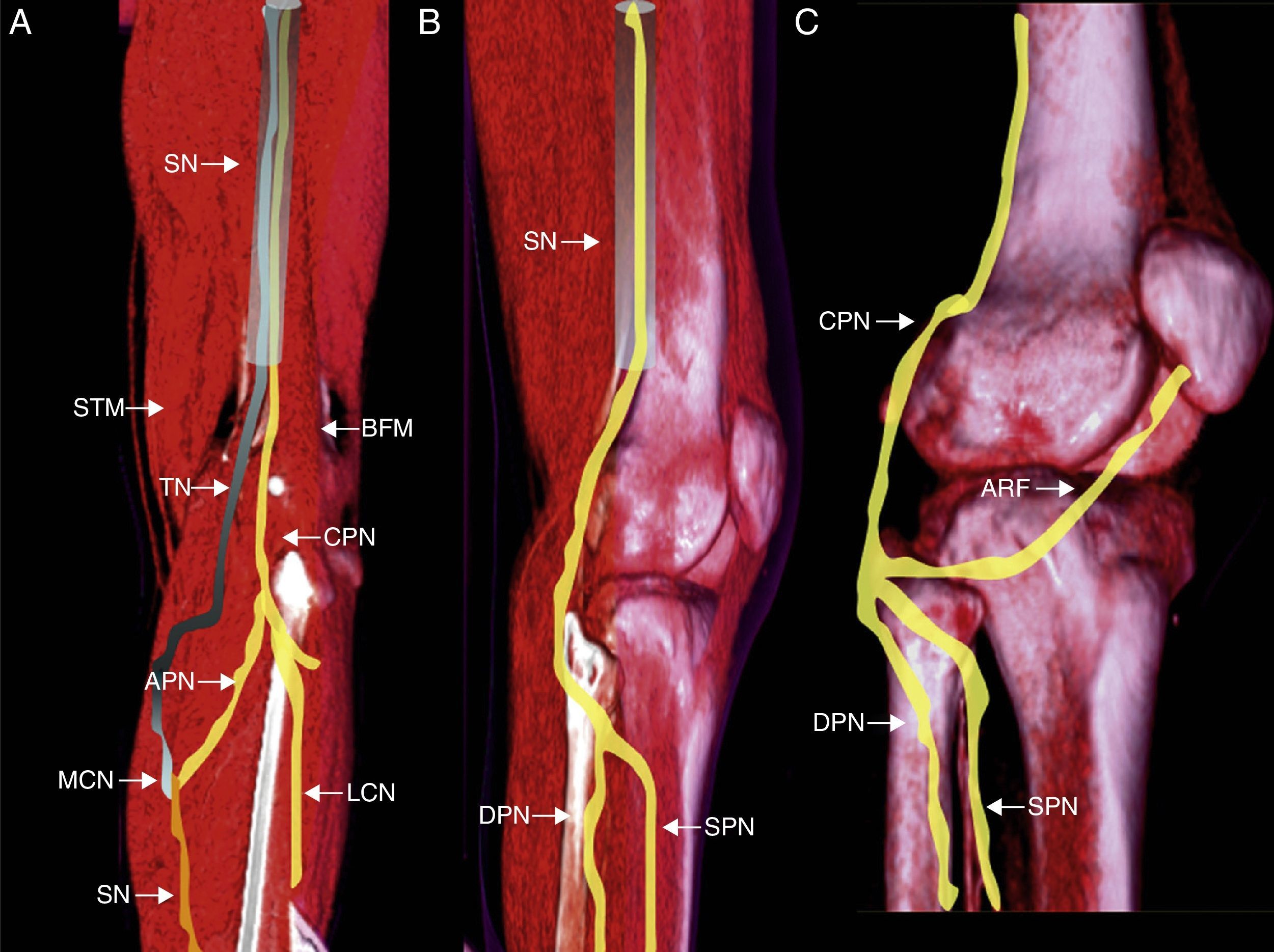
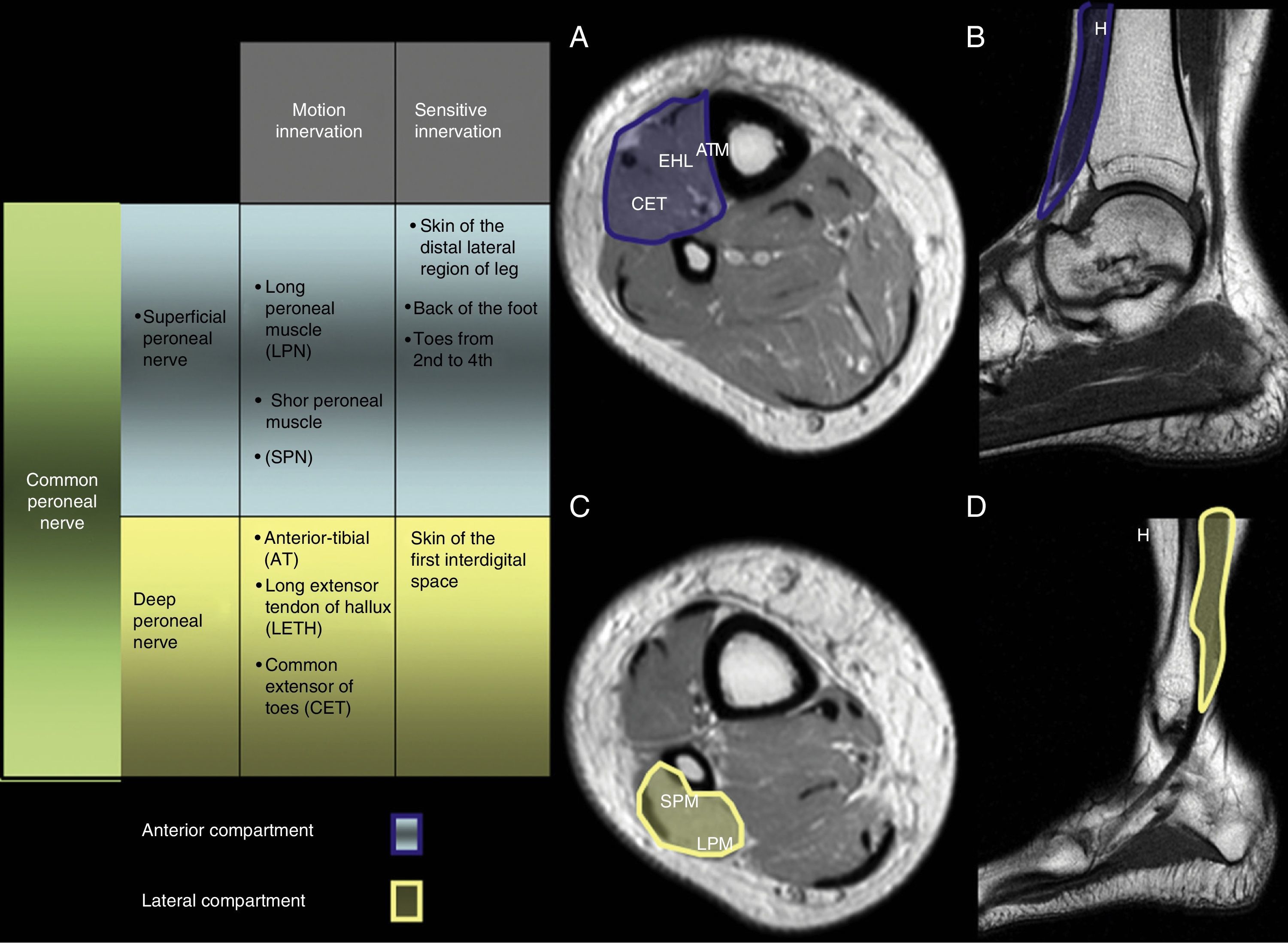
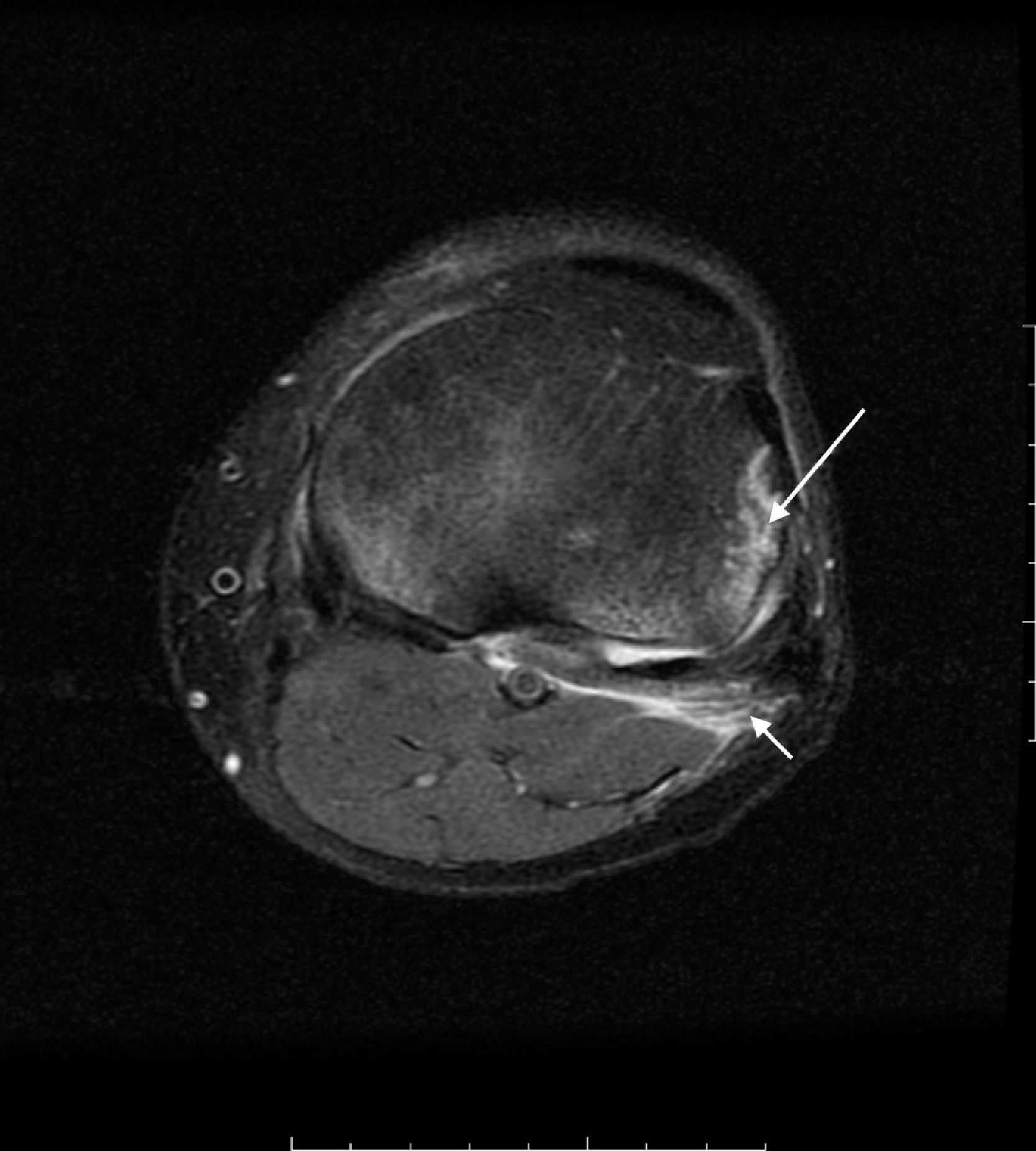
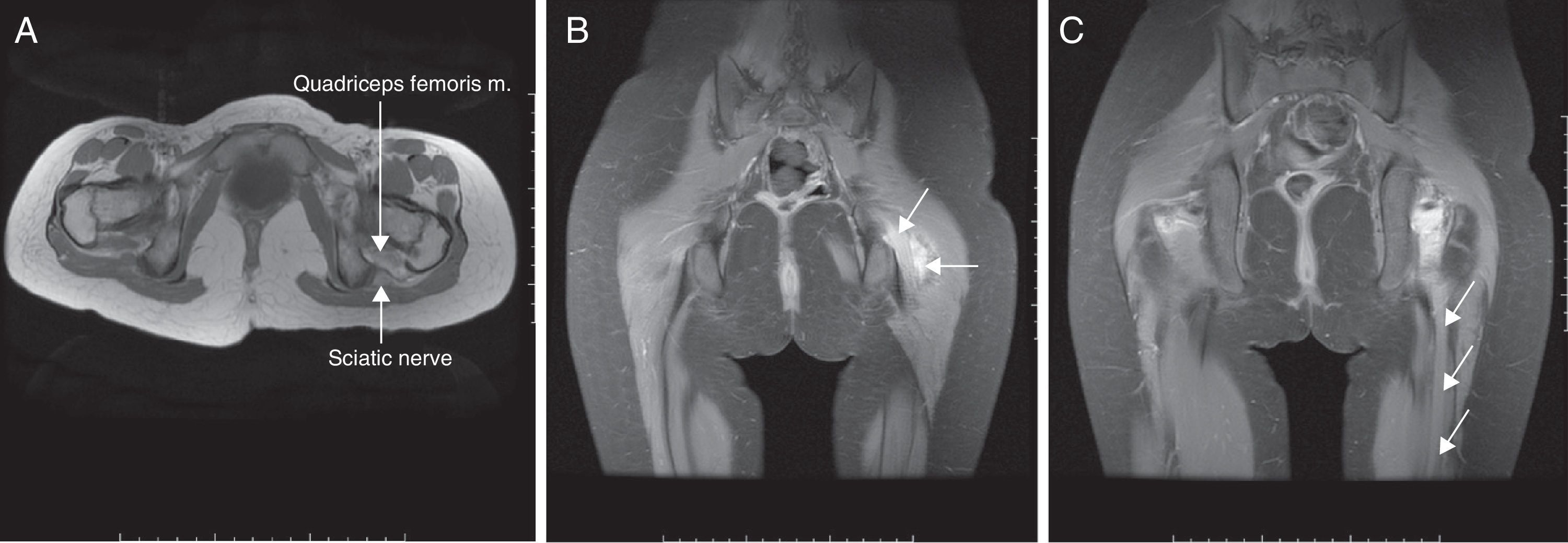
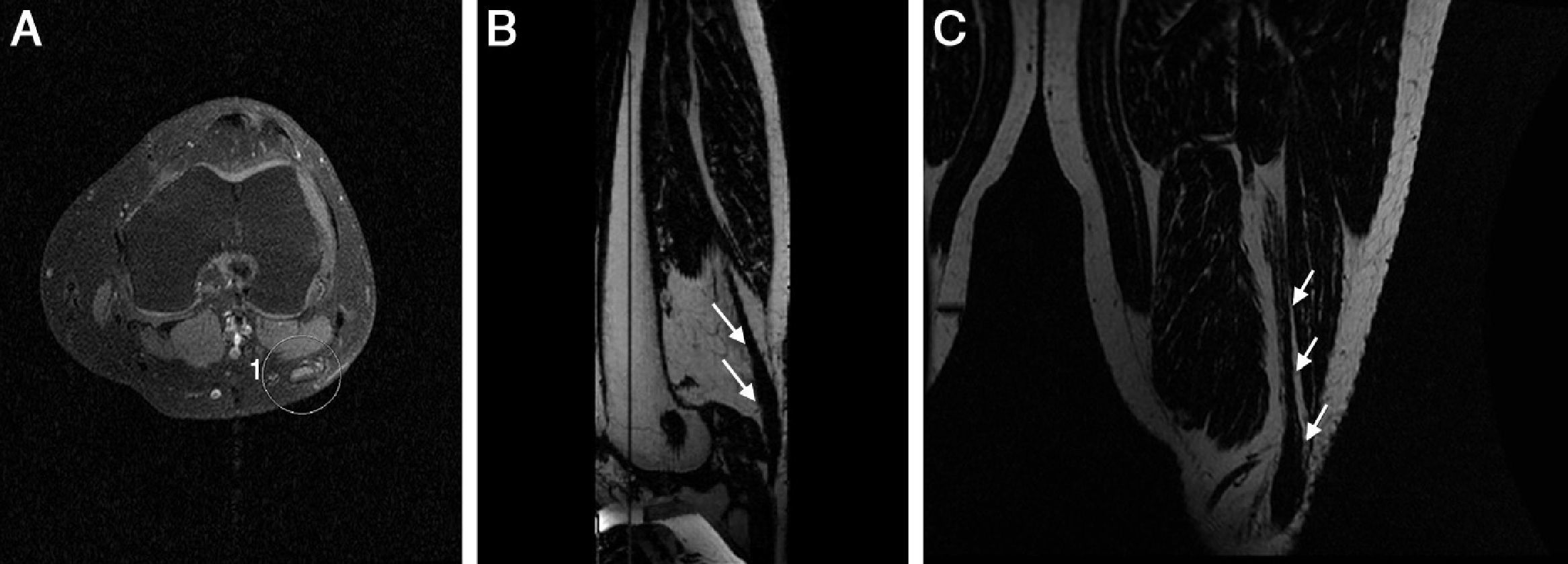
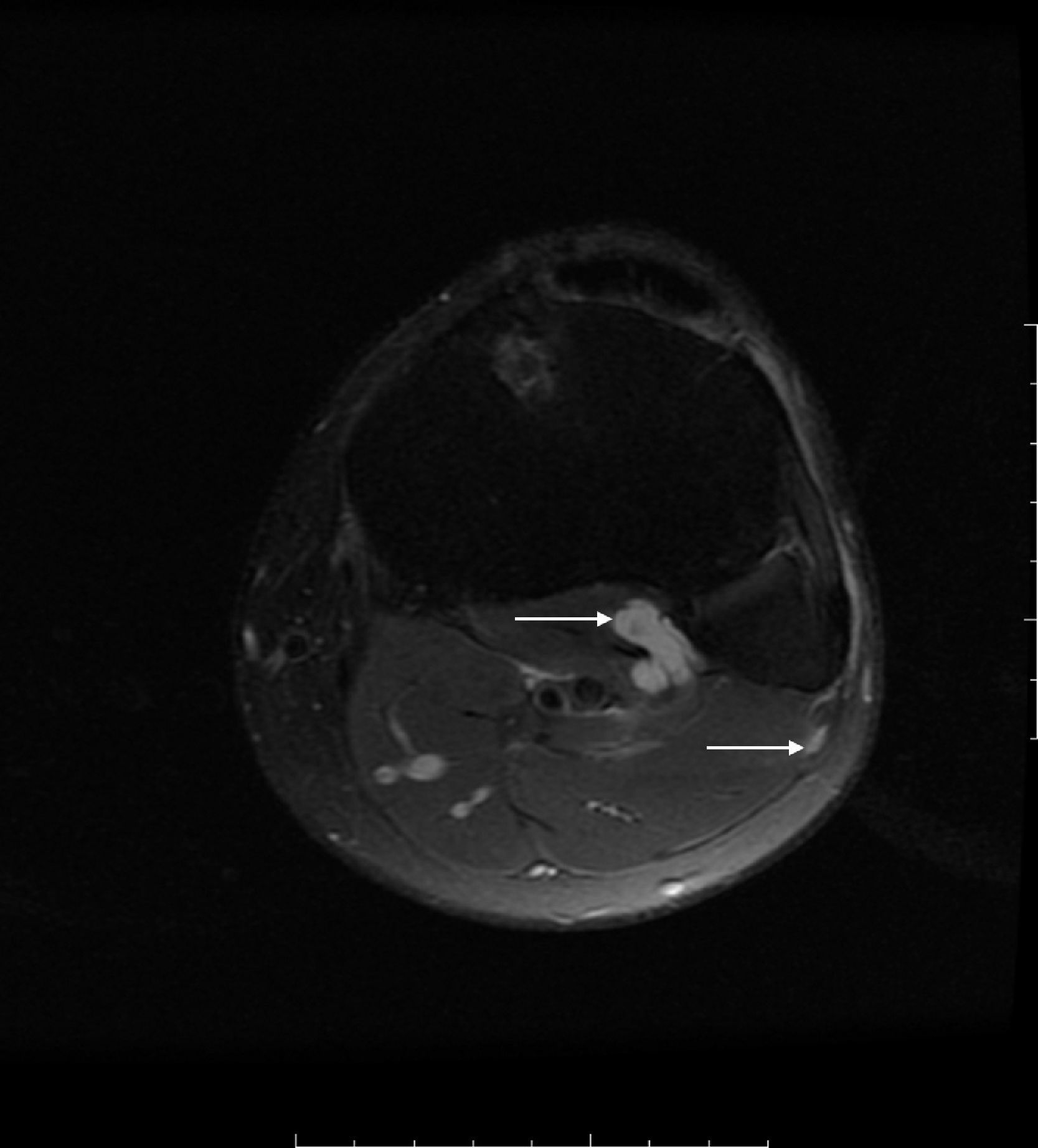
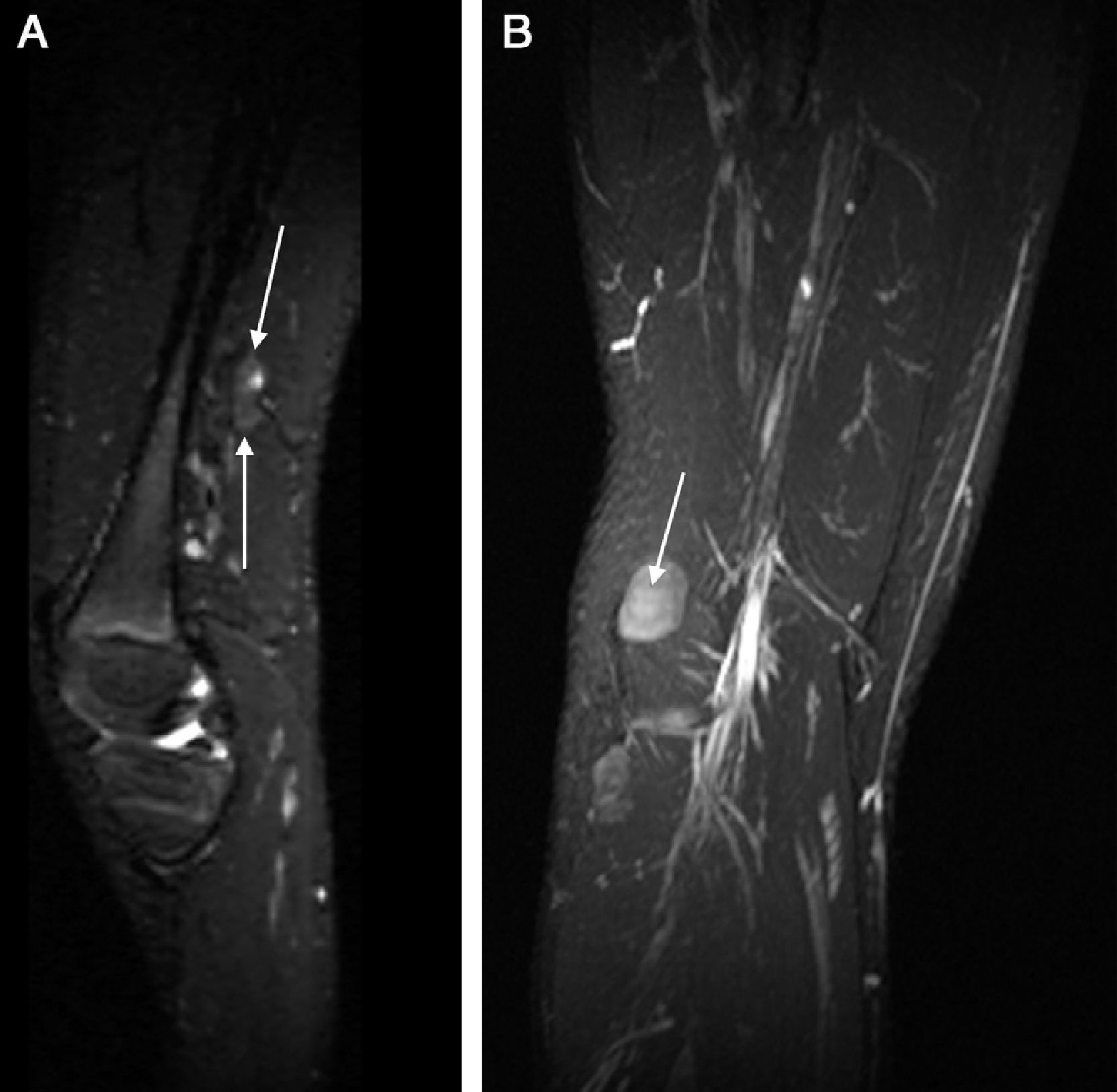
