The effect of immunomodulatory therapy with tocilizumab for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in real-life clinical practice remains controversial.
MethodsSingle-center retrospective matched cohort analysis including 47 consecutive patients treated with intravenous tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 pneumonia (“TCZ group”), matched by age, comorbidities, time from symptoms onset and baseline SpO2/FiO2 ratio with 47 patients receiving standard of care alone (“SoC group”).
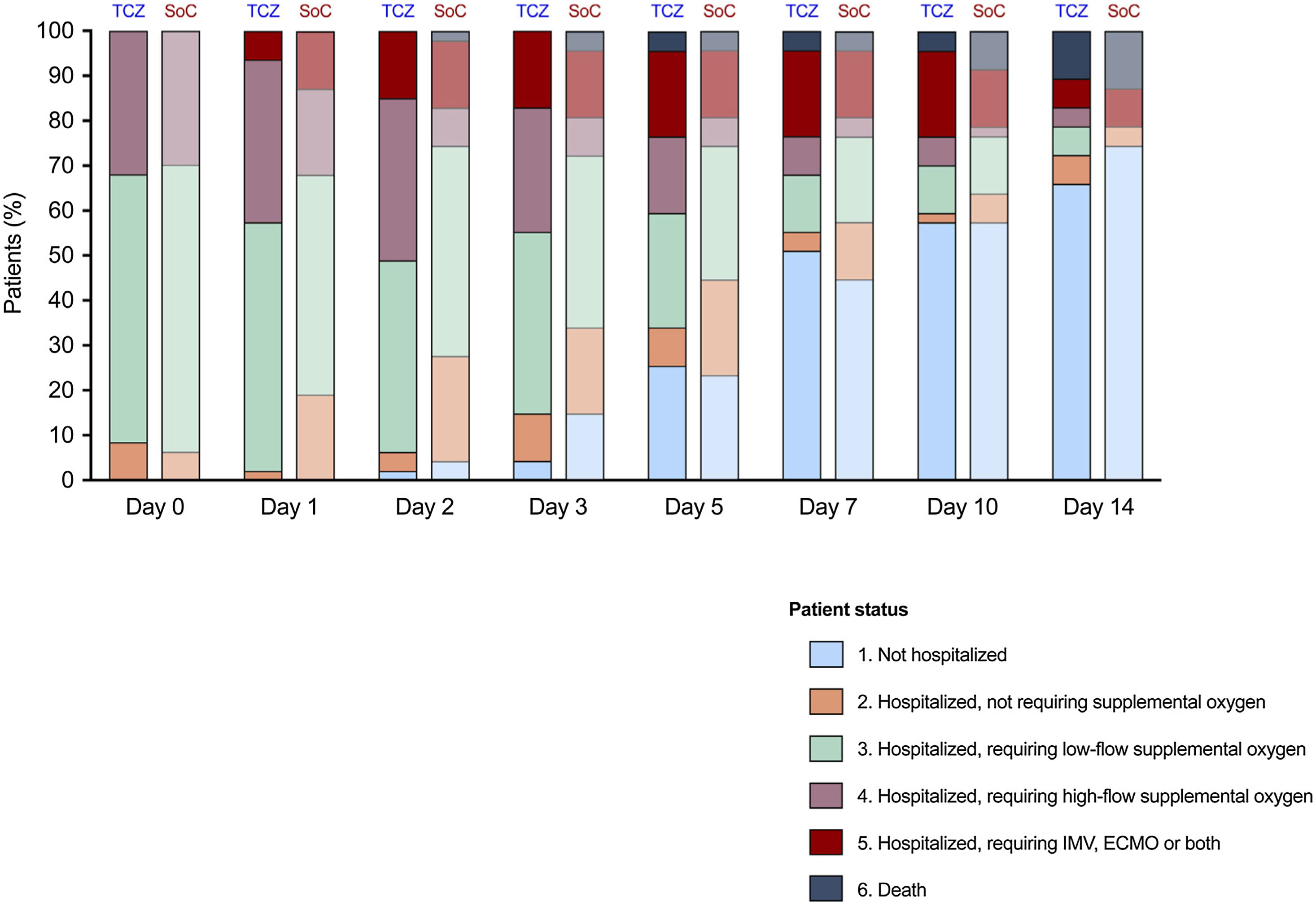
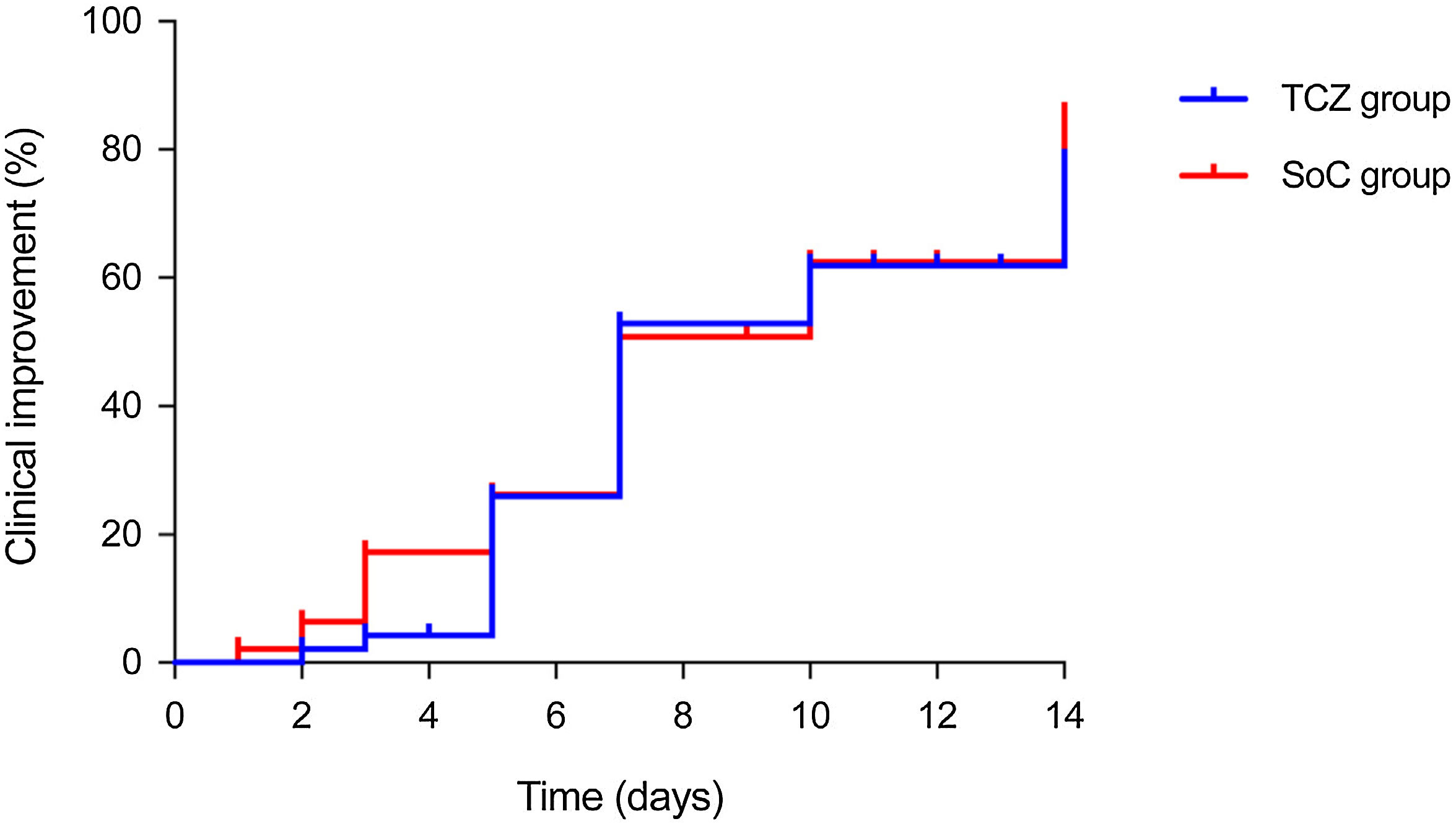
ResultsThere were no significant differences between the TCZ and SoC groups in the rate of clinical improvement (hospital discharge and/or a decrease of ≥2 points on a six-point ordinal scale) by day 7 (51.1% [24/47] versus 48.9% [23/47]; P-value=1.000). No differences were observed at day 14 in terms of clinical improvement (72.3% versus 76.6%; P-value=0.791), all-cause mortality (10.6% versus 12.8%; P-value=1.000), and the composite of invasive mechanical ventilation and/or death (25.5% versus 23.4%; P-value=1.000) either. Patients in the TCZ group had a more rapid normalization of C-reactive protein levels.
