To evaluate the diagnostic performance of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) in detecting significant hepatic fibrosis in children.
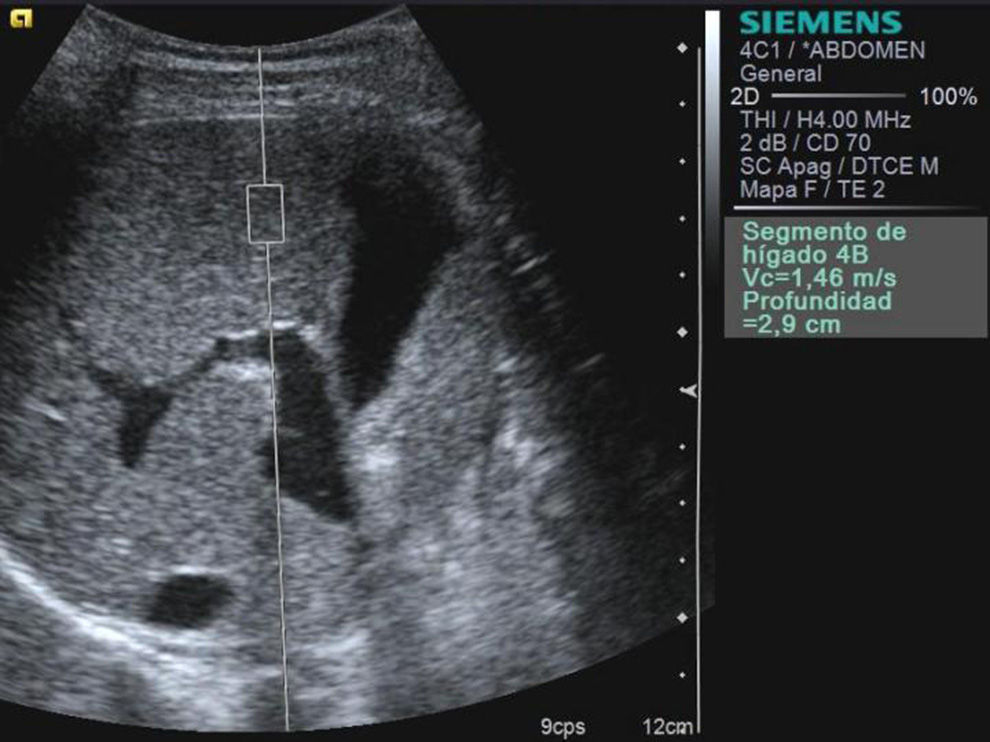
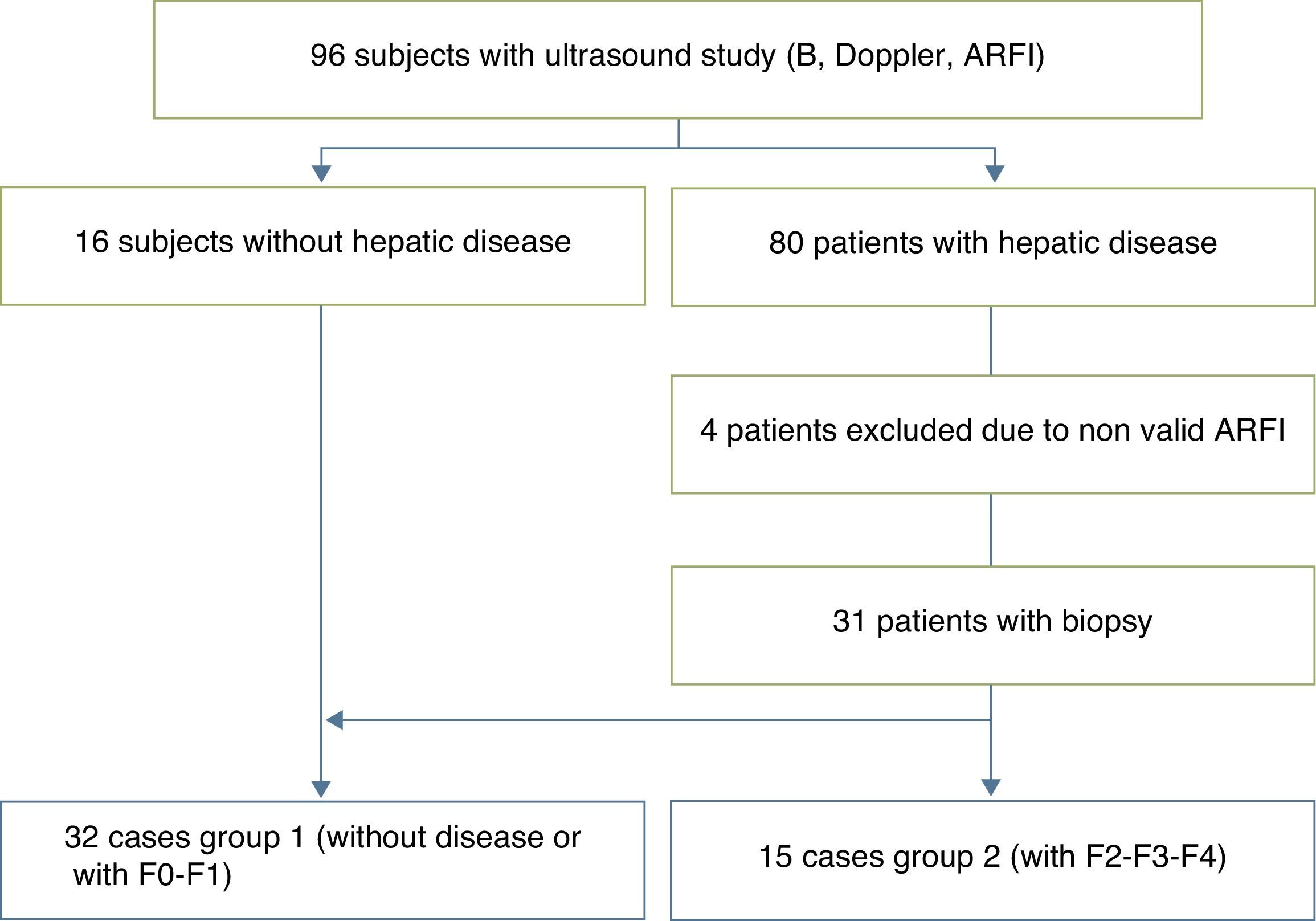
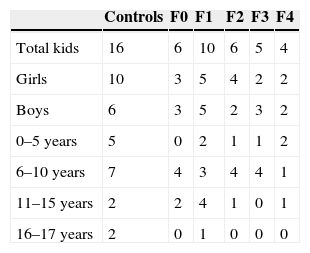
Material and methodsOur hospital's ethics committee approved the study and all patients or their representatives provided informed written consent. We included 96 children (50 boys, 46 girls; mean age, 8 years). We also studied 16 volunteers without liver disease as controls and 80 patients with diseases that can lead to fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver. The final sample included 31 patients with biopsies and the 16 controls. All patients underwent abdominal ultrasonography including Doppler imaging and elastography with ARFI. The ARFI value, expressed as velocity (m/s) of shear wave propagation through the tissue, was calculated by averaging 16 measurements in both liver lobes. We used one-way analysis of variance to compare means between groups; we set statistical significance at P<0.05. We used Student's t-tests and chi-square tests for categorical data.
