To compare the diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the preoperative assessment of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
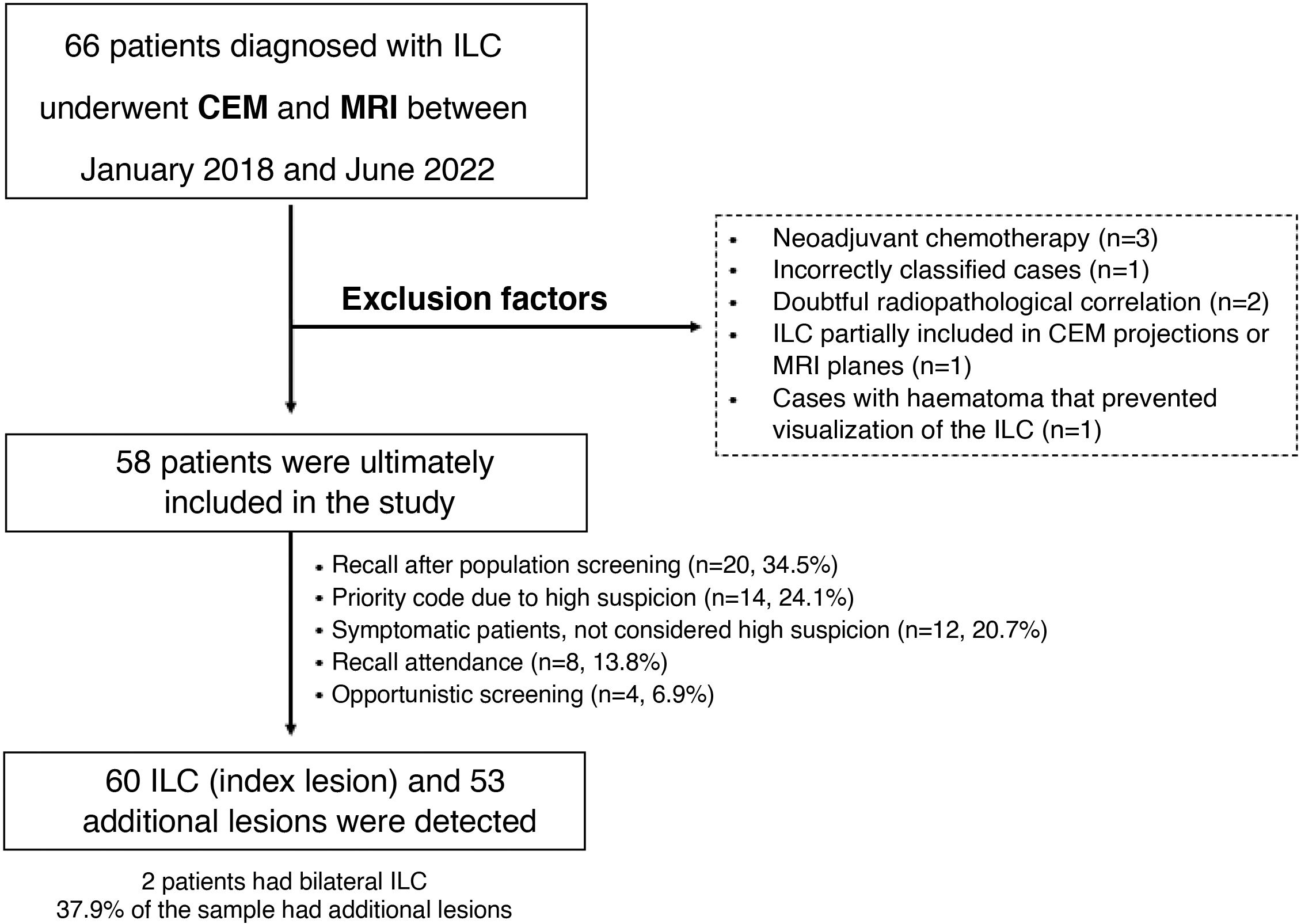
Materials and methodsThis was a single-centre, retrospective observational study including women with histologically confirmed ILC who underwent both preoperative CEM and MRI between January 2018 and June 2022. The detection sensitivity of ILC was evaluated using low-energy images (LEI), recombined images (RCI), CEM (LEI + RCI), and MRI. We analysed the correlation of tumour size estimated by each imaging modality and pathology, and the correlation between lesion conspicuity and tumour grade. We also assessed the detection of additional lesions (AL).