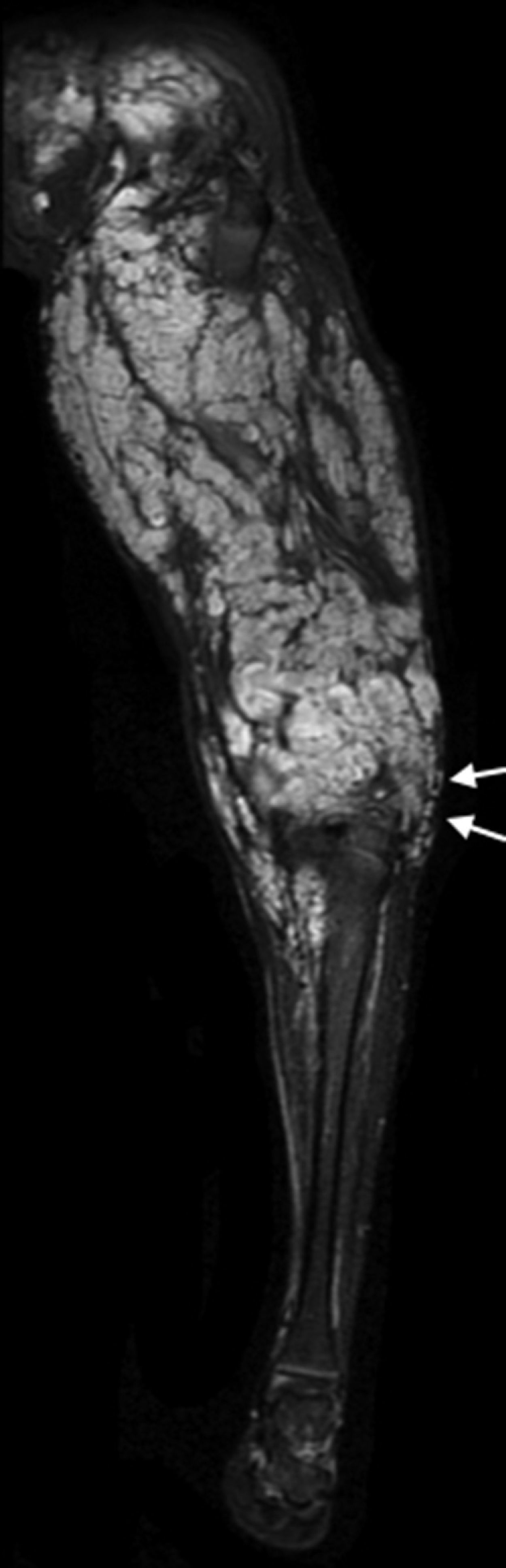
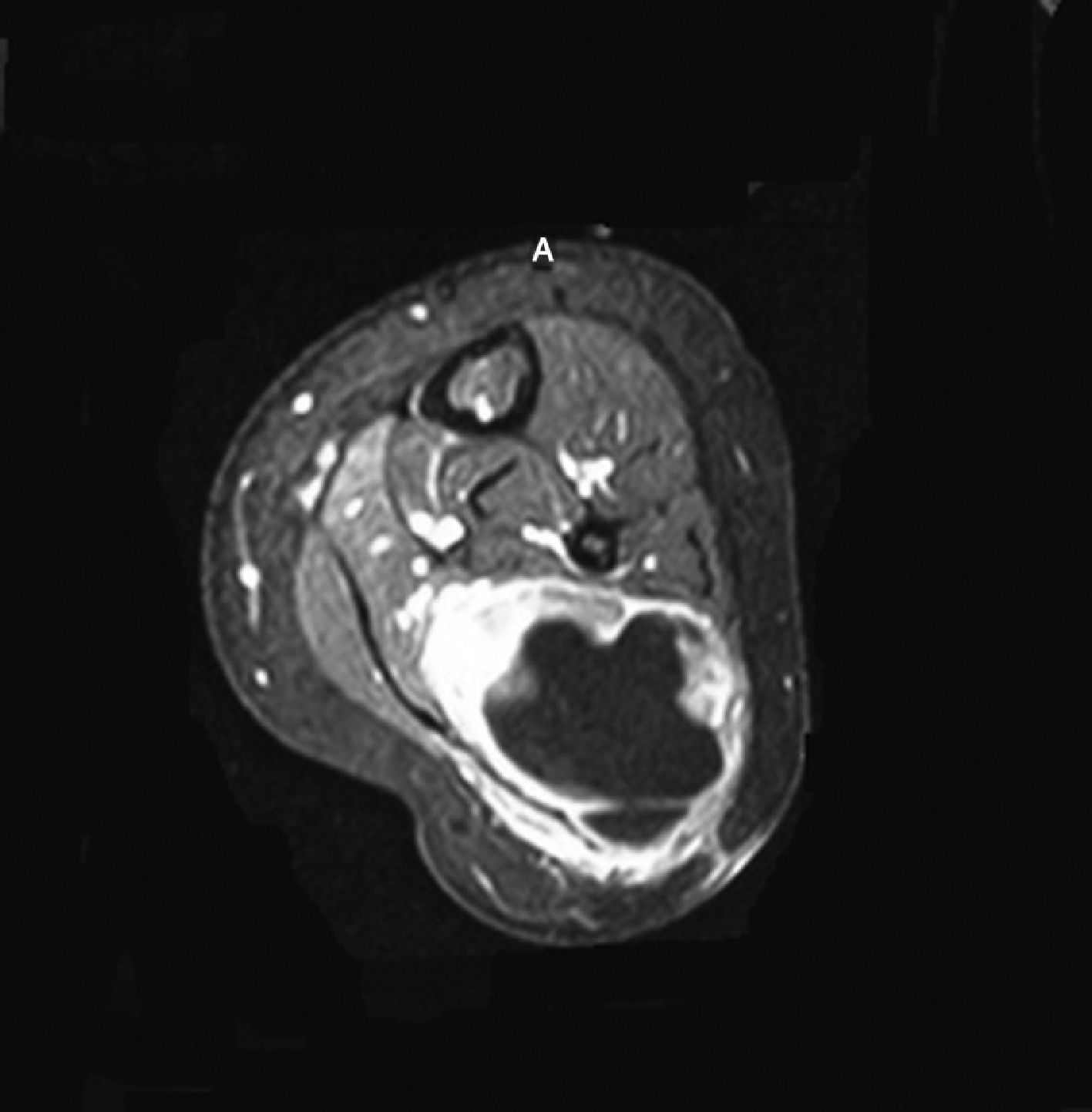
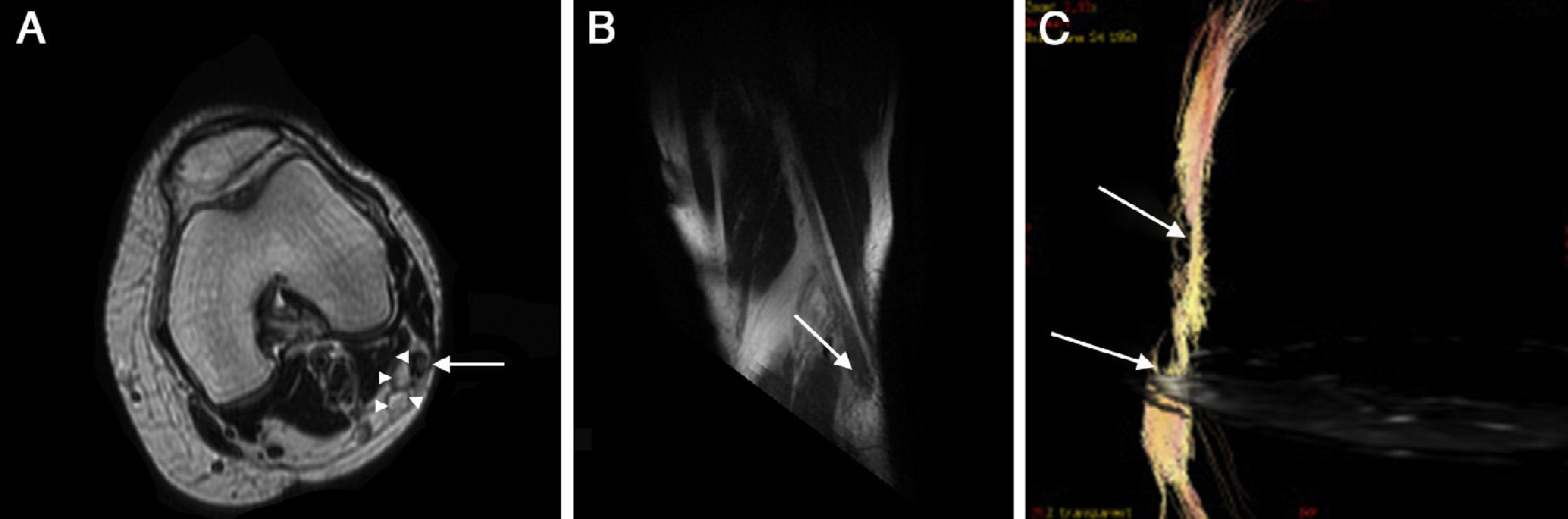
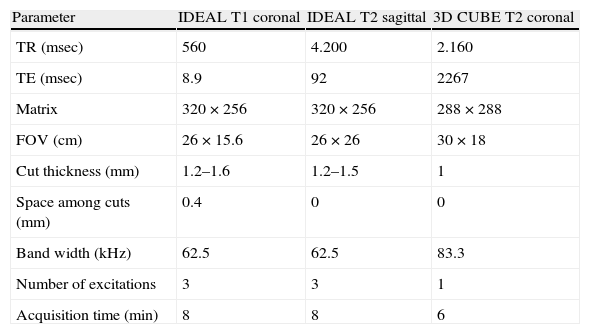
Peroneal neuropathy is the most common mononeuropathy of the lower limbs. The causes of peroneal neuropathy