Romiplostim and eltrombopag are thrombopoietin receptor (TPOr) agonists that promote megakaryocyte differentiation, proliferation and platelet production. In 2012, a systematic review and meta-analysis reported a non-statistically significant increased risk of thromboembolic events for these drugs, but analyses were limited by lack of statistical power. Our objective was to update the 2012 meta-analysis examining whether TPOr agonists affect thromboembolism occurrence in adult thrombocytopenic patients.
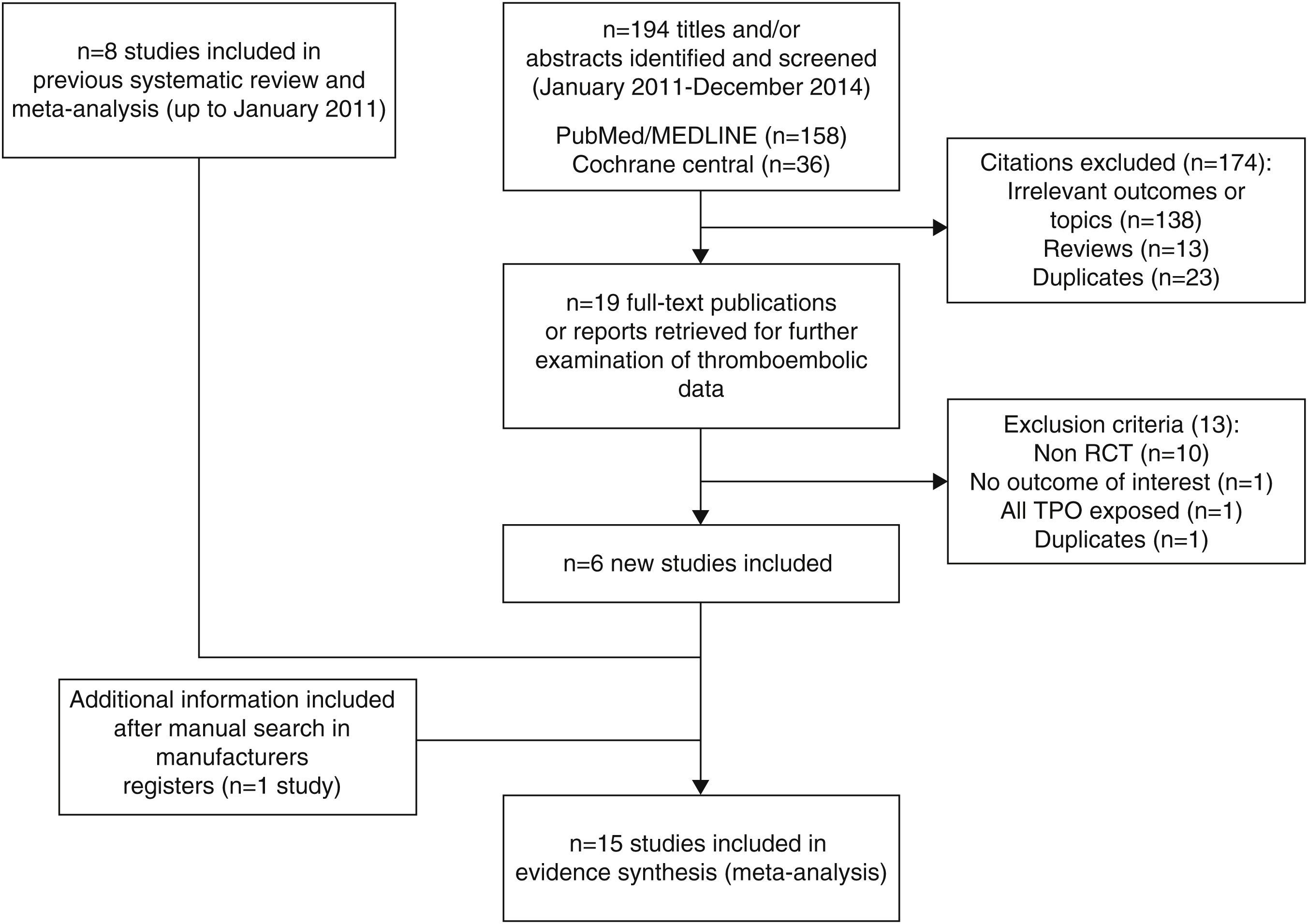
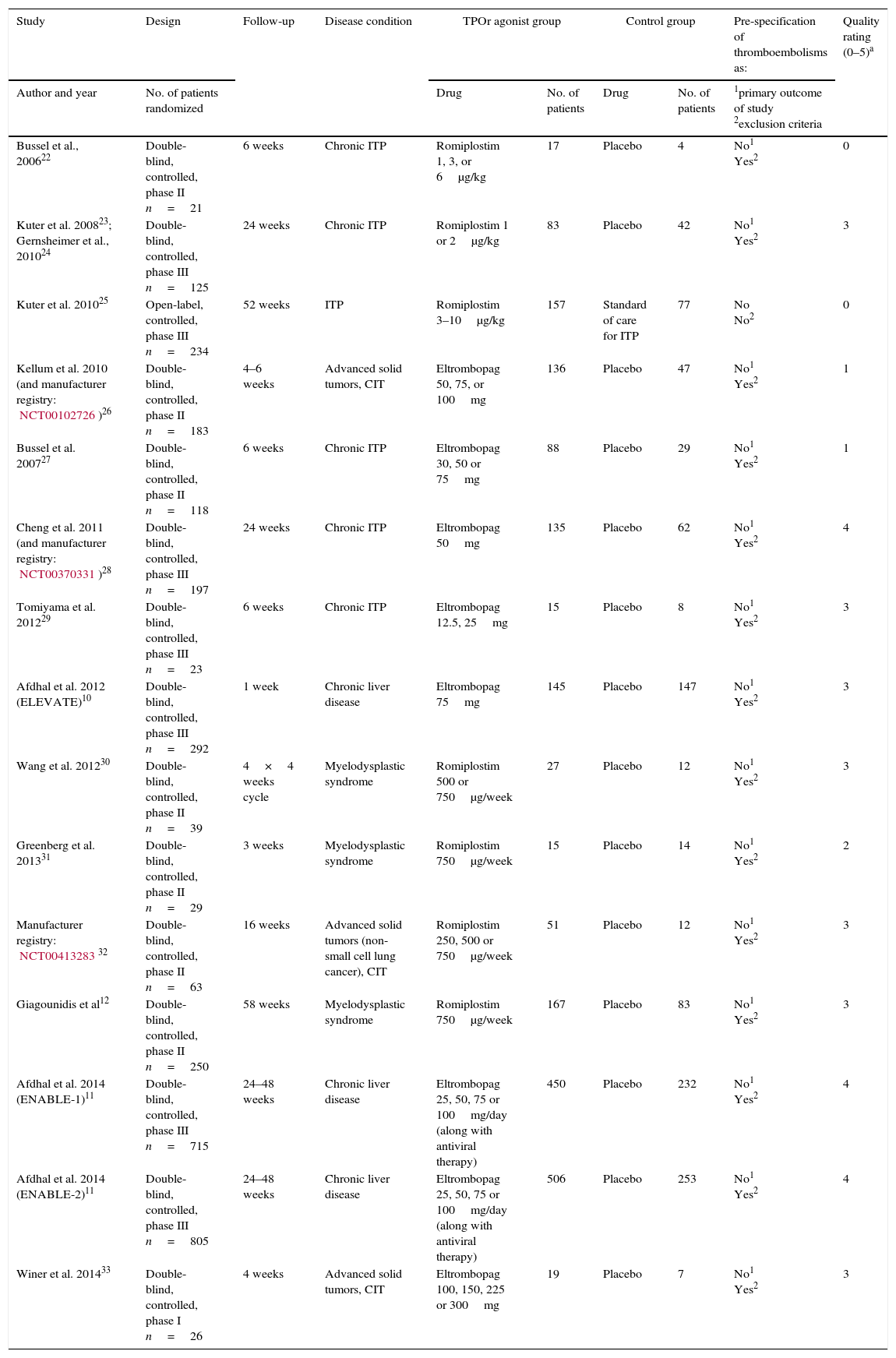
Materials and methodsWe conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Updated searches were conduced on PubMed, Cochrane Central, and publicly available registries (up to December 2014). RCTs using romiplostim or eltrombopag in at least one group were included. Relative risks (RR), absolute risk ratios (ARR) and number needed to harm (NNH) were estimated. Heterogeneity was analyzed using Cochran's Q test and I2 statistic.