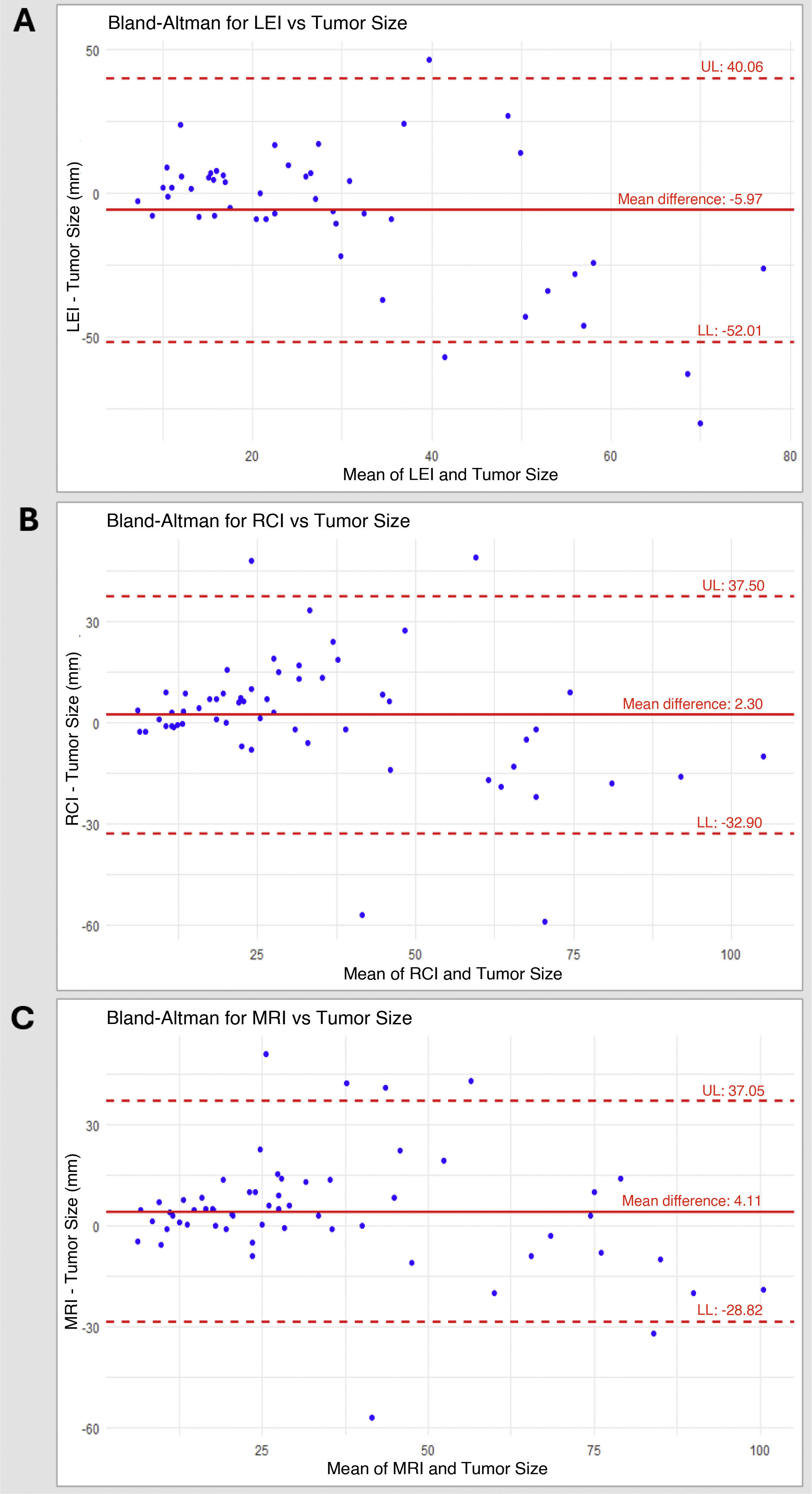
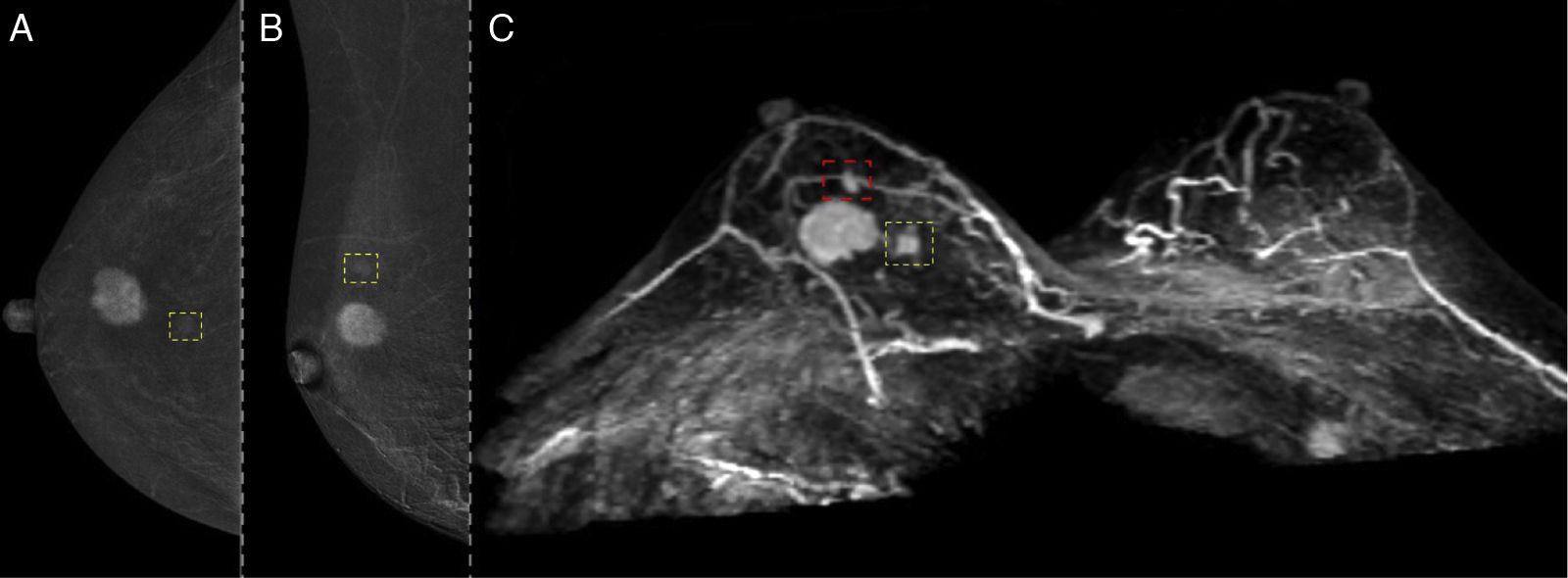
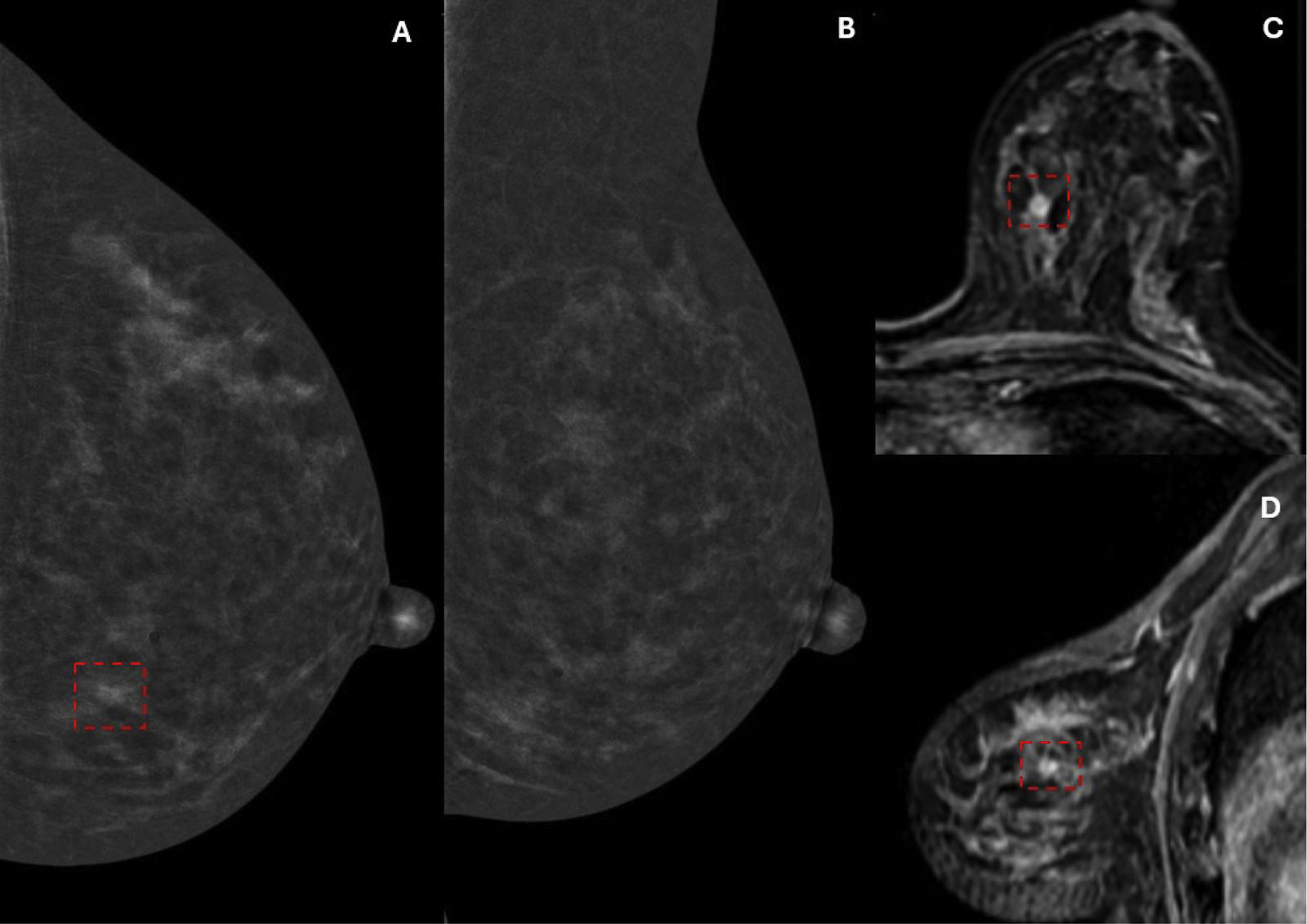
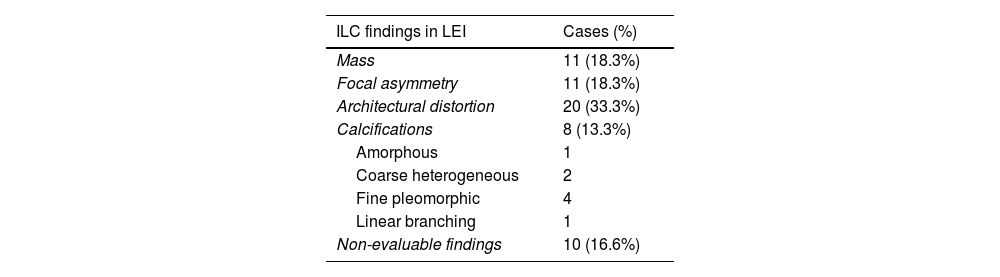
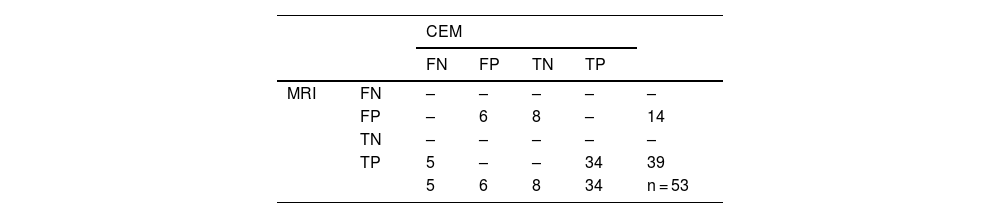
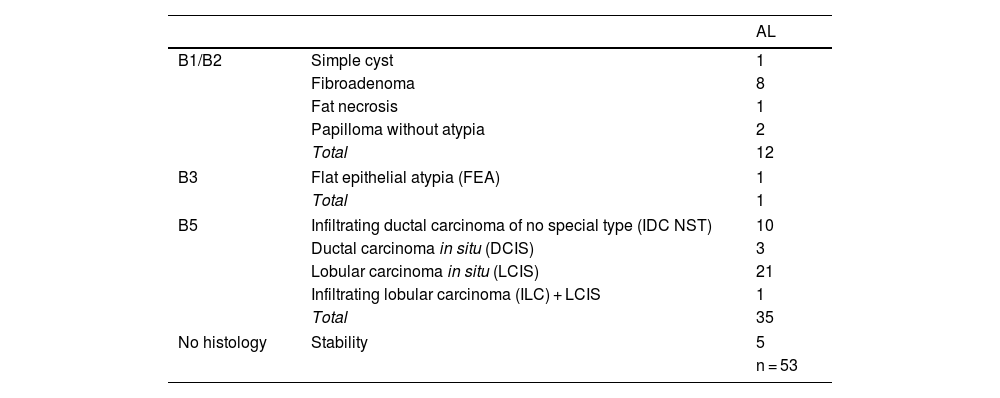
ResultsFifty-eight patients with 60 ILCs were included. LEIs showed a sensitivity of 83.3% compared to 100% for RCI, CEM and MRI. MRI demonstrated the strongest correlation with tumour size on HP (r = 0.792). High conspicuity was observed in 68% of ILCs and strongly correlated with MRI enhancement level (ρ = 0.81; P < .001). No significant association was found between