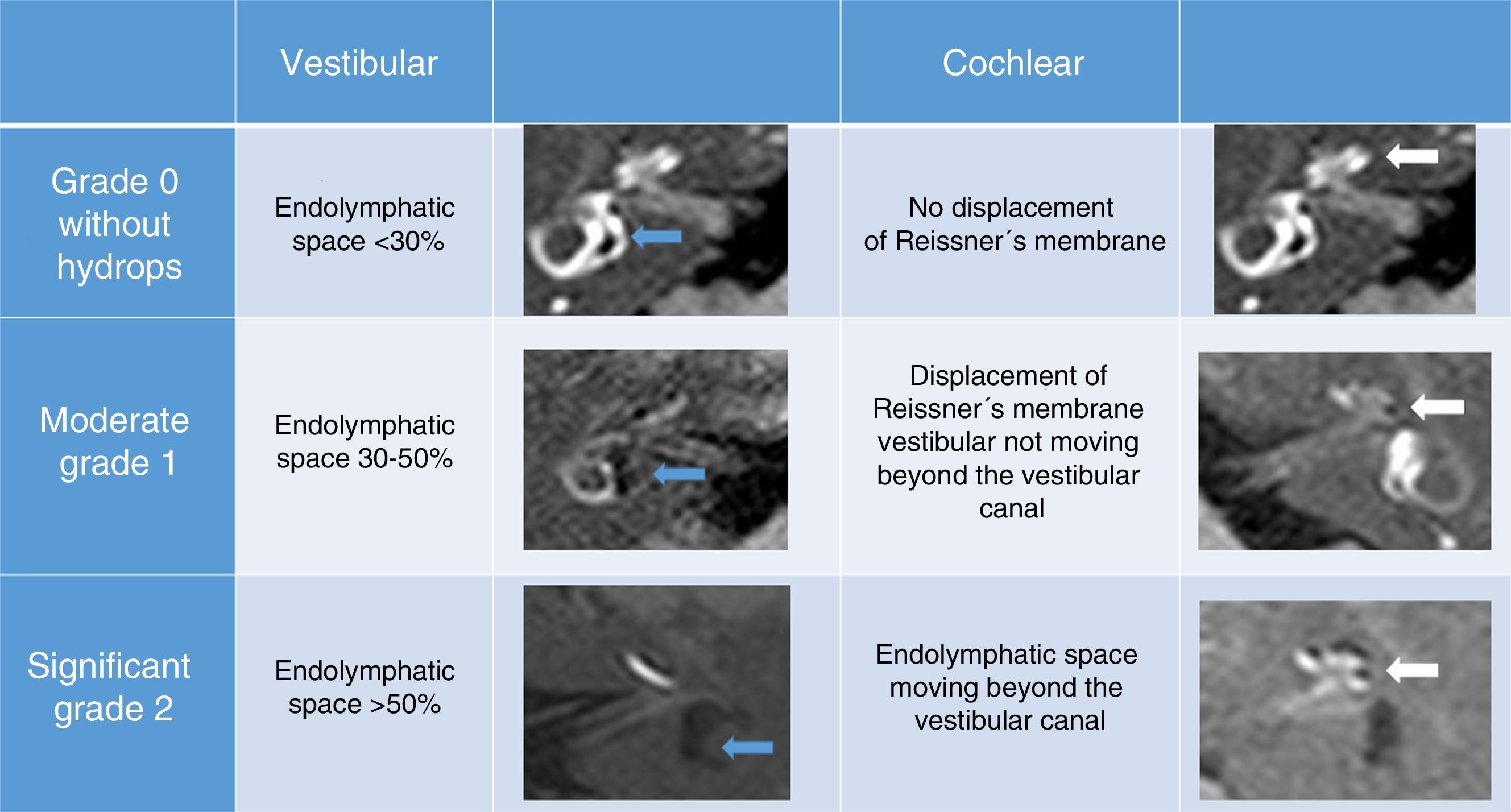
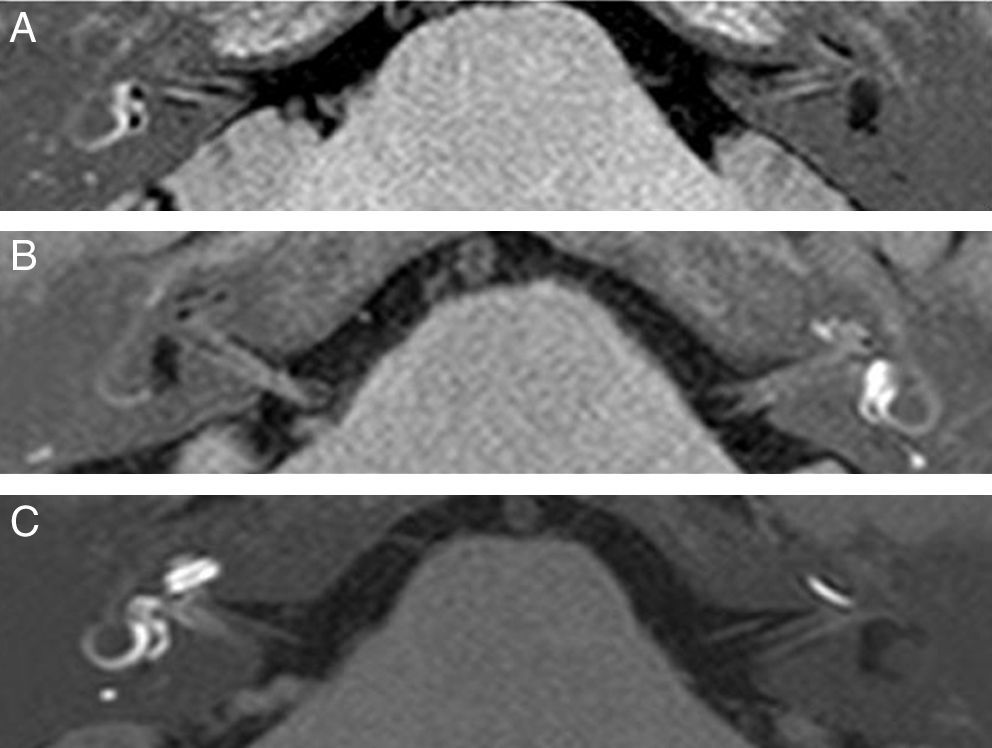
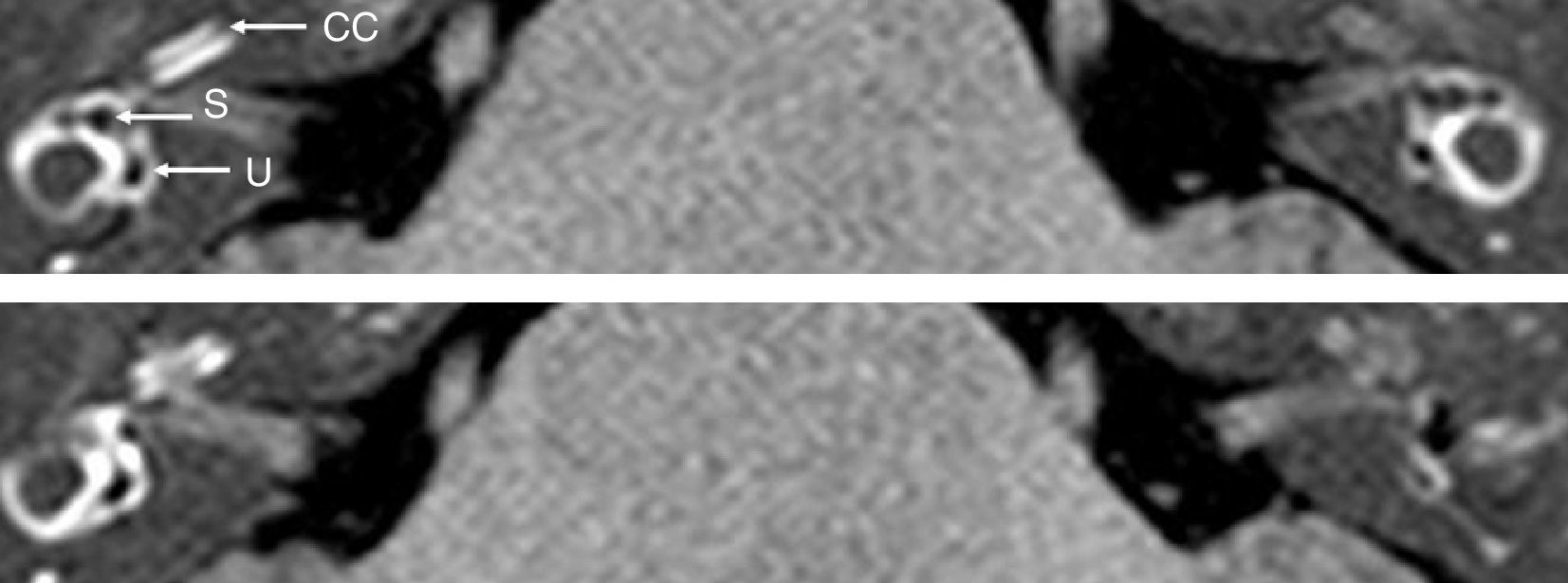