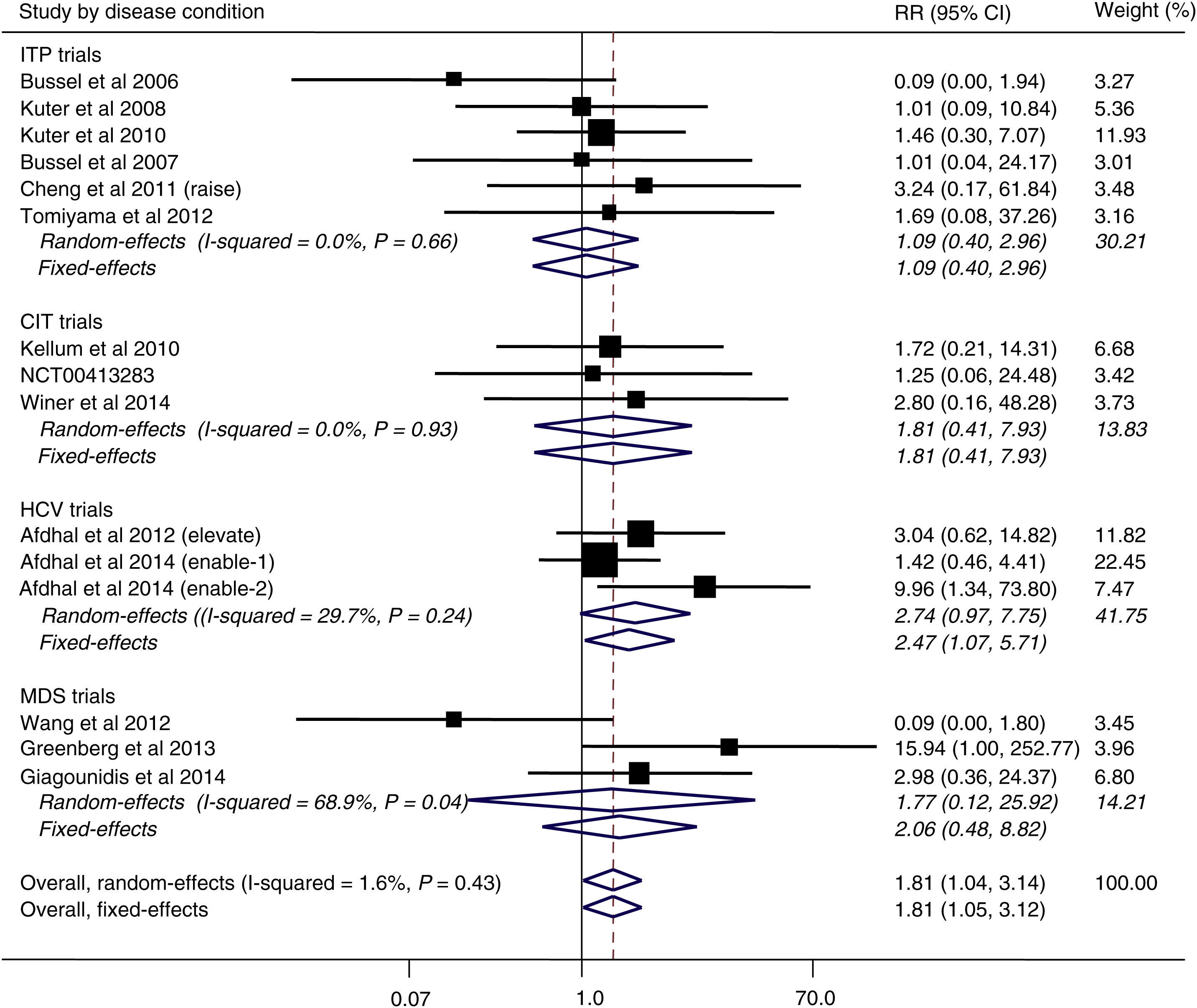
