The objective of the study was to determine the ability of faecal calprotectin to differentiate functional and organic intestinal diseases in paediatric patients, and to evaluate the correlation between inflammatory parameters and levels of faecal calprotectin.
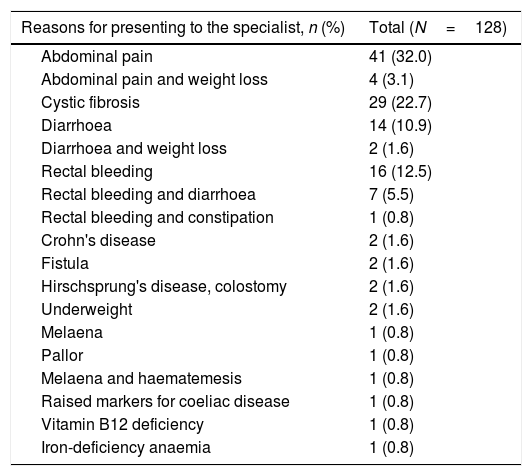
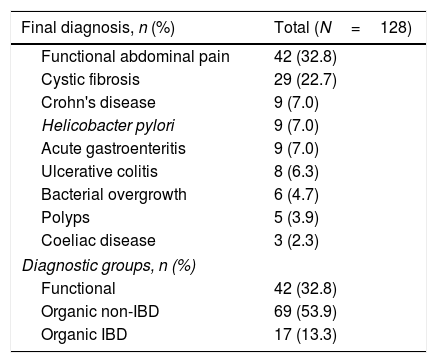
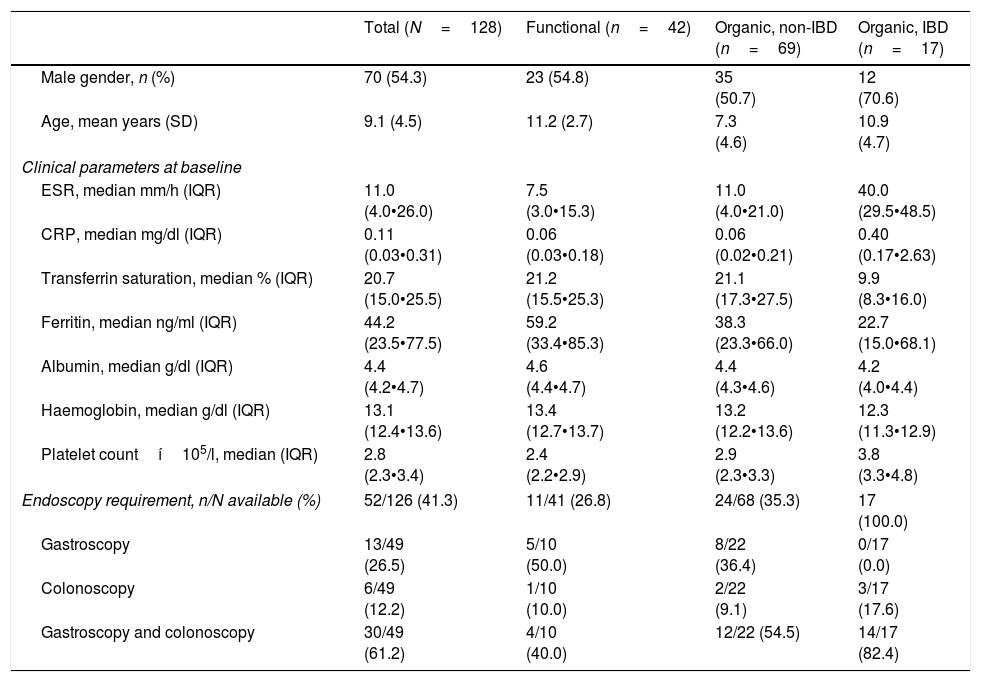
Patients and methodsThis retrospective study involved clinical data from 129 paediatric patients with symptoms of intestinal pathology. Faecal calprotectin was determined by quantitative immunoassay. Patients were classified into three groups: functional (32.8% of patients); organic non-inflammatory bowel disease (IBD, 53.9%); and organic IBD (13.3%).
