Turner syndrome (TS) is characterized by short stature, gonadal dysgenesis, and total or partial loss of X chromosome.
Patients and methodsA historical cohorts study of patients with TS≤18 years old followed up in public hospitals in Castilla and Leon was undertaken.
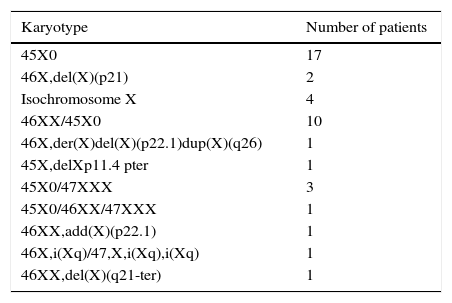
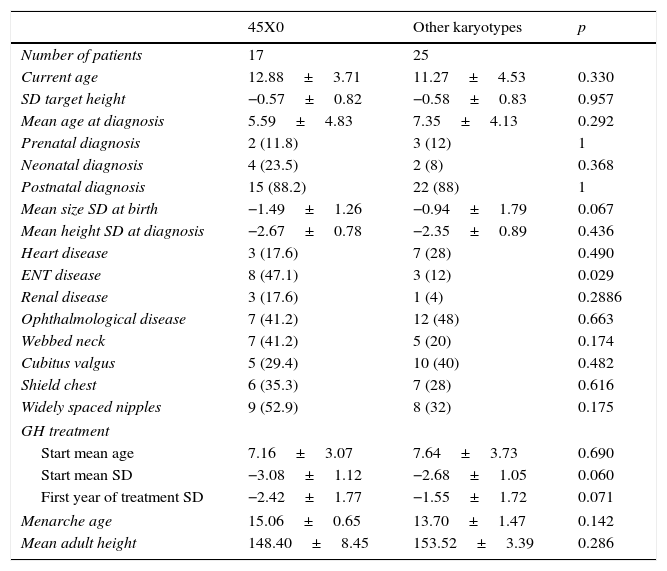
ResultsForty-two female patients were included (prenatal diagnosis 11.9%, neonatal diagnosis 14.3%) with current median age 11.9±4.2 years. Short stature was the reason for consultation in 87.1%. Total monosomy of X chromosome was present in 40.5%. The most frequently associated comorbidity was opthalmological (50%), with heart defects in 23.8%. Ninety-three percent were treated with growth hormone (GH), mean age at the beginning of treatment was 7.43±3.4 years and mean height standard deviation was −2.84±1.08. Final height was reached in 10 patients only (mean final height 151.47±6.09cm). Chronological age of puberty induction was 13.2±0.94 years (bone age 12.47±1.17 years).
ConclusionsShort stature was an important clinical sign for the diagnosis of TS, accompanied in some cases by other findings, with good response to GH treatment.
El síndrome de Turner (ST) se asocia con talla baja, disgenesia gonadal y monosomía parcial o total del cromosoma X.
Pacientes y métodosSe realizó un estudio de cohortes histórico de las pacientes con ST≤18 años seguidas en los hospitales públicos de Castilla y León.
ResultadosSe registraron 42 pacientes (diagnóstico prenatal 11,9%, neonatal 14,3%) con una edad media actual de 11,9±4,2 años. La talla baja fue el motivo de consulta en el 87,1%. El 40,5% presentaban monosomía total del cromosoma X. La enfermedad asociada más frecuente fue la oftalmológica (50%), con problemas cardiacos en el 23,8%. El 93% reciben tratamiento con growth hormone (GH, «hormona de crecimiento»), con una edad media al inicio de 7,43±3,4 años y una DE media de talla de −2,84±1,08. Solamente 10 pacientes han alcanzado talla final (talla media 151,47±6,09cm). La edad cronológica media de inducción puberal fue 13,2 años±0,94 años (edad ósea 12,47±1,17).
ConclusionesUno de los datos clave para el diagnóstico fue la talla baja acompañada en algunos casos de otros hallazgos, siendo el tratamiento con GH efectivo.