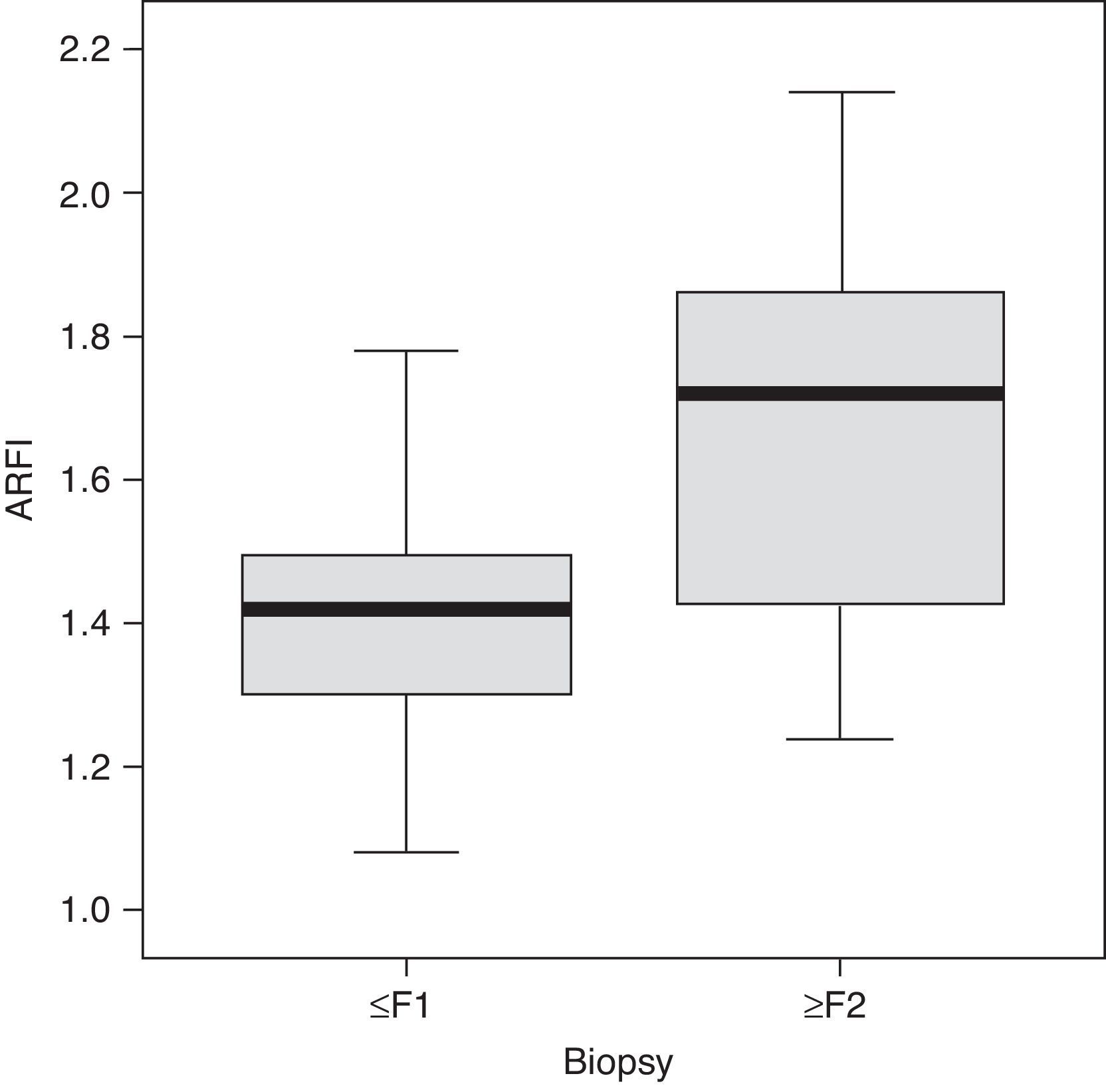
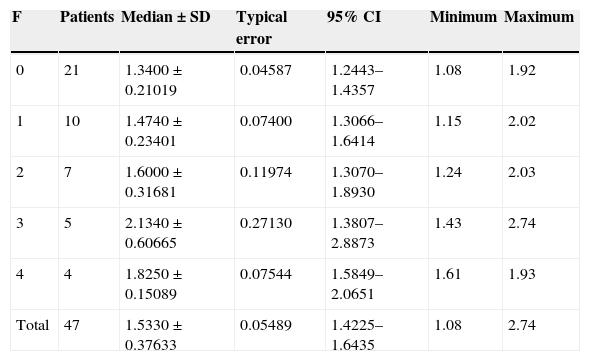
ResultsThe ARFI value in children with fibrosis ≥F2 was higher (1.80±0.45m/s) than in controls and higher than in patients with F0–F1 (1.38±0.22m/s). The difference was significant (P<0.001) for detecting ≥F2. Steatosis was not related with the ARFI value (Student's t-test, P>0.84). Necroinflammatory activity was strongly associated with the ARFI value (Student's t-test, P<0.01). Fibrosis and necroinflammatory activity were strongly associated with each other (chi-square test, P<0.0001).
ConclusionThe speed of shear wave propagation is significantly associated with the degree of hepatic fibrosis in children.
Evaluar el rendimiento diagnóstico de ARFI para detectar fibrosis hepática significativa en la edad pediátrica.
Material y métodosEl estudio fue aprobado por el comité de ética hospitalario, con el consentimiento informado de los pacientes o sus representantes. Estudiamos 96 niños (50 varones, 46 hembras; edad media 8 años); 16 voluntarios sin enfermedad hepática conocida y 80 con patologías que pueden evolucionar a fibrosis y cirrosis hepática. La muestra final incluyó 31 pacientes con biopsia y 16 controles sanos. En todos los casos se realizó ecografía abdominal incluyendo Doppler y elastografía con ARFI. El valor ARFI expresado como velocidad (m/s) de propagación de las ondas transversales a través del tejido se calculó promediando 16 medidas en ambos lóbulos hepáticos. Comparamos las medias con el test de ANOVA de un factor. Los tests t de Student y chi cuadrado se usaron para datos categóricos. La significación estadística se estableció para una p<0,05.
ResultadosLa velocidad en niños con fibrosis ≥ F2 fue significativamente más alta (1,80±0,45m/s) que en controles y pacientes con F0-F1 (1,38±0,22m/s) (p<0,001). La esteatosis no se relacionó con la velocidad. La actividad necroinflamatoria se relacionó muy significativamente con la velocidad (p<0,01). Fibrosis y actividad necroinflamatoria se relacionaron muy significativamente (p<0,0001).
ConclusiónLa velocidad de propagación de las ondas ARFI se relacionó significativamente en los niños con el grado de fibrosis hepática.