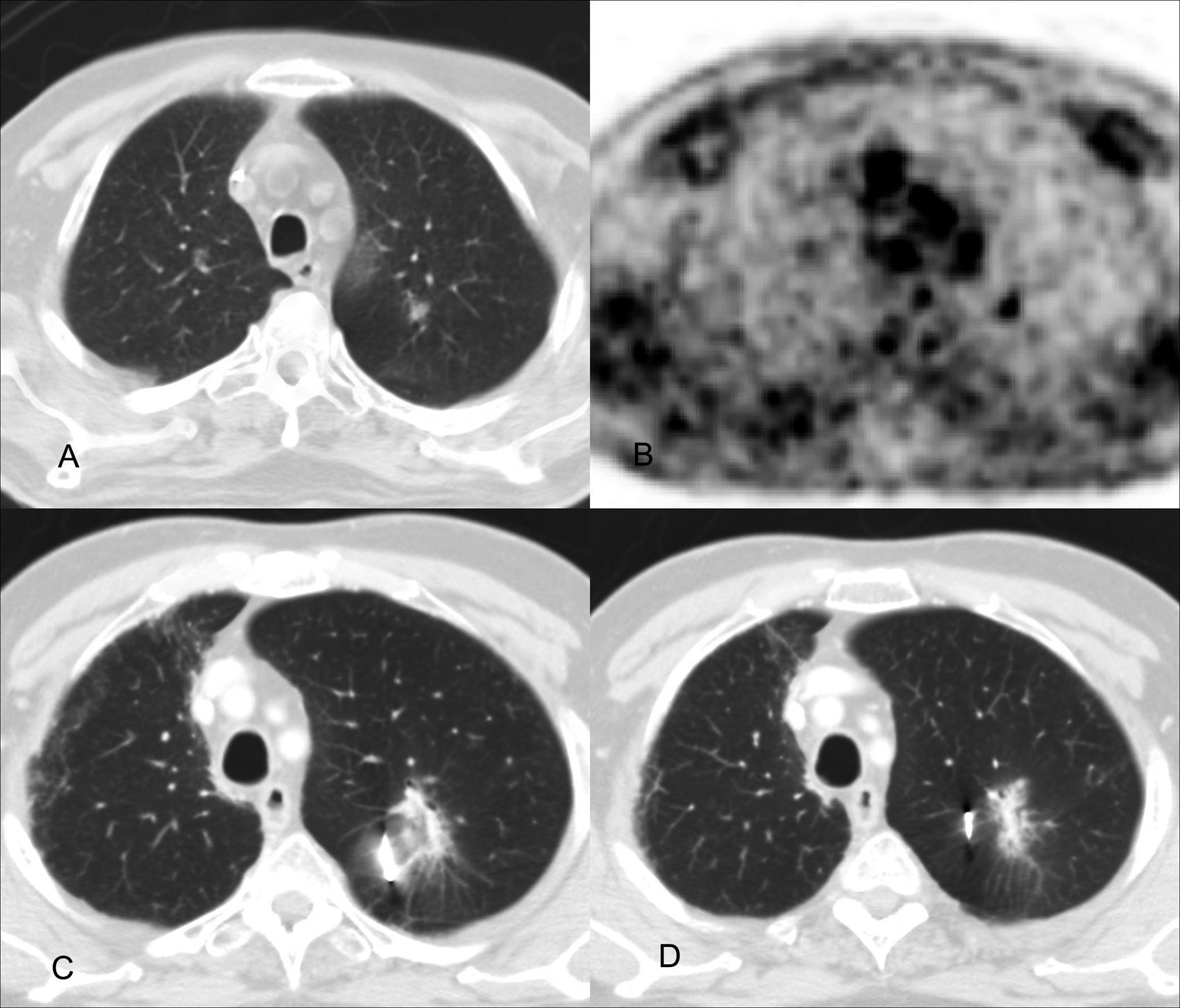
To describe the technique of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of lung lesions after the computed tomography (CT) guided placement of an internal fiducial marker and to assess the results, complications and secondary effects of these procedures.
