To compare the real time skin dosimeter values at lens between with the lens included in the scan range (orbitomeatal base line [OML]) or without the lens included in the scan range (superior orbitomeatal line [SOML]) at different tube voltages.
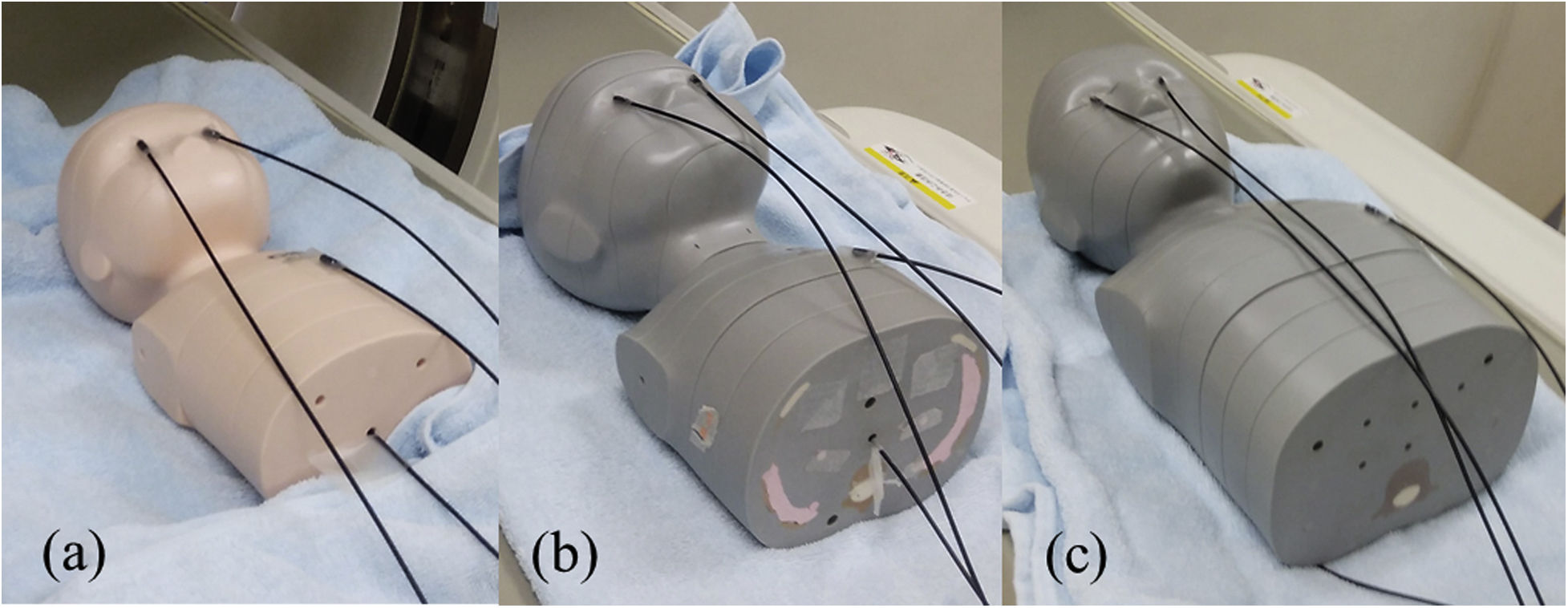
Materials and methodsWe used three pediatric anthropomorphic phantoms with a 64 detector-row computed tomography (CT) scanner with the OML- or SOML-protocol at different tube voltages during the head CT. A real time skin dosimeter was inserted into the phantom center of the head, and surfaces of the lens. We compared the real time skin dosimeter values at lens between the OML- and SOML-protocol.
ResultsThere were no significant differences in the real time skin dosimeter values for the head in the scan area for each phantom at different tube voltages between the OML- and SOML-protocol (p > 0.05 for all phantom). Compared with the OML protocol, it is possible to reduce the real time skin dosimeter values at lens by approximately 80% by using the SOML protocol (p < 0.05) at all tube voltages. Compared with the OML protocol, it is possible to reduce the real time skin dosimeter values at mammary gland by approximately 20% by using the SOML protocol (p < 0.05) at all tube voltages.
ConclusionsDuring the pediatric head CT examination, SOML protocol was possible to reduce the real time skin dosimeter values at lens by approximately 80% compared with OML protocol at all tube voltages.
Comparar los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en el cristalino entre los cristalinos incluidos en el rango de exploración (línea orbitomeatal base [OML]) o sin los cristalinos incluidos en el rango de exploración (línea orbitomeatal superior [SOML]) a diferentes tensiones de tubo.
Materiales y métodosSe utilizaron tres maniquíes antropomórficos pediátricos con un escáner de tomografía computarizada (TC) de 64 filas de detectores con el protocolo OML o SOML a diferentes tensiones de tubo durante la TC de la cabeza. Se insertó un dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en el centro de la cabeza del maniquí y en las superficies de los cristalinos. Comparamos los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en los cristalinos del protocolo OML y del protocolo SOML.
ResultadosNo se observaron diferencias significativas en los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real de la cabeza en el área de exploración de cada maniquí a diferentes tensiones de tubo entre el protocolo OML y el protocolo SOML (p > 0,05 para todos los maniquíes). En comparación con el protocolo OML, es posible reducir los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en los cristalinos en aproximadamente el 80% mediante el uso del protocolo SOML (p < 0,05) en todas las tensiones de tubo. En comparación con el protocolo OML, es posible reducir los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en la glándula mamaria en aproximadamente el 20% mediante el uso del protocolo SOML (p < 0,05) en todas las tensiones de tubo.
ConclusionesDurante la exploración mediante TC de la cabeza pediátrica el protocolo SOML permite reducir los valores del dosímetro cutáneo en tiempo real en los cristalinos en aproximadamente el 80% en comparación con el protocolo OML en todas las tensiones de tubo.