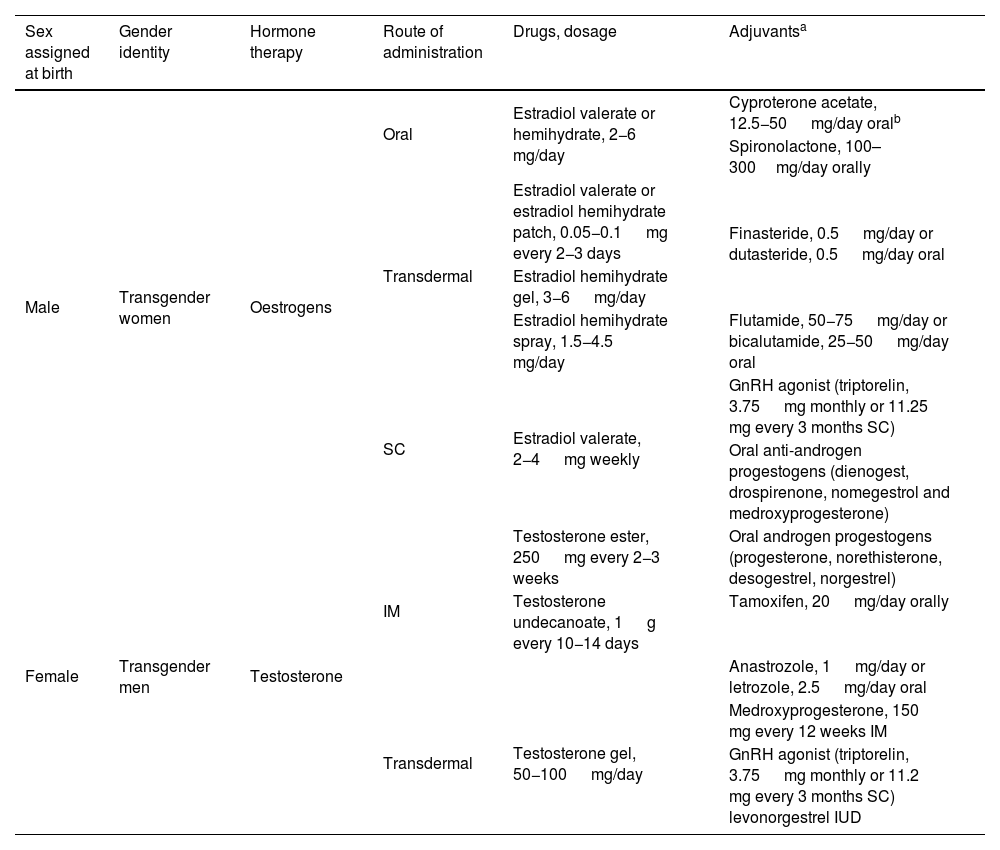
Hormone therapy is associated with an increased thrombotic risk. The objective of this systematic review is to assess the incidence of venous thromboembolism in the transgender population undergoing gender-affirming hormone therapy and compare it with that in cisgender individuals of the same sex assigned at birth.
Materials and methodA literature search was conducted in databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, and EMBASE, encompassing all studies that report data related to the incidence of venous thromboembolism in transgender individuals on hormone therapy.
ResultsTwenty-one studies were included. Five studies assessed the incidence of thromboembolic events in both populations. The occurrence of thrombosis was higher in transgender women than cisgender men (OR 2.23; 95% CI: 1.93–2.57; p<0.001). No differences between transgender men and cisgender women (OR 0.96; 95% CI: 0.87–2.31; p=0.60) were found.
ConclusionOur systematic review suggests that hormone therapy in transgender women may increase the risk of venous thromboembolism.
La terapia hormonal está asociada con un aumento del riesgo trombótico. El objetivo de esta revisión sistemática es conocer la incidencia de enfermedad tromboembólica venosa en población transgénero en terapia hormonal de afirmación de género y compararla con personas cisgénero del mismo sexo asignado al nacer.
Material y métodoSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica en las bases PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus y EMBASE, incluyendo todos los estudios que reportan datos relacionados con la incidencia de tromboembolia venosa en personas transgénero en terapia hormonal.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 21 estudios. Las mujeres transgénero presentaron una tasa más elevada de fenómenos trombóticos que los hombres cisgénero (OR 2,23; IC 95%: 1,93–2,57; p<0,001). No se encontraron diferencias entre hombres transgénero y mujeres cisgénero (OR 0,96; IC 95%: 0,87–2,31; p=0,60).
ConclusiónNuestra revisión sistemática sugiere que la terapia hormonal en mujeres transgénero podría aumentar el riesgo de tromboembolia venosa.