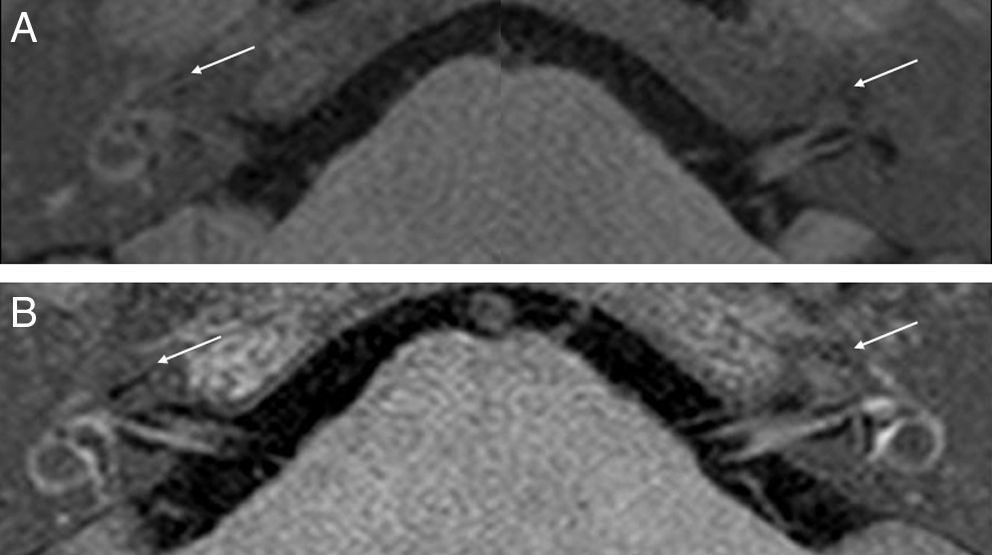
To detect and graduate endolymphatic hydrops or endolymphatic space dilations in patients with suspected Meniere's disease or immune-mediated inner ear disease by magnetic resonance imaging.