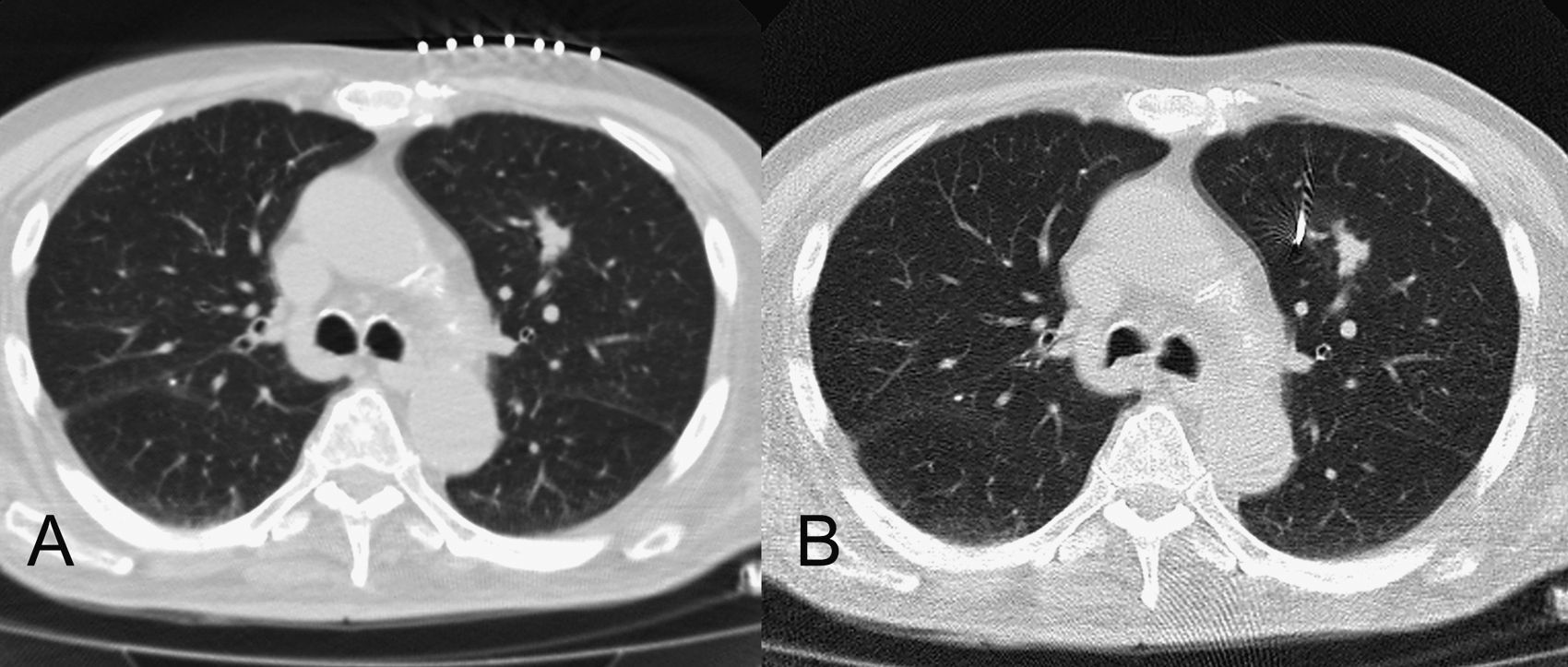
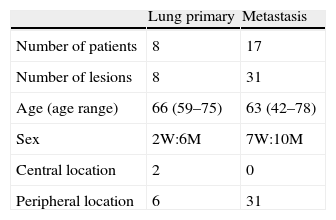
Materials and methodsA series of 39 lesions (8 primary and 31 metastases) in 25 patients treated using this procedure were analyzed. A CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic puncture was performed for placing the internal marker in the lesion or near to it. The procedure did not require sedation.