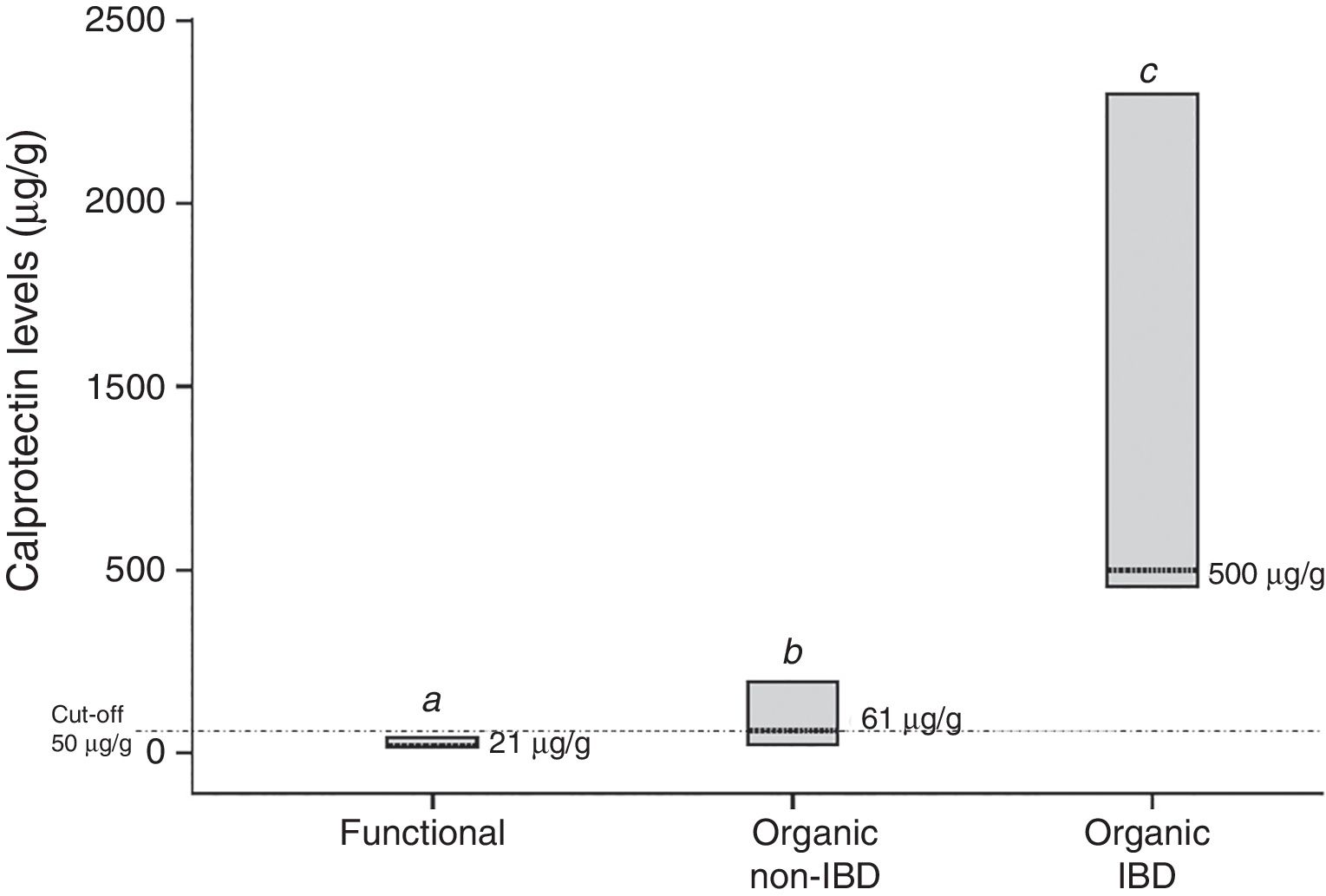
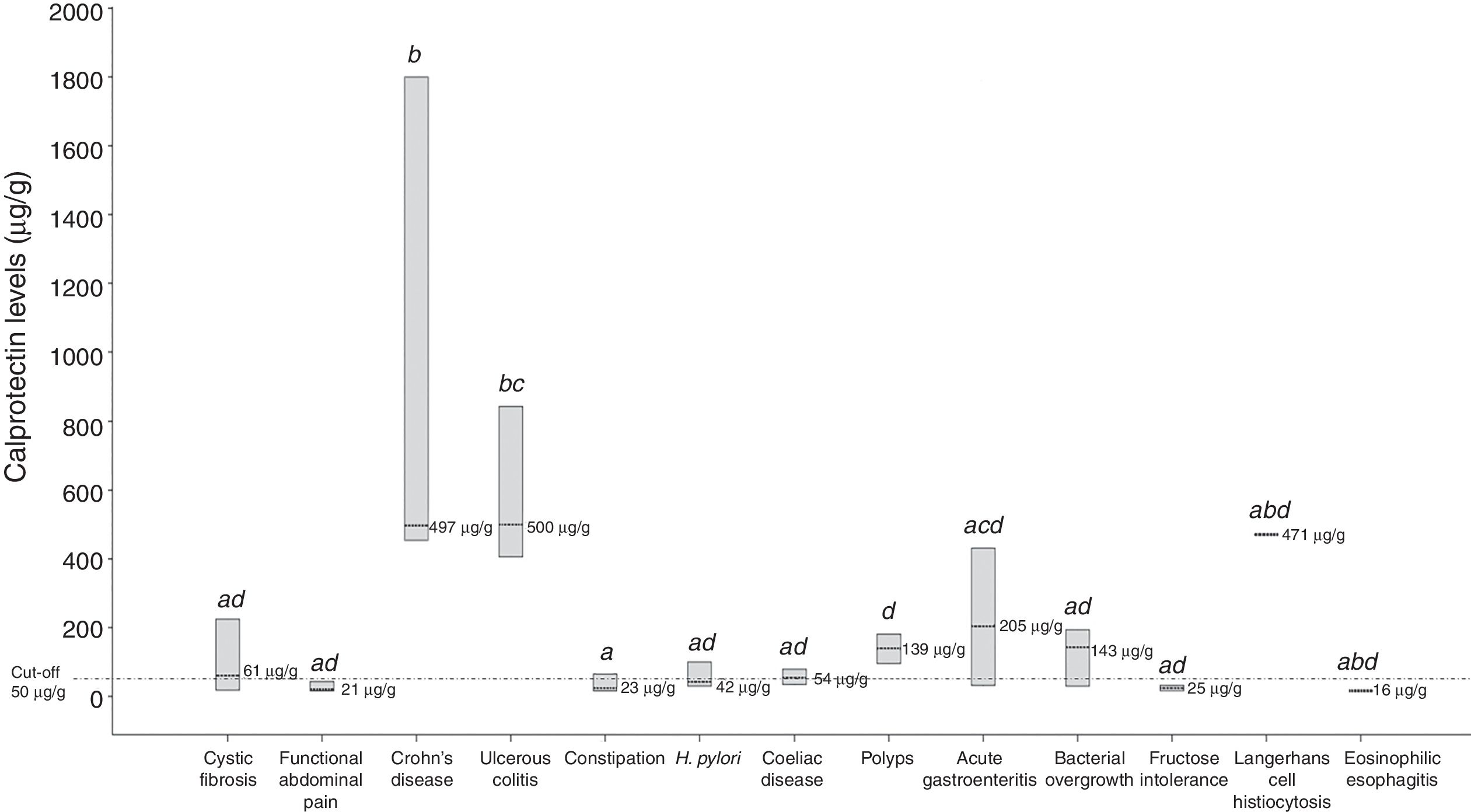
ResultsCalprotectin levels were significantly different among the three groups; between patients with IBD and the others, and also between patients with non-organic IBD and functional. Positive associations were found between high levels of calprotectin and higher erythrocyte sedimentation rate (rho=0.497), C-reactive protein (rho=0.460), and platelet count (rho=0.232). Nevertheless, an inverse correlation was found between high levels of calprotectin and transferrin saturation (rho=∧0.310), albumin (rho=∧0.412), and haemoglobin levels (rho=∧0.309).
DiscussionDetermination of faecal calprotectin is a complementary tool in clinical practice for discriminating between functional and organic IBD, avoiding, according to the levels of calprotectin, unnecessary invasive procedures in paediatric patients.
El objetivo de este estudio fue determinar la capacidad de la calprotectina fecal para diferenciar las enfermedades funcionales y orgánicas en los pacientes pediátricos, y evaluar la correlación entre los parámetros inflamatorios y los niveles de calprotectina fecal.
