The dynamic increase in the number of triplet repeats of cytosine–guanine–guanine (CGG) in the FMR1 gene mutation is responsible for three OMIM syndromes with a distinct clinical phenotype: Fragile X syndrome (FXS) and two pathologies in adult carriers of the premutation (55–200 CGG repeats): primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI) and tremor–ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) associated with FXS.
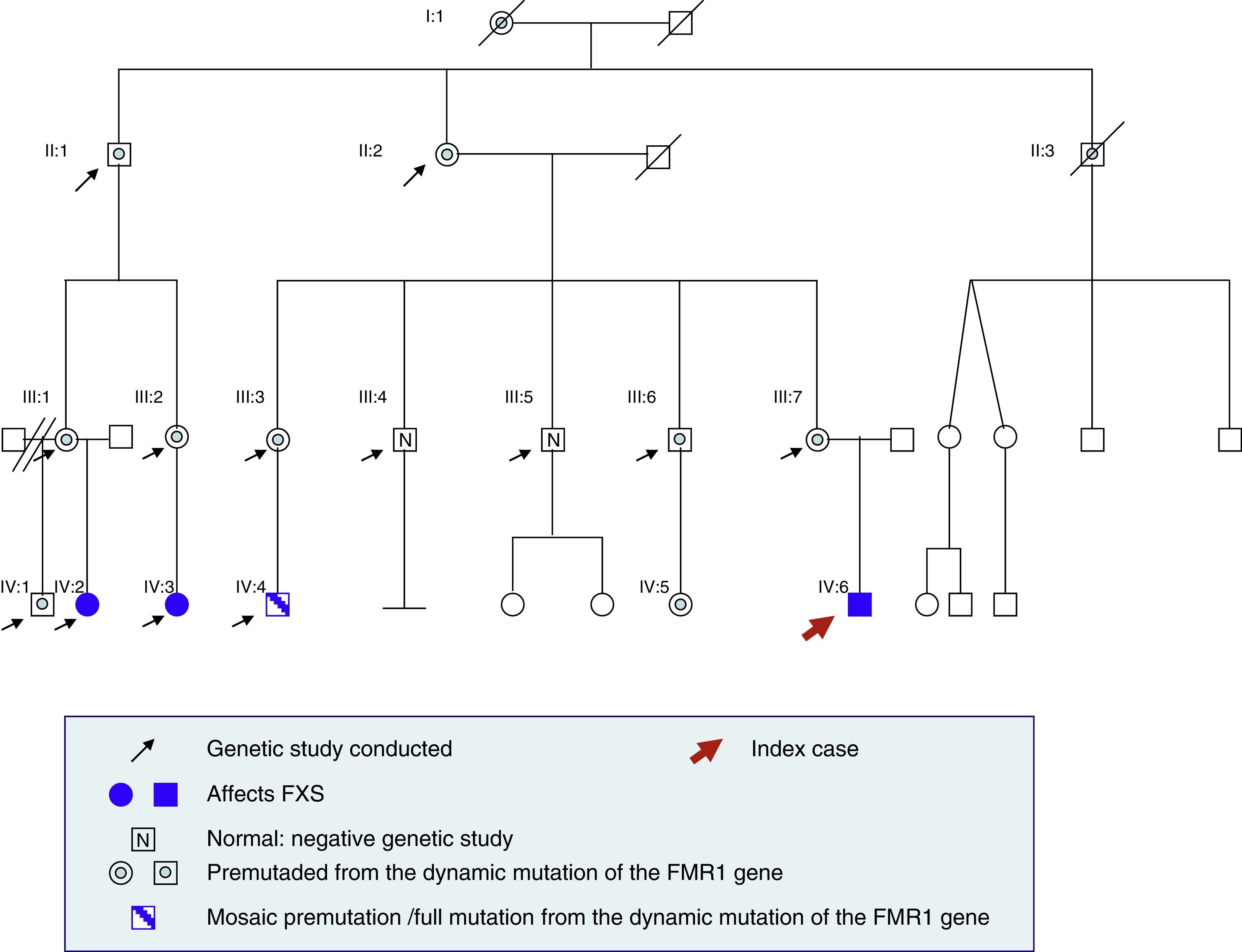
Clinical observation and methodsCGG mutation dynamics of the FMR1 gene were studied in DNA samples from peripheral blood from the index case and other relatives of first, second and third degree by TP-PCR, and the percentage methylation.