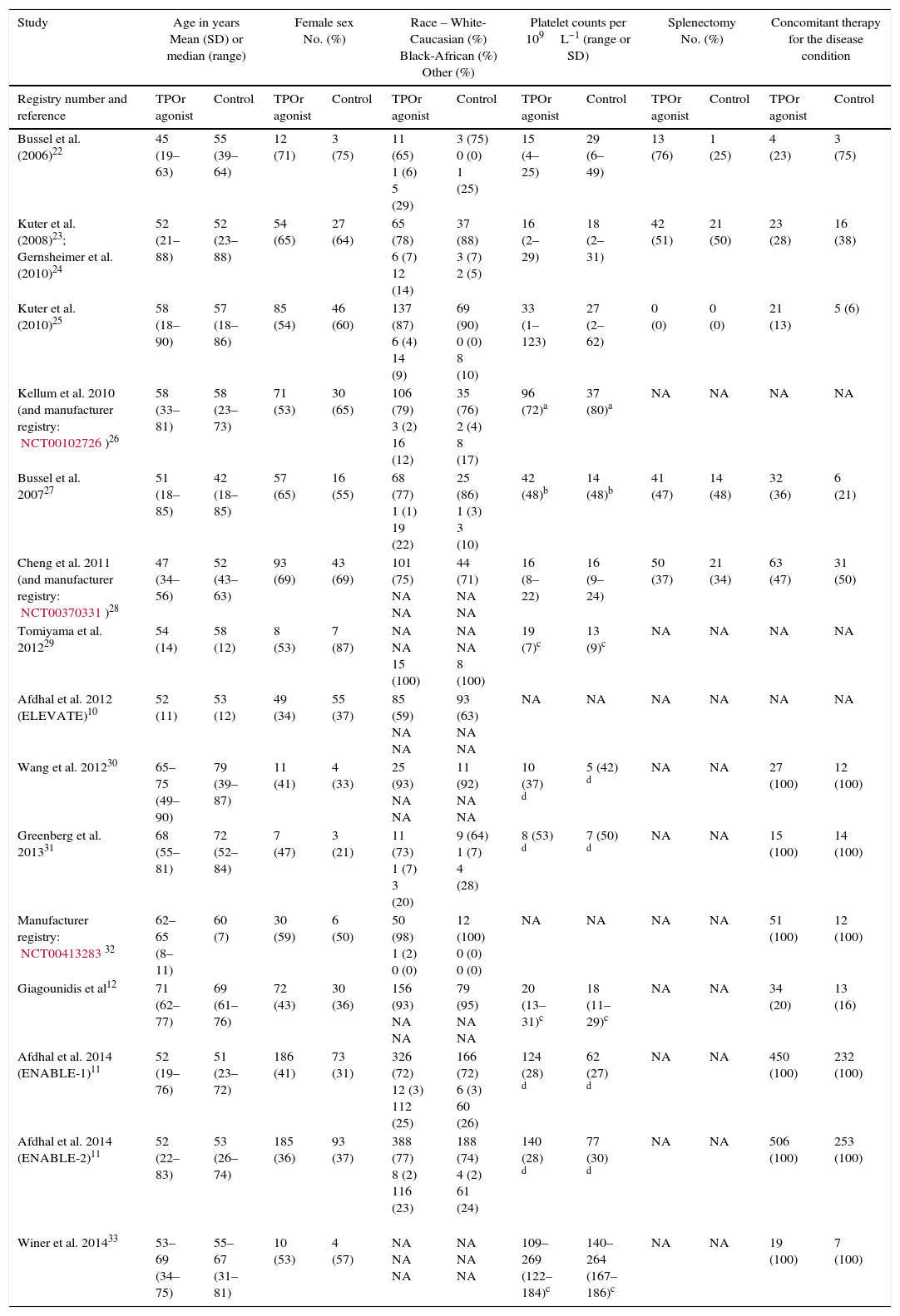