Pacientes y mèc)todosEste estudio retrospectivo incluyó los datos clínicos de 129 pacientes pediátricos con síntomas de enfermedad intestinal. Se determinaron los valores de calprotectina fecal mediante inmunoensayo cuantitativo. Se clasificaron los pacientes en 3 grupos: funcionales (32,8% de pacientes), enfermedad intestinal inflamatoria no orgánica (EII, 53,9%) e EII orgánica (13,3%).
ResultadosLos niveles de calprotectina fueron significativamente diferentes entre los 3 grupos; entre los pacientes con EII y el resto, y tambièc)n entre los pacientes con EII no orgánica e EII funcional. Se encontraron asociaciones positivas entre los niveles altos de calprotectina y la tasa de sedimentación eritrocítica alta (Rho=0,497), proteína C reactiva (Rho=0,460) y recuento plaquetario (Rho=0,232). Sin embargo, se encontró una correlación inversa entre los niveles altos de calprotectina y la saturación de transferrina (Rho=∧0,310), albúmina (Rho=∧0,412) y niveles de hemoglobina (Rho=∧0,309).
DiscusiónLa determinación de la calprotectina fecal es una herramienta complementara en la práctica clínica para discriminar entre EII funcional y EII orgánica, y evitar con arreglo a los niveles de calprotectina, los procedimientos invasivos innecesarios en pacientes pediátricos.