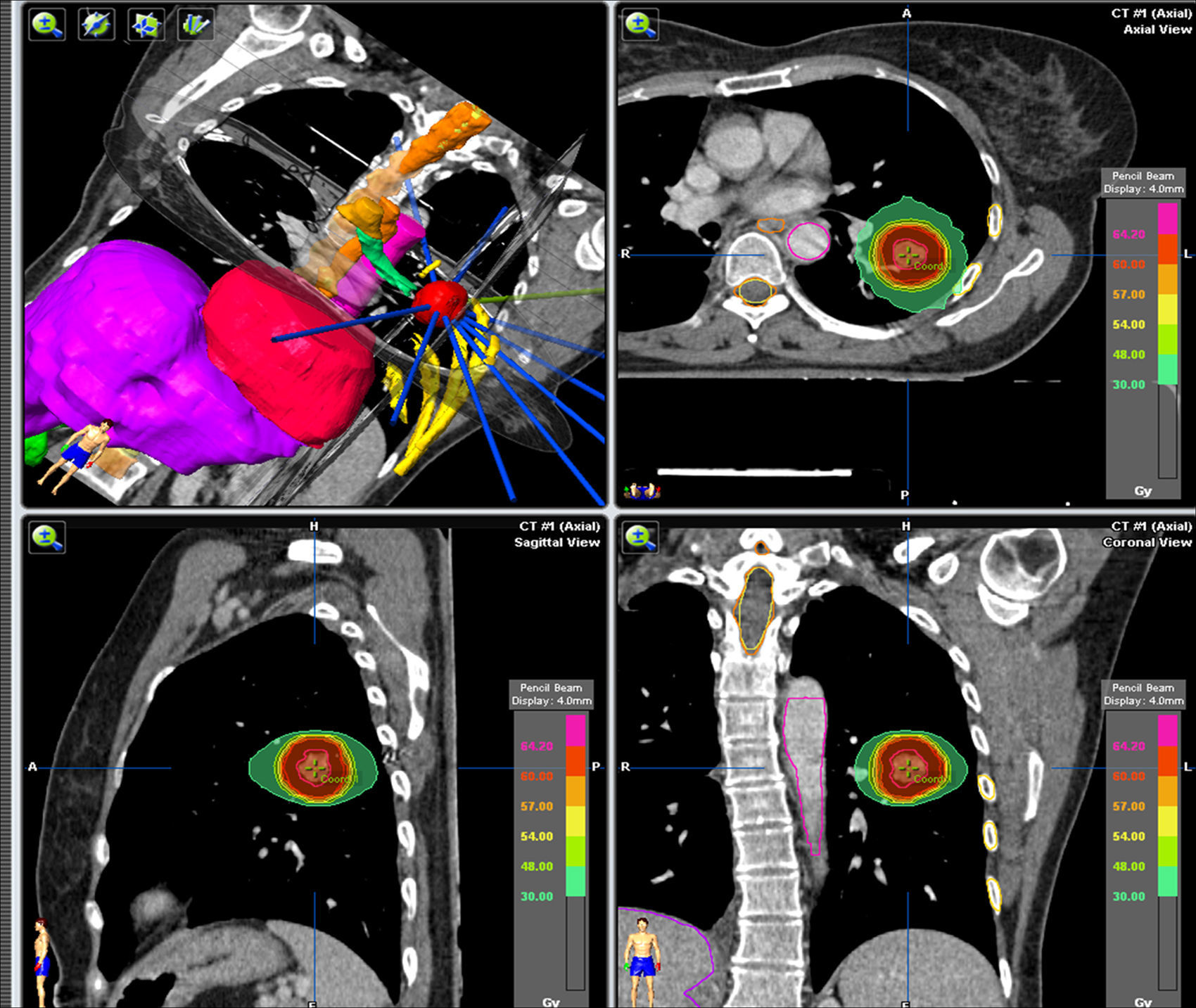
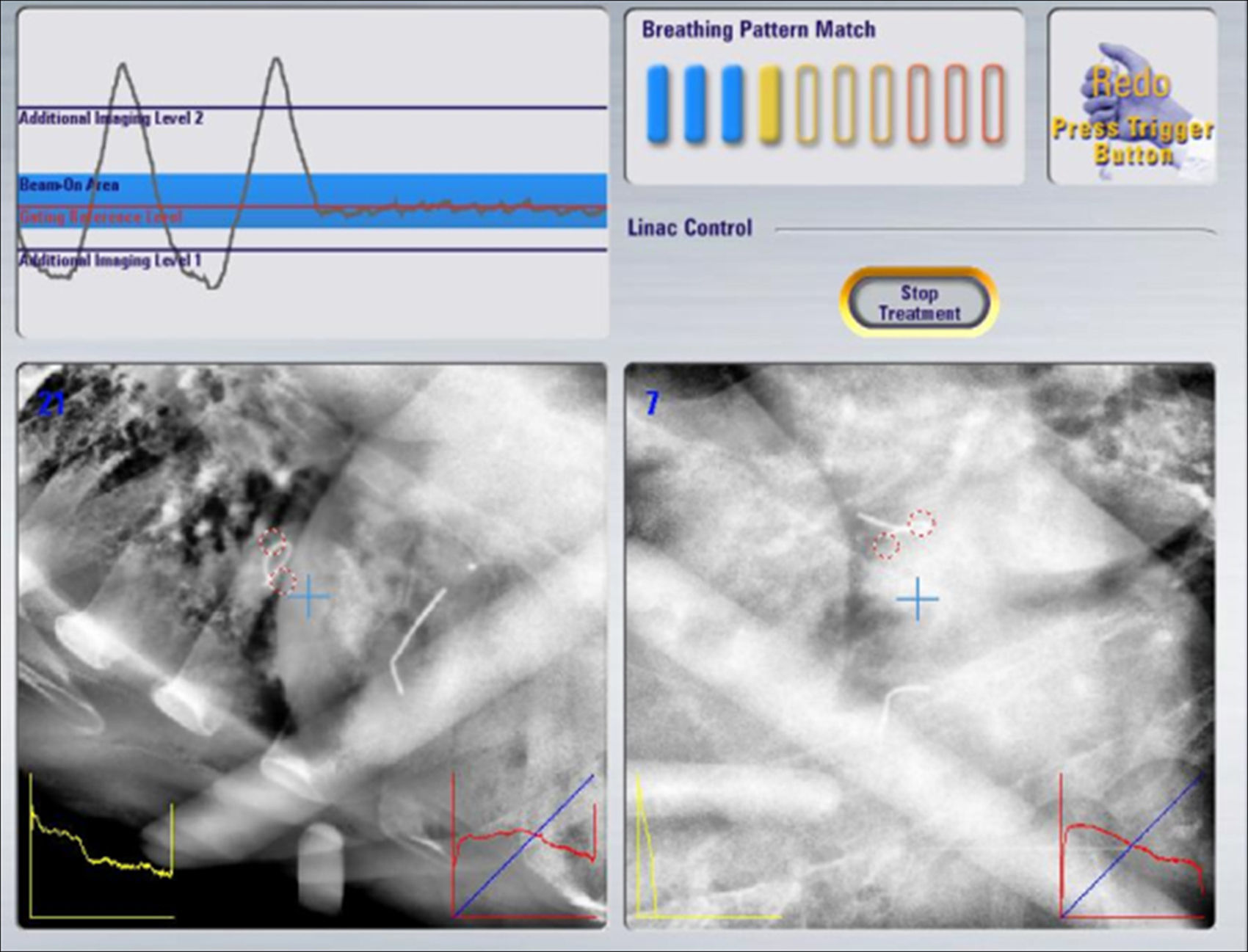
The marker serves as a guide for the treatment of the lesion using SBRT with respiratory synchronism, which allows the movement of the tumor to be controlled and to decrease the radiation volume, giving high doses with precision to the tumor, and minimal to the surrounding healthy tissue.
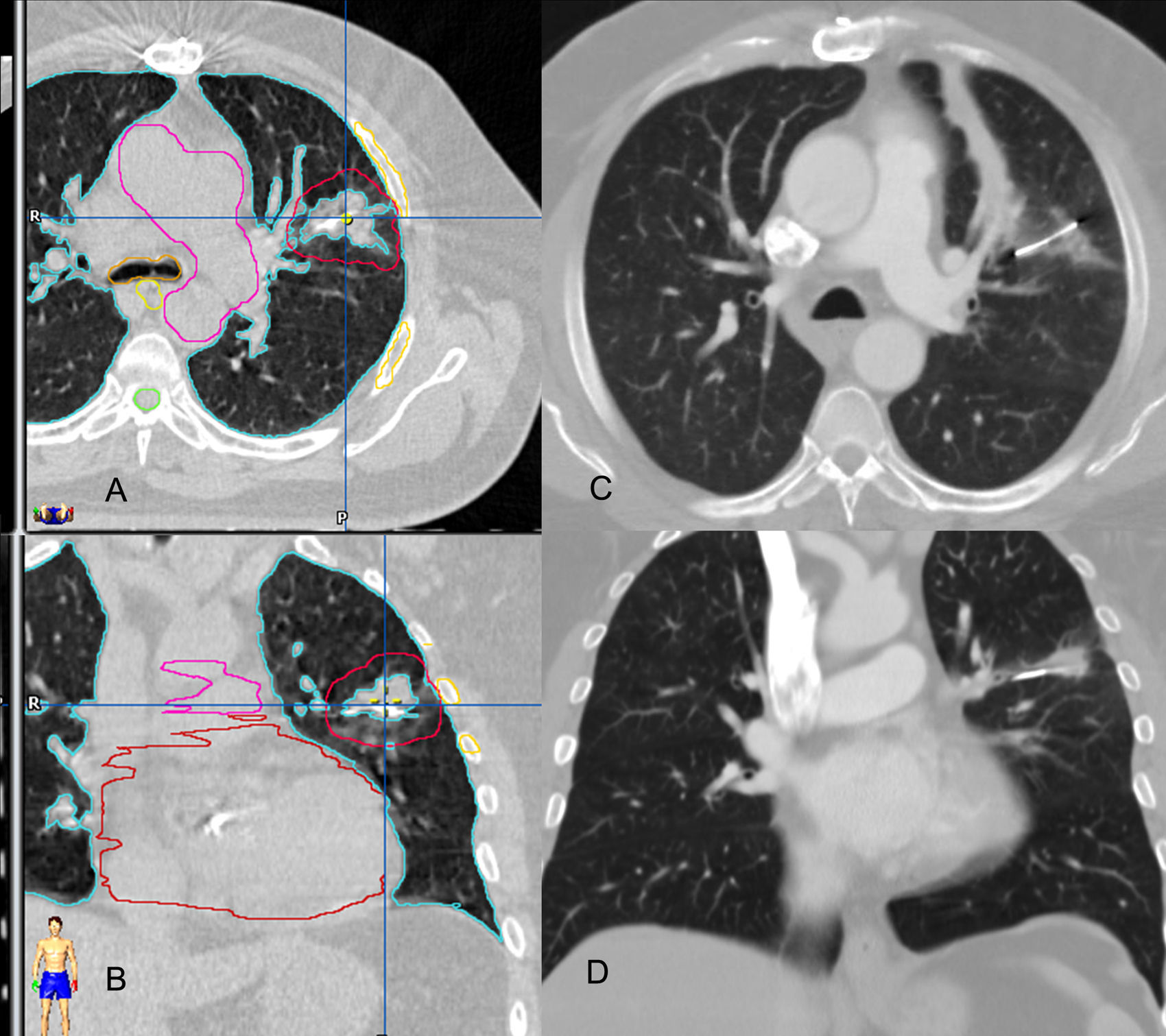
ResultsThe only complication of the percutaneous fiducial placement was a pneumothorax in 6 (24%) patients. A pleural drain had to be placed in 3 patients. Local control was achieved in 96.7% of the lesions. The radiation produced a Grade 1 asthenia in 1 patient, a Grade 2 pneumonitis in one patient and a Grade 1 pneumonitis in the remainder.