conspicuity and tumour grade (P = .074). Of the 53 ALs detected, 39 were malignant. MRI identified all malignant lesions, whereas CEM failed to detect five.
ConclusionCEM may be a comparable alternative to MRI in the detection and size estimation of ILC; however, MRI appears to be superior in identifying malignant additional lesions.
Comparar el rendimiento diagnóstico de la mamografía con contraste (CEM) frente a la resonancia magnética (RM) en el estudio preoperatorio del carcinoma lobulillar invasivo (CLI).
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo observacional, unicéntrico, que incluyó a aquellas mujeres con diagnóstico histológico de CLI, sometidas a CEM y RM preoperatorias entre enero de 2018 y junio de 2022. Se evaluó la capacidad de detección del CLI mediante imágenes de baja energía (LEI), recombinadas (RCI), CEM (LEI + RCI) y RM para el CLI. Se analizó la correlación entre el tamaño tumoral estimado por cada técnica respecto a la anatomía patológica (AP), así como la de la visibilidad con el grado tumoral. Asimismo, se valoró la detección de lesiones adicionales (LA).
ResultadosFueron incluidas 58 pacientes con 60 CLI. La LEI mostró una sensibilidad del 83,3% vs. 100% de RCI, CEM, y RM. La RM mostró la mejor correlación con el tamaño tumoral en AP (r = 0,792). El 68% de los CLI presentaron alta visibilidad y una fuerte correlación con el nivel de realce en RM (ρ = 0,81; P < ,001). No se observó una asociación significativa entre la visibilidad y el grado tumoral (P = ,074). De las 53 LA detectadas, 39 resultaron malignas. La RM identificó todas las lesiones malignas, mientras que la CEM no logró detectar cinco de ellas.
ConclusiónLa CEM puede ser una alternativa comparable a la RM en la detección y estimación del tamaño tumoral del CLI, aunque la RM parece ser superior en la detección de LA malignas.