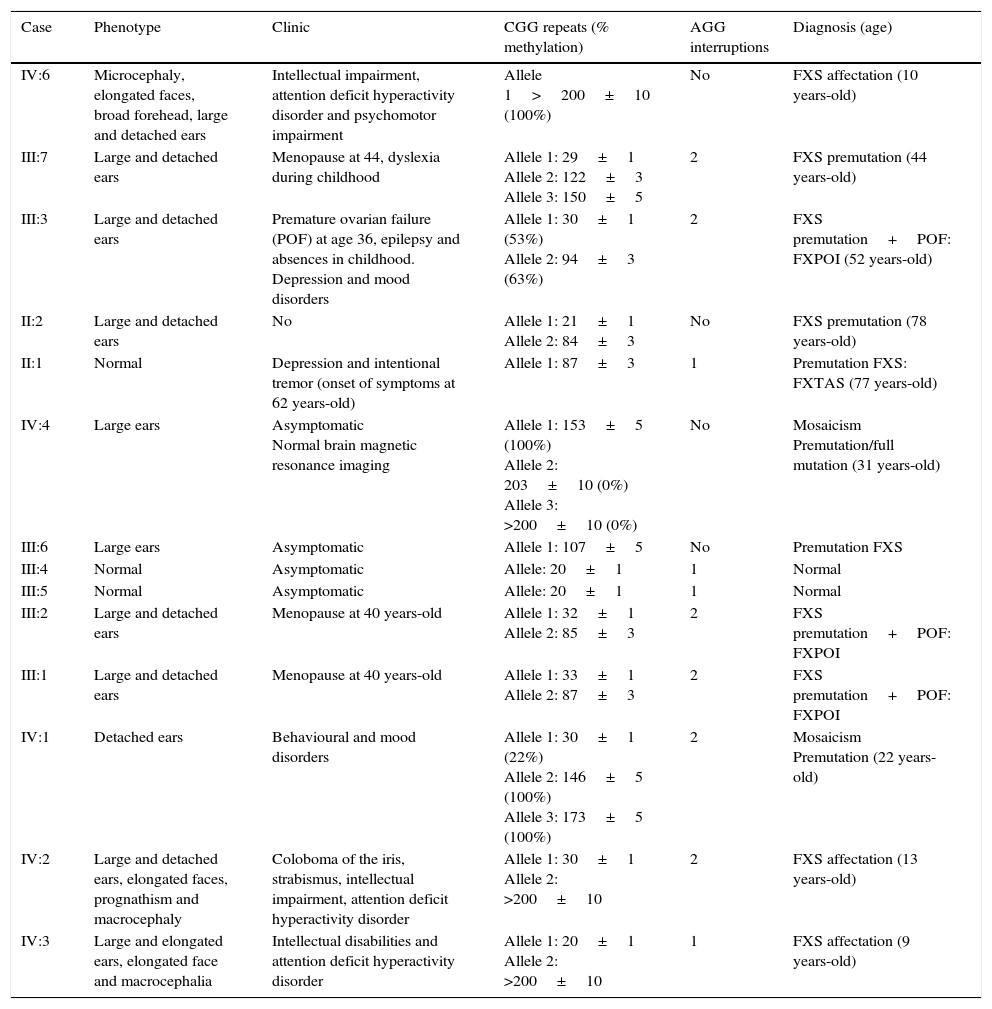
ResultsDiagnosis of FXS was confirmed in three patients (21.4%), eight patients (57.1%) were confirmed in the premutation range transmitters, one male patient with full mutation/permutation mosaicism (7.1%) and two patients (14.3%) with normal study. Of the eight permutated patients, three had FXPOI and one male patient had FXTAS.
DiscussionOur study suggests the importance of making an early diagnosis of SXF in order to carry out a family study and genetic counselling, which allow the identification of new cases or premutated patients with FMR1 gene-associated syndromes (FXTAS, FXPOI).
El aumento del número de repeticiones del triplete citosina-guanina-guanina (CGG), en el gen FMR1 es responsable de 3 síndromes OMIM con fenotipo clínico bien diferenciado: síndrome de X frágil (SXF) y 2 enfermedades en adultos portadores de la premutación (55-200 repeticiones CGG): insuficiencia ovárica primaria (FXPOI) y síndrome de temblor-ataxia (FXTAS) asociado al SXF.
Observación clínica o métodosSe estudió la mutación dinámica CGG del gen FMR1 en muestras de ADN de sangre periférica del caso índice y familiares de primer, segundo y tercer grado mediante TP-PCR, así como el porcentaje de metilación.
ResultadosSe confirmó el diagnóstico del SXF en 3 pacientes (21,4%), 8 pacientes (57,1%) se encontraban en el rango de premutación, un paciente varón con mosaicismo premutación-mutación completa (7,1%) y 2 pacientes (14,3%) con estudio normal. De los 8 pacientes premutados, 3 presentaron FXPOI y un paciente varón FXTAS.
DiscusiónNuestro estudio muestra la importancia de realizar un diagnóstico precoz del SXF y su consecuente estudio familiar y consejo genético, que permita identificar nuevos pacientes afectos o pacientes premutados con síndromes relacionados con el gen FMR1 (FXTAS, FXPOI).