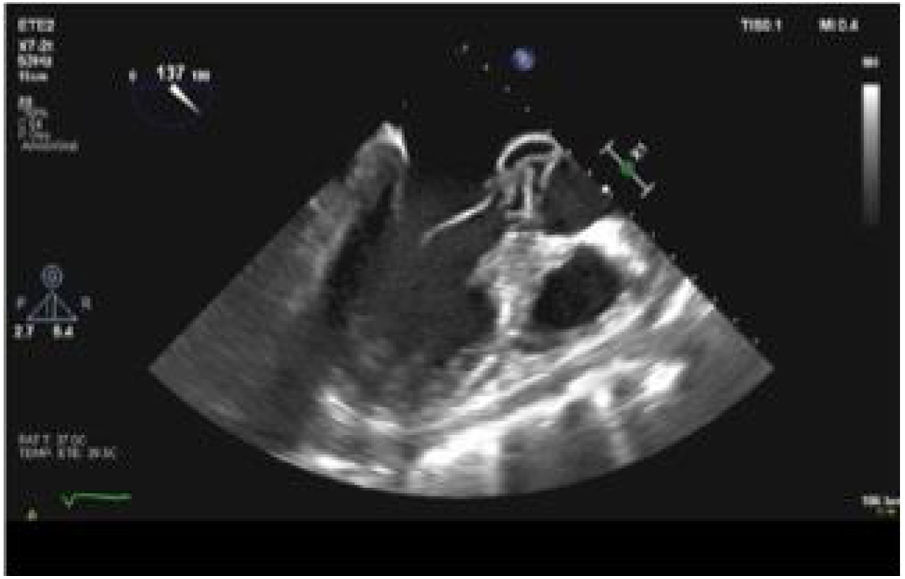
Infective endocarditis (IE) due to Escherichia coli is a rare disease, although increasingly frequent. Persistent fever in septic patients despite adequate treatment raises the need to consider IE as a differential diagnosis. We present the case of a 36-year-old male patient who underwent a radical right nephrectomy as a result of diagnosis of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, presenting in the postoperative period a state of septic shock with persistent fever of 41 °C. Given the finding of a new-onset murmur, he was diagnosed with a mitroaortic IE by means of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), having to undergo cardiac surgery for valve replacement. After multiple postoperative complications, he is successfully discharged.
La endocarditis infecciosa (EI) debida a Escherichia coli es una enfermedad rara, aunque cada vez más frecuente. La fiebre persistente en pacientes sépticos a pesar de un tratamiento adecuado plantea la necesidad de considerar la EI como diagnostico diferencial. Presentamos el caso de un paciente varón de 36 años al que se le practica una nefrectomía radical derecha por diagnóstico de pielonefritis xantogranulomatosa, presentando en el postoperatorio un estado de shock séptico con fiebre persistente de hasta 41 °C. Ante el hallazgo de un soplo de nueva aparición se le diagnostica de EI mitroaórtica mediante Ecocardiograma transesofágico (ETE) teniendo que someterse a cirugía cardiaca para sustitución valvular. Tras múltiples complicaciones postoperatorias es dado de alta exitosamente.