include trauma, tumors of the nerve and nerve sheath, entrapment, and others such as perineurioma, fibromatosis, lymphoma, and intraneural and extraneural ganglia. The diagnosis is based on clinical manifestations and electrophysiological studies. Nowadays, however, magnetic resonance (MR) neurography is a complementary diagnostic technique that can help determine the location and cause of peroneal neuropathy. In this article, we describe the MR anatomy of the peroneal nerve, its relations, and the muscles it innervates. We also discuss the clinical and electrophysiological manifestations of peroneal neuropathy, describe the technical parameters used at our institution, and illustrate the MR appearance of various diseases that involve the peroneal nerve.
La neuropatía del nervio peroneo es la mononeuropatía más común de los miembros inferiores. Entre las causas se incluyen el traumatismo, los tumores del nervio y de la vaina, el atrapamiento, y otras como el perineuroma, la fibromatosis, el linfoma y el ganglión intraneural y extraneural. El diagnóstico se basa en las manifestaciones clínicas y los estudios electrofisiológicos. Actualmente, sin embargo, el complemento diagnóstico con neurografía por resonancia magnética (RM) permite aproximarse al lugar y la causa de esta neuropatía. El objetivo de este trabajo es describir con la RM la anatomía del nervio peroneo, sus relaciones y los músculos que inerva; mencionar las manifestaciones clínicas y electrofisiológicas de sus lesiones; describir los parámetros técnicos que se emplean en nuestra institución; y mostrar la apariencia en RM de las diversas enfermedades que afectan al nervio peroneo.