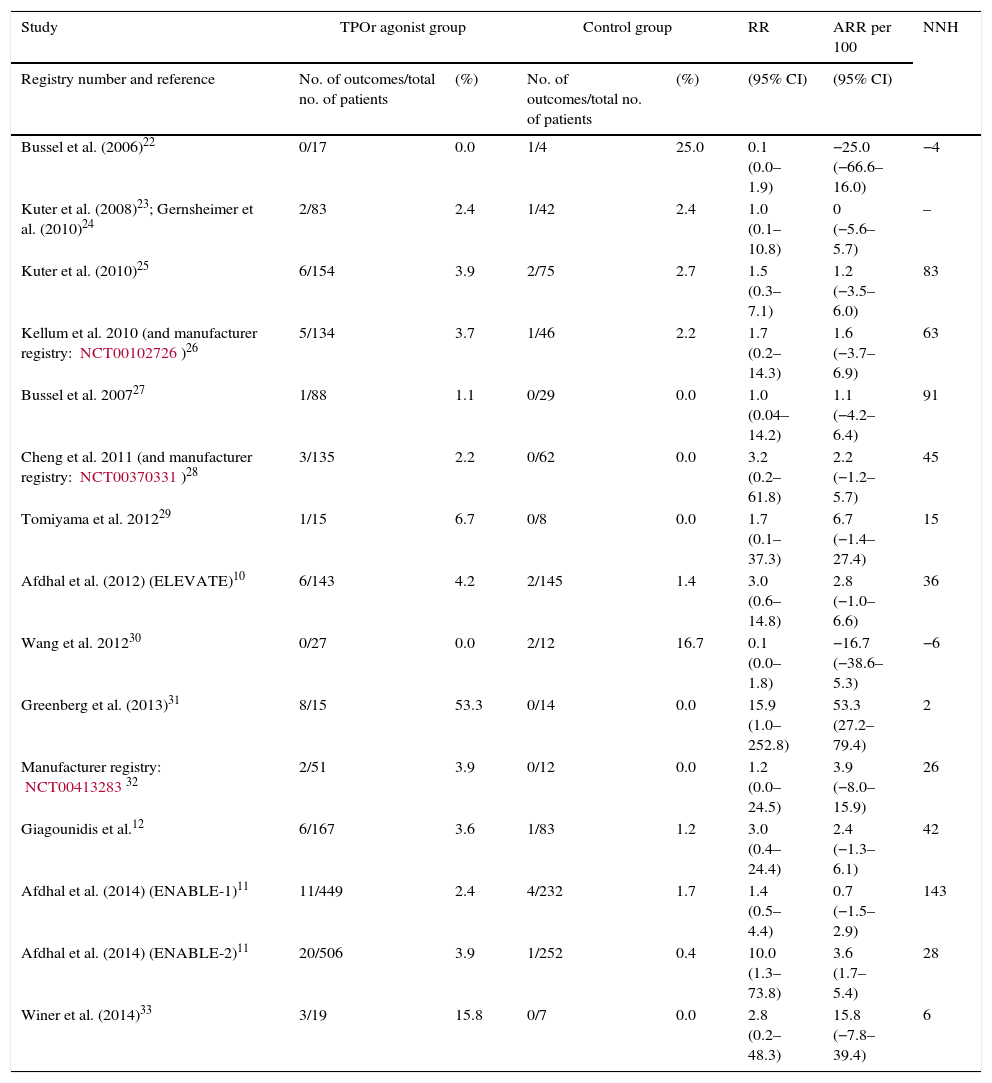