ConclusionsThe CT-guided placement of internal markers in lung lesions is a safe technique that may be performed as ambulatory procedure. SBRT with respiratory synchronism allows the dose to the tumor to be increased, and reduces the volume of healthy lung treated, with few secondary effects.
Describir la técnica de radioterapia estereotáxica extracraneal (RTEE) de lesiones pulmonares tras colocar un marcador interno guiada por tomografía computarizada (TC) y valorar los resultados, complicaciones y efectos secundarios de estos procedimientos.
Material y métodoAnalizamos una serie de 39 lesiones en 25 pacientes (8 primarias y 31 metastásicas) tratadas mediante este procedimiento. Se realizó una punción percutánea transtorácica guiada por TC para la colocación de un marcador interno en la lesión o próximo a ella. El procedimiento no requiere sedación.
El marcador sirve de guía para el tratamiento de la lesión mediante RTEE con sincronismo respiratorio que permite controlar el movimiento del tumor y disminuir el volumen de irradiación administrando con precisión dosis altas al tumor y mínimas a los tejidos sanos circundantes.
ResultadosLa única complicación de las punciones transtorácicas fue el neumotórax en 6 pacientes (24%). Fue necesaria la colocación de un drenaje pleural en tres pacientes. Se consiguió el control local en el 96,7% de las lesiones. La irradiación produjo astenia grado 1 en un paciente, neumonitis grado 2 en un paciente y neumonitis grado 1 en el resto.
ConclusionesLa colocación guiada por TC de marcadores internos en las lesiones pulmonares es una técnica segura que se puede realizar de forma ambulante. La RTEE con sincronismo respiratorio permite aumentar la dosis al tumor y reducir el volumen de pulmón sano tratado con pocos efectos secundarios.