ConclusionsNo apparent benefit was observed in patients with severe COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab as compared to a matched retrospective cohort.
El efecto del tratamiento inmunomodulador con tocilizumab en la COVID-19 sigue siendo controvertido.
MétodosEstudio unicéntrico de cohortes retrospectivas pareadas que incluyó a 47 pacientes con COVID-19 grave tratados con tocilizumab intravenoso («grupo TCZ»), emparejados por edad, comorbilidades mayores, evolución de síntomas y cociente SpO2/FiO2 basal con 47 pacientes que recibieron tratamiento estándar únicamente («grupo SoC»).
ResultadosNo observamos diferencias significativas entre los grupos de TCZ y SoC en la tasa de mejoría clínica (alta hospitalaria y/o descenso de ≥ 2 puntos en una escala ordinal de 6 puntos) al día 7 (51,1% [24/47] vs. 48,9% [23/47]; P=1,000). Tampoco hubo diferencias al día 14 en las tasas de mejoría clínica (72,3% vs. 76,6%; P=0,791), mortalidad (10,6% vs. 12,8%; P=1,000) o en el compuesto de ventilación mecánica invasiva y/o muerte (25,5% vs. 23,4%; P=1,000). Los pacientes en el grupo de TCZ presentaron una normalización más rápida de la proteína C reactiva.
ConclusionesRespecto a una cohorte retrospectiva pareada, no detectamos un beneficio asociado al tratamiento con tocilizumab en pacientes con neumonía por COVID-19.