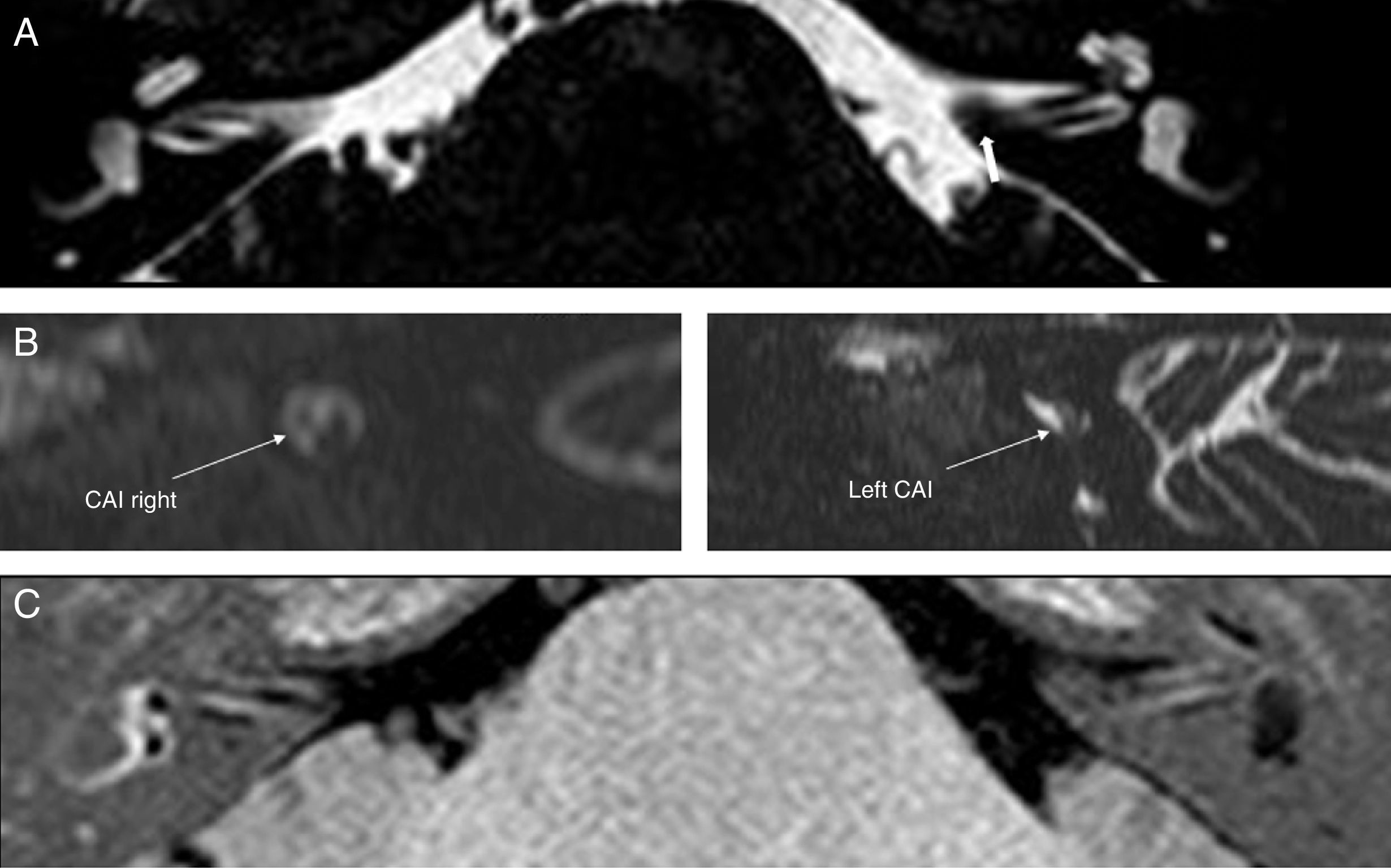
Material and methodsA prospective study was performed including all the patients with clinical suspicion of Meniere's disease or immune-mediated inner ear disease treated at the Otolaryngology department during a one year period. In all cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed in a 3T scanner. IR sequence was performed after 24–28h prior intratimpanic injection of gadolinium on both ears. Two neurorradiologist graduated endolymphatic space volume as agreed on normal, moderate and significant in the obtained images.
