Vitrectomy surgery is a common procedure for the treatment of several types of ophthalmologic conditions. It can be performed under regional anaesthesia with peribulbar block (PB) or general anaesthesia (GA). There are no evidence-based recommendations on the optimal anaesthesia strategy for this procedure. The aim of this study was to compare the advantages of PB and GA for vitrectomy surgery.
Materials and methodsA prospective observational study was conducted on adults submitted for mechanical vitrectomy between January 2017 and December 2017. Demographic and perioperative data were collected, namely ASA physical status, median arterial pressure, heart rate, postoperative opioid consumption, postoperative nausea and vomiting, times of induction, surgery, recovery, and hospital stay and costs considering medication and material needed. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v.25, with chi-square, Fisher and Mann-Whitney U tests, according to the type of variables analysed.
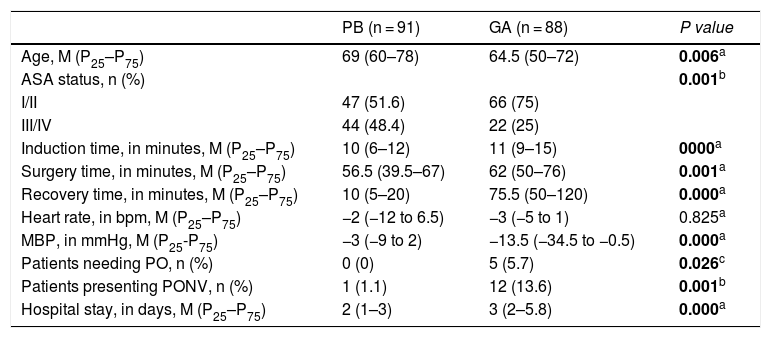
Results and discussionWe included 179 patients submitted for mechanical vitrectomy: 91 (51 %) with PB and 88 (49 %) under GA. Patients submitted to PB were older (69.0 vs. 64.5 years, p = .006) and presented with higher ASA physical status (p = .001). For haemodynamic outcomes, patients submitted to PB presented with less variation of median arterial pressure (−3.0 vs. −13.5 mmHg, p = .000) and with no significant differences in heart rate (−2.0 vs. −3.0 bpm, p = .825). In the postoperative period, the PB group presented with decreased need of postoperative analgesia (0.0 vs. 5.0, p = .026) and a lower incidence of nausea and vomiting (1.0 vs. 12.0, p = .001). Times related to anaesthesia and surgery were better in PB group, with shorter induction time (10.0 vs. 11.0 min, p = .000), surgery time (56.5 vs. 62.0 min, p = .001), recovery time (10.0 vs. 75.5 min, p = .000), and hospital stay (2.0 vs. 3.0 days, p = .000). When analysing costs, PB was less expensive than GA (4.65 vs. 12.09 euros, p = .021).
ConclusionPB is a reliable and safe alternative to GA for patients undergoing mechanical vitrectomy, permitting good anaesthesia and akinesia conditions during surgery, better haemodynamic stability, and less postoperative complications, especially in older patients and those with more comorbidities.
La cirugía de vitrectomía es un procedimiento común para el tratamiento devarios tipos de afecciones oftalmológicas, y se puede realizar bajo anestesia regional con blo-queo peribulbar (BP) o anestesia general (AG). No hay recomendaciones basadas en evidenciasobre el mejor tipo de anestesia para este procedimiento. En este contexto, nuestro objetivoes comparar AG y BP para la cirugía de vitrectomía.
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo en adultos sometidos a vitrectomíamecánica entre enero de 2017 y diciembre de 2017. Se recogieron datos demográficos y perioperatorios, en particular: estado físico ASA, presión arterial media, frecuencia cardiaca, consumode opioides postoperatorio, náuseas y vómitos postoperatorios, tiempos de inducción, cirugía, recuperación y estadía en el hospital y costes considerando los fármacos y el material necesario. El análisis estadístico se realizó con SPSS v.25, con pruebas de chi cuadrado, Fisher y Mann–Whitney U, según el tipo de variables analizadas.
Resultados y discusiónSe incluyeron 179 pacientes, de los cuales 91 (51 %) estaban bajo BP y88 (49 %) bajo AG. Los pacientes sometidos a BP presentaban una edad más avanzada (69 vs.64,5 años, p = 0,006 y se presentaron con valores en la escala ASA más elevados p = 0,001.Para los resultados hemodinámicos, los pacientes sometidos a BP presentaron una menor variación de la presión arterial media −3 vs. −13,5 mmHg, p = 0,000 y sin diferencias significativasen la frecuencia cardiaca −2 vs. −3 ppm, p = 0,825. En el período postoperatorio, el grupo deBP presentó una menor necesidad de analgesia postoperatoria 0 vs. 5, p = 0,026 y una menorincidencia de náuseas y vómitos 1 vs. 12, p = 0,001. Los tiempos relacionados con la anestesia y la cirugía fueron mejores en el grupo BP, con un tiempo de inducción más corto 10vs. 11 min, p = 0,000, tiempo de cirugía 56,5 vs. 62 min, p = 0,001, tiempo de recuperación 10 vs. 75,5 min, p = 0,000, y estancia hospitalaria 2 vs. 3 días, p = 0,000. Al analizar los costes, el BP fue más económico que AG 4,65 frente a 12,09 euros, p = 0,021.
ConclusiónEl bloqueo peribulbar es una alternativa segura a la anestesia general para pacientes sometidos a vitrectomía, especialmente pacientes mayores y aquellos con más comor-bilidades.