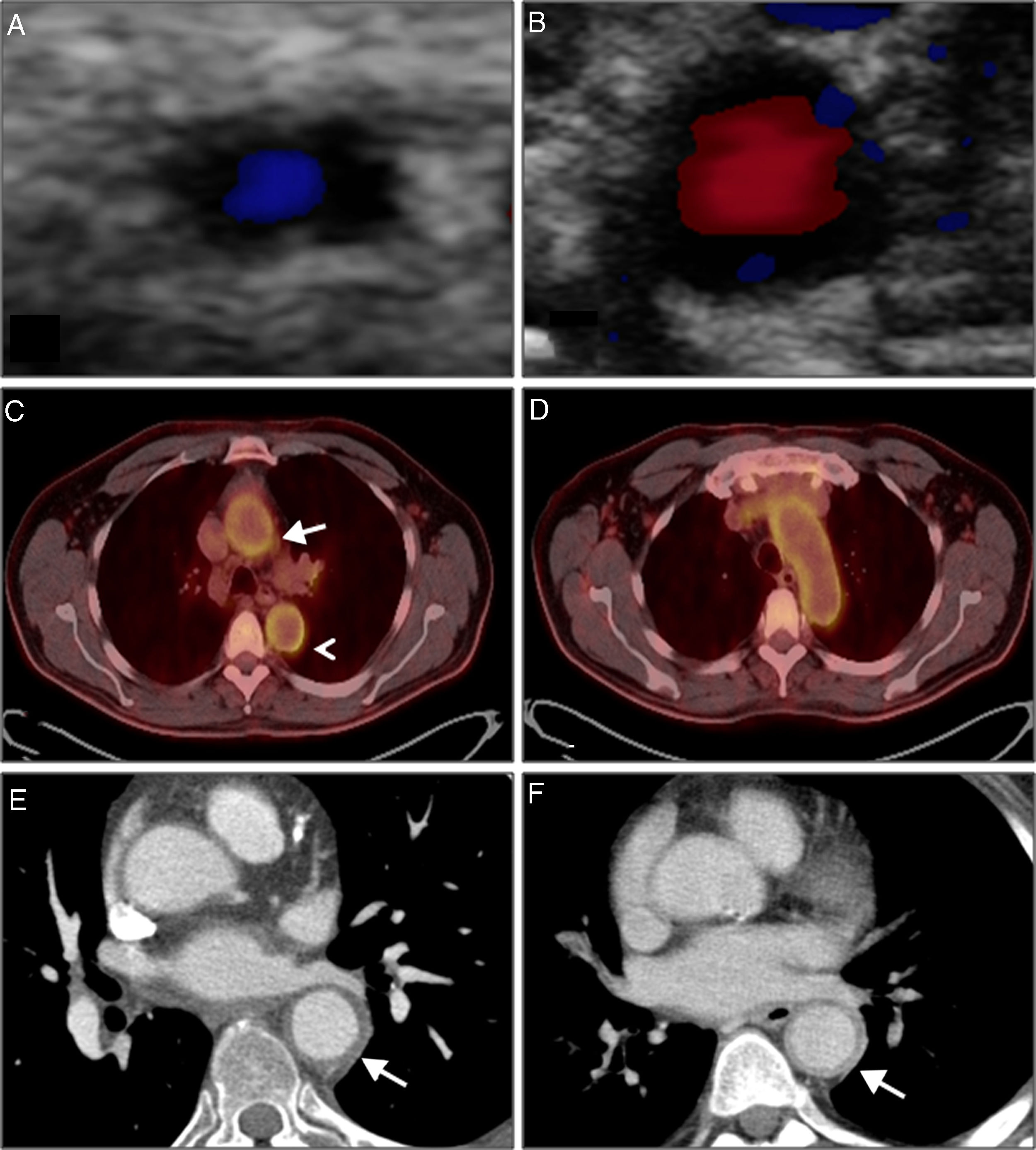
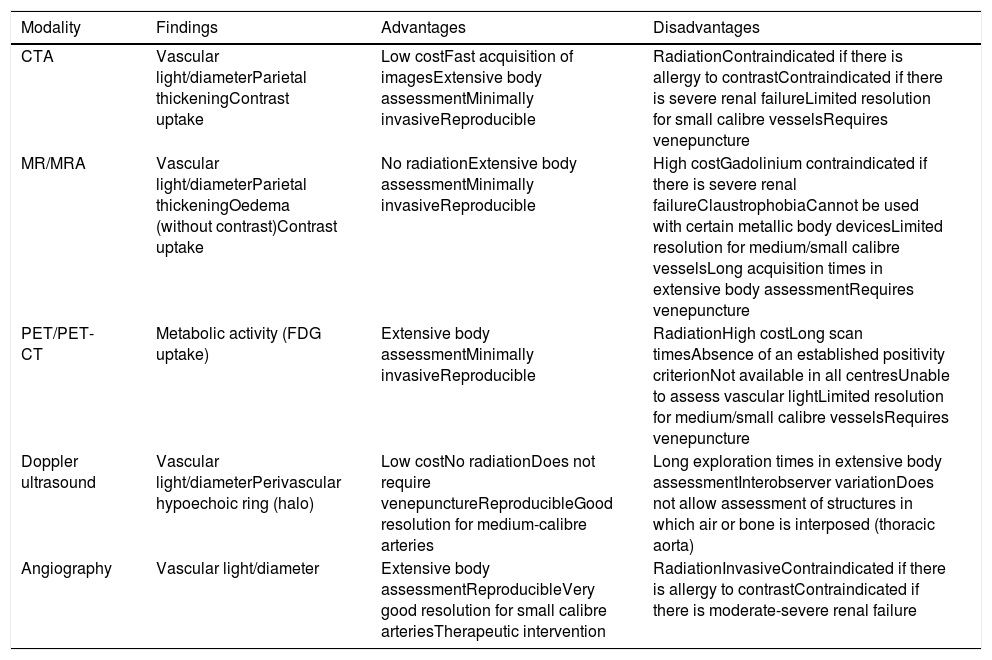
Imaging has become an essential tool in the management of patients with giant cell arteritis. Cranial involvement detected by Doppler ultrasonography is an unquestionable diagnostic finding. Imaging of the aorta and its branches with positron emission tomography, computed tomography angiography or magnetic resonance imaging may also have a role in diagnosis and in the assessment of disease activity and response to treatment, but standardisation and validation are still needed before their widespread use as an outcome measure. Aortic structural damage is associated with increased mortality in giant cell arteritis; therefore, periodic screening is recommended.
Las técnicas de imagen se han convertido en una herramienta esencial en la valoración de los pacientes con arteritis de células gigantes. La detección del compromiso del territorio craneal con la ecografía Doppler tiene una utilidad diagnóstica indudable. La afectación de la aorta y sus ramas detectada mediante la tomografía por emisión de positrones, la tomografía computarizada con angiografía o la resonancia magnética con angiografía puede ayudar también en el diagnóstico y en la valoración de la actividad de la enfermedad y la respuesta al tratamiento, pero es necesaria la estandarización y validación de su uso. El desarrollo de daño vascular aórtico puede influir en la supervivencia de los pacientes con arteritis de células gigantes por lo que se recomienda su cribado periódico.