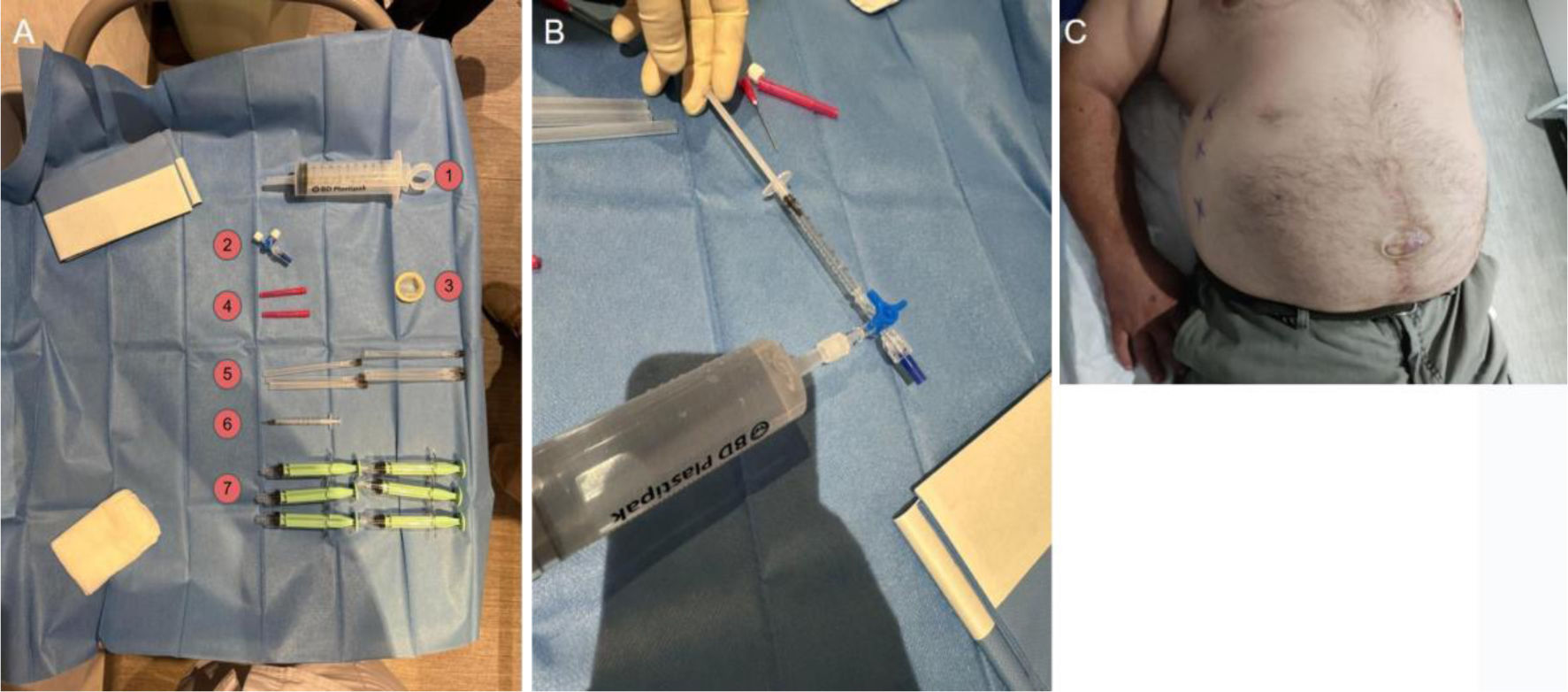
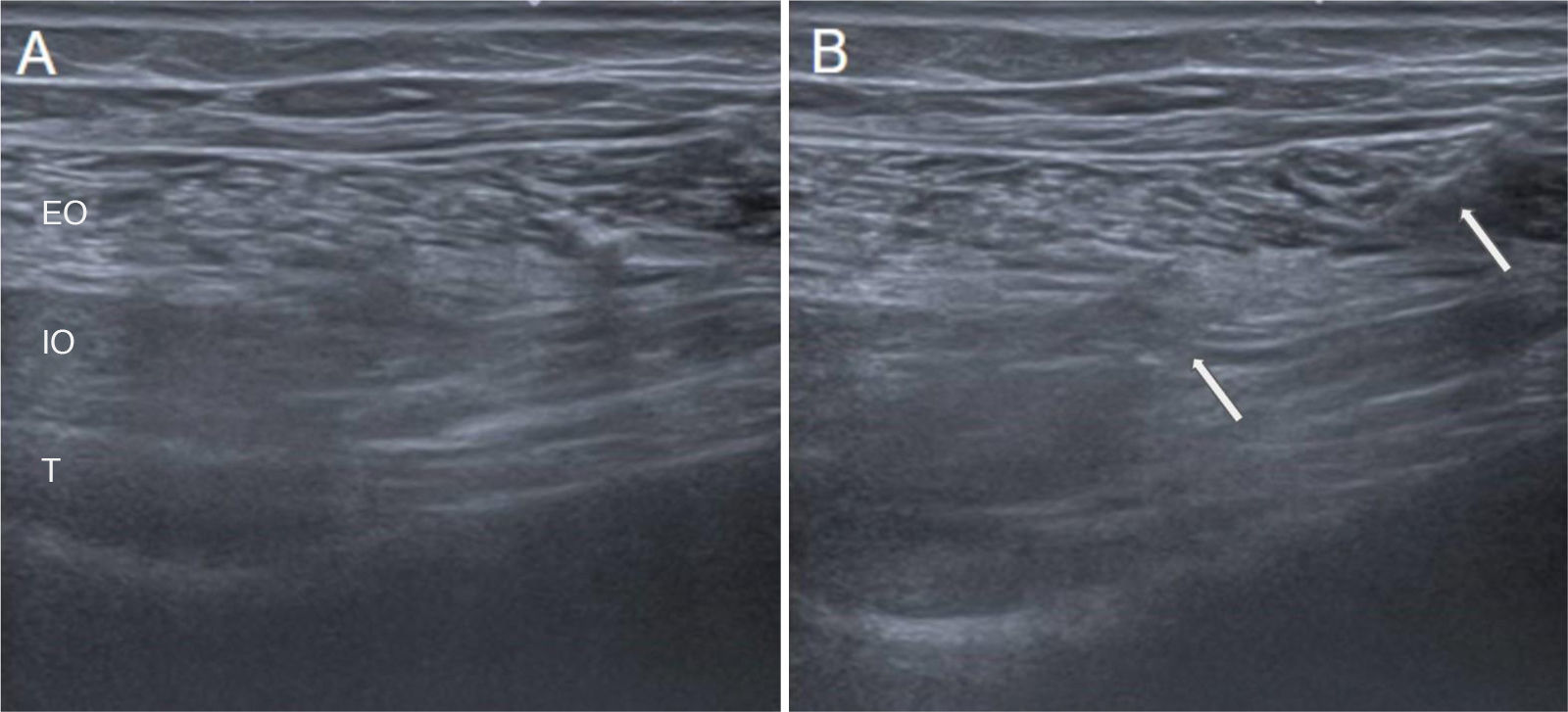
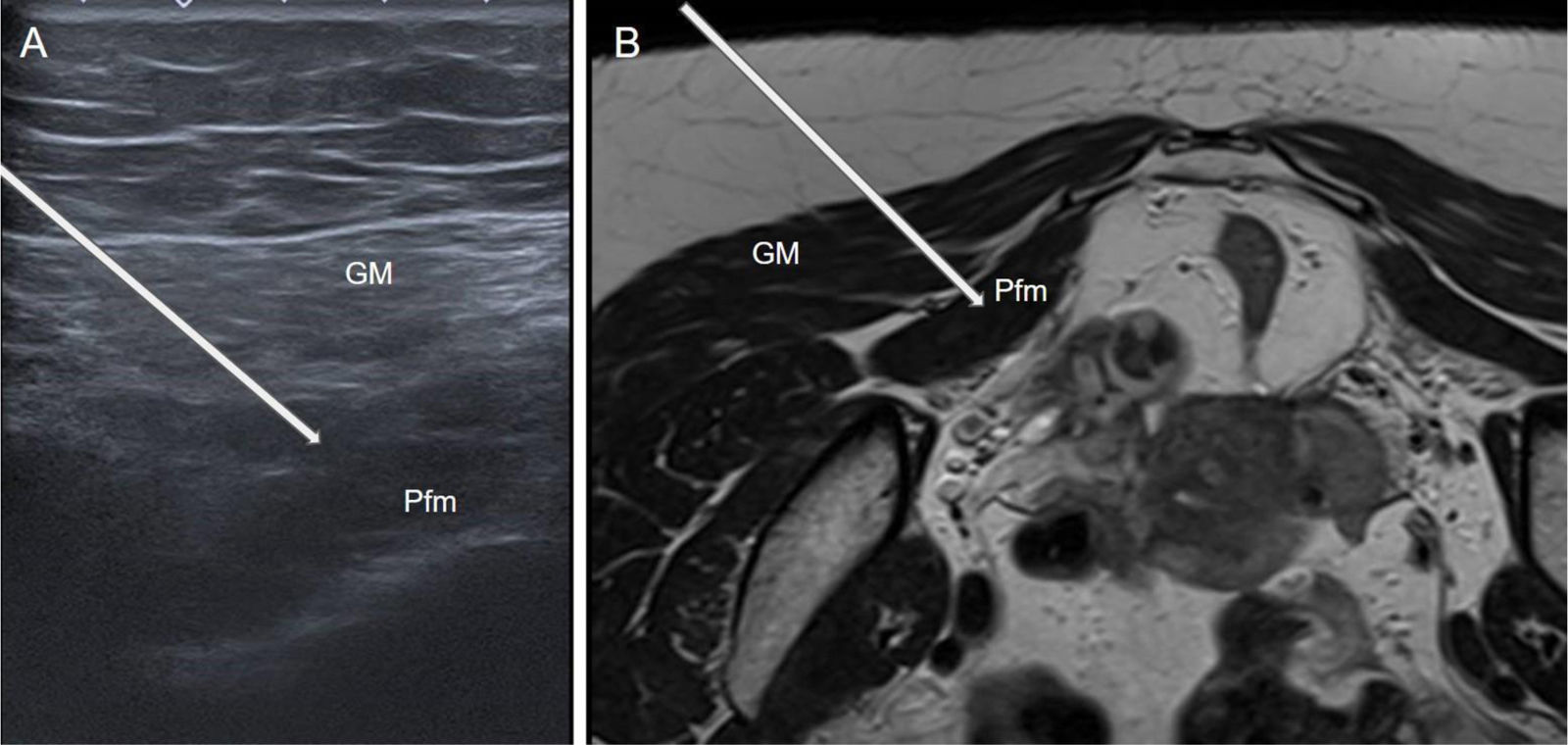
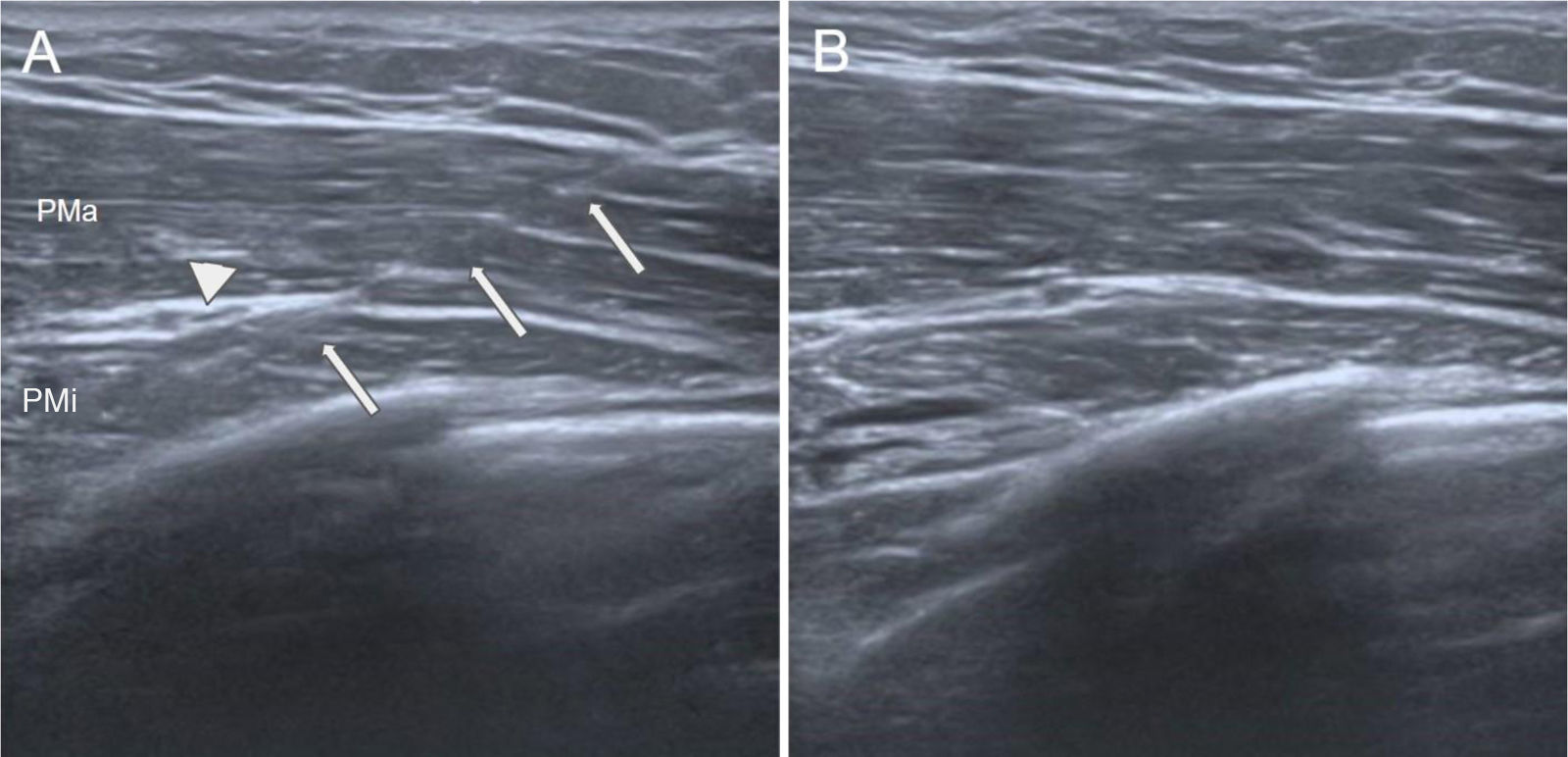
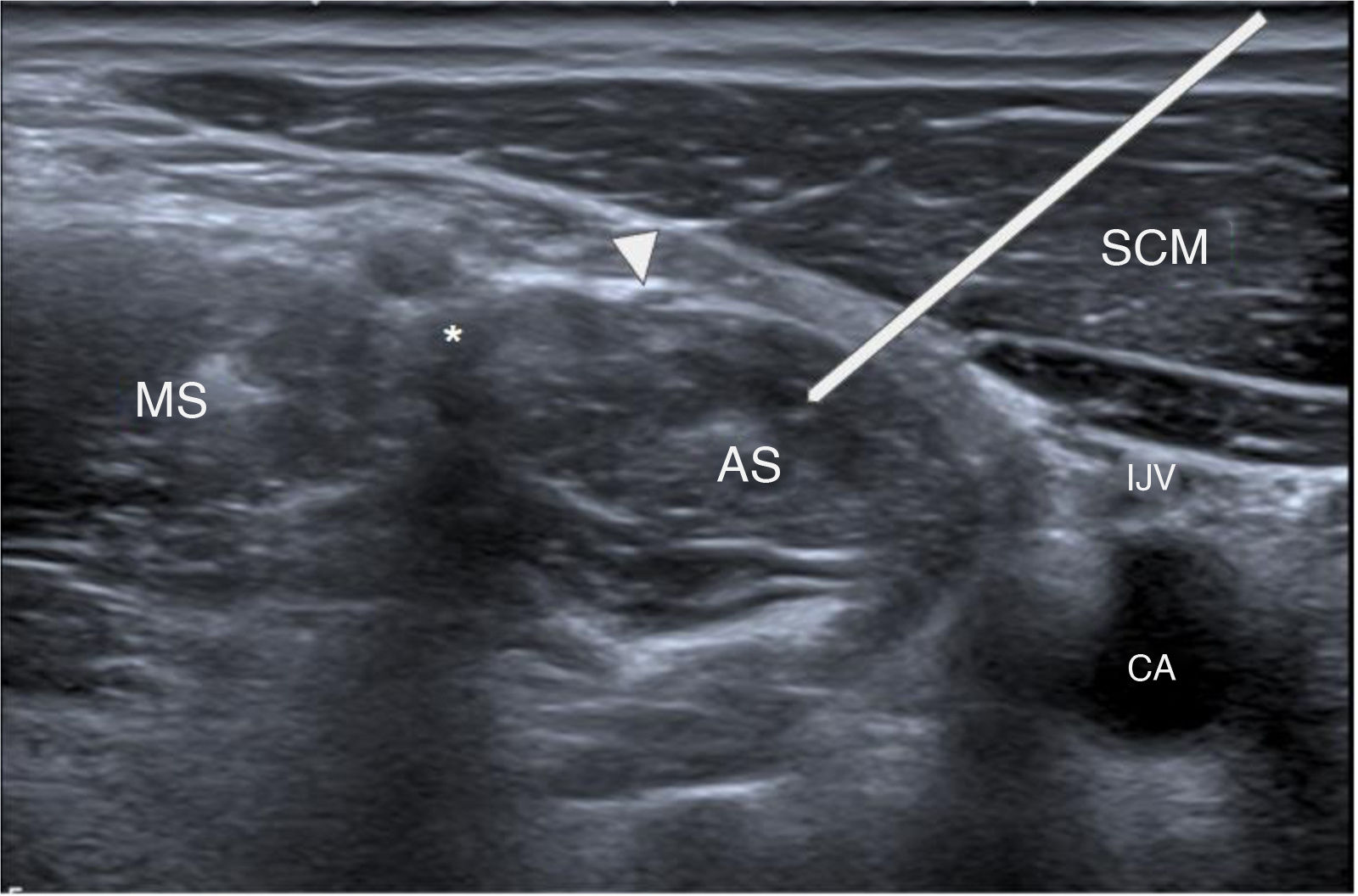
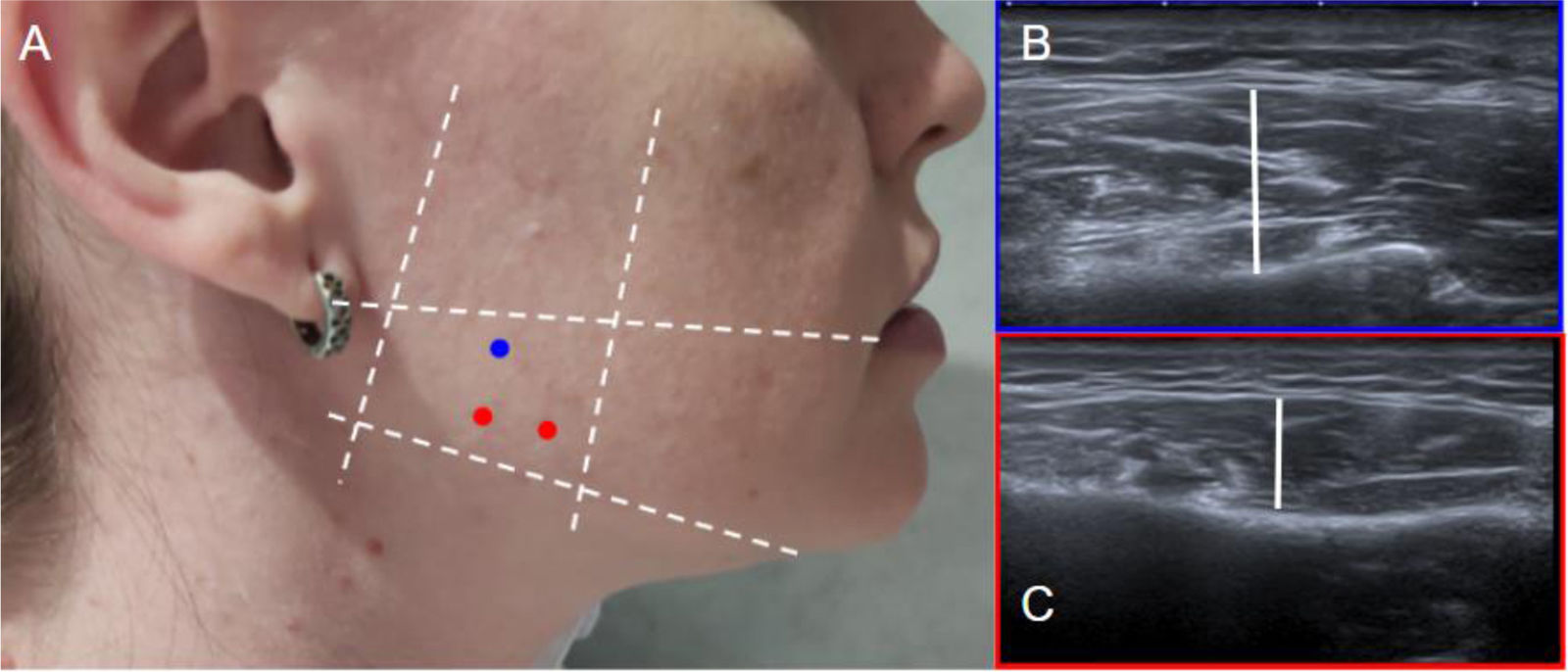
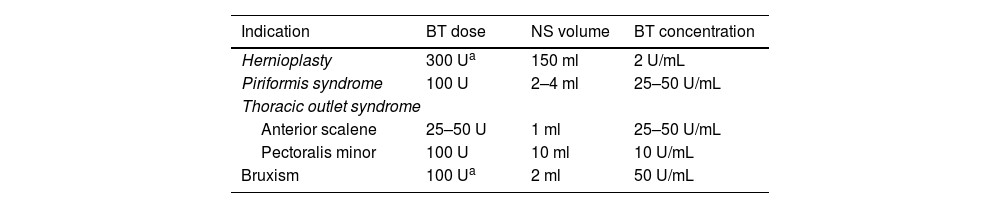
Botulinum toxin (BT) is a neurotoxin that causes flaccid paralysis by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, and it may lead to long-term muscle atrophy. It is used to treat conditions associated with muscle hypertrophy or to enhance muscle flexibility, thereby facilitating surgical procedures. It has been shown that ultrasound-guided administration is superior to the anatomical landmarks technique as it reduces side effects and improves efficacy. Although some applications are not officially approved, evidence supports its efficacy and safety in the treatment of various conditions. Some of these more established conditions include anterior abdominal wall hernias, piriformis syndrome, thoracic outlet syndrome, bruxism, spasticity and cervical dystonia. The objective of this study is to review the uses of botulinum toxin in muscular and neuromuscular disorders, analysing its efficacy, safety and the importance of ultrasound guidance in its administration.
La toxina botulínica (TB) es una neurotoxina que, al inhibir la liberación de acetilcolina en la unión neuromuscular, provoca parálisis flácida y puede llevar a atrofia muscular a largo plazo. Se emplea en patologías asociadas a hipertrofia muscular o para incrementar la flexibilidad muscular, facilitando así las cirugías. Se ha demostrado que su administración guiada por ecografía es superior a la técnica basada en referencias anatómicas, ya que disminuye los efectos secundarios y mejora la eficacia. Aunque algunas aplicaciones no están incluidas en la ficha técnica, hay evidencia de su eficacia y seguridad en el tratamiento de múltiples patologías, algunas de ellas más estandarizadas como hernias de la pared abdominal anterior, síndrome del piriforme, síndrome del opérculo torácico, bruxismo, espasticidad y distonía cervical. El objetivo de este estudio es revisar los usos de la toxina botulínica en patologías musculares y neuromusculares, analizando su eficacia, seguridad y la importancia de la guía ecográfica en su administración.