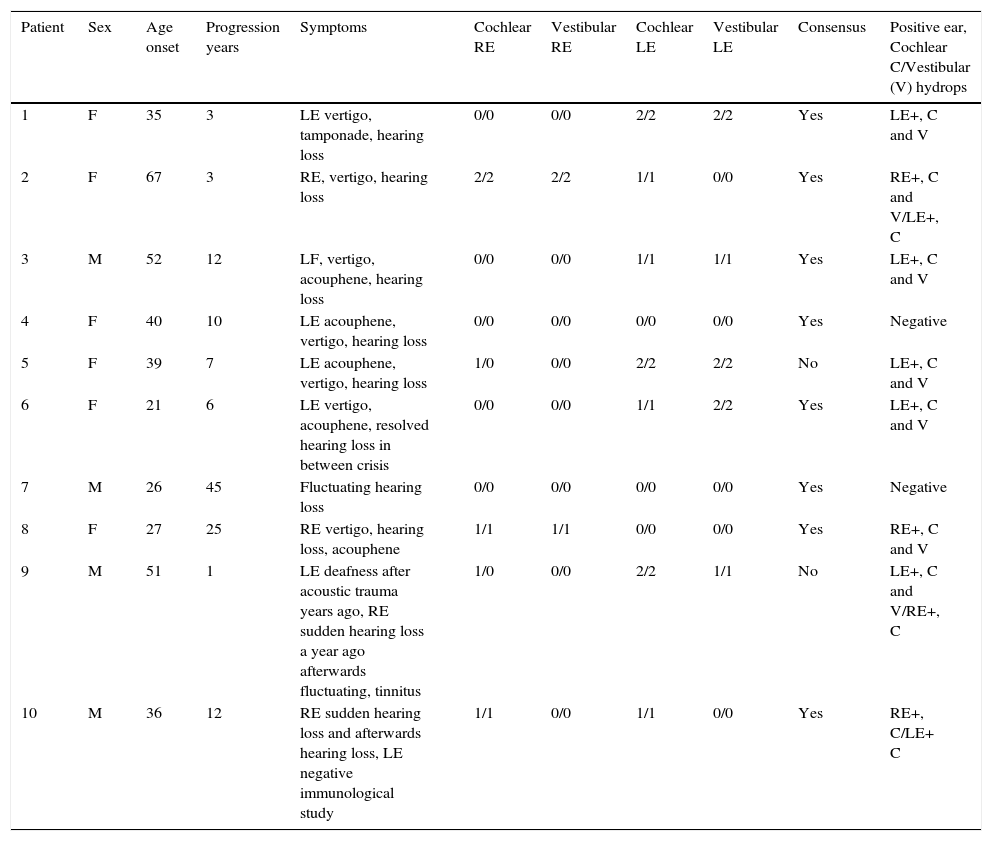
ResultsThe presence of hydrops was documented by MRI in six patients with definite or probable Meniere's disease. In two of the four cases without vertigo hydrops was not demonstrated. In the other two cases with a high clinical suspicion of immune-mediated disease but with negative autoimmune tests hydrops was proved. There was only disagreement on cochlear hydrops presence on two patients.
ConclusionThe detection of endolymphatic hydrops in patients with definite or probable Meniere's disease served to confirm the final diagnosis. Moreover, hydrops was detected in patients with suspected immune-mediated inner ear disease, which could have an impact on the diagnosis and treatment of these patients. Therefore, we suggest that this test could be included for the diagnosis of these inner ear diseases.
Detectar la dilatación del espacio endolinfático o hidrops endolinfático (HE) con resonancia magnética (RM) en pacientes con sospecha de enfermedad de Ménière (EM) o enfermedad inmunomediada del oído interno (EIOI).
Material y métodosIncluimos prospectivamente todos los pacientes con sospecha clínica de EM (seis pacientes) o EIOI (cuatro pacientes) atendidos en el servicio de otorrinolaringología en el último año. En todos los casos se realizó una RM con un equipo de 3T y se adquirió una secuencia 3D real IR tras la inyección de gadolinio intratimpánico en ambos oídos 24–28 horas antes. Dos neurorradiólogos graduaron el volumen del espacio endolinfático según convenio en normal, moderado y significativo en las imágenes obtenidas.
ResultadosSe documentó la presencia de HE mediante RM en seis pacientes con EM definida o probable. En dos de los cuatro casos que no presentaban vértigo no se demostró hidrops. En los otros dos casos, con alta sospecha clínica de EIOI, pero con pruebas autoinmunitarias negativas, sí se demostró hidrops. Solo hubo discordancia sobre la presencia de hidrops coclear en dos pacientes.
ConclusiónLa detección de HE en los pacientes con EM definida o probable sirvió para confirmar el diagnóstico definitivo. Por otro lado, se detectó hidrops en pacientes con sospecha de EIOI, lo cual podría tener repercusión sobre el diagnóstico y el tratamiento de estos pacientes. Por ello, habría que valorar la necesidad de incluir esta prueba en el diagnóstico de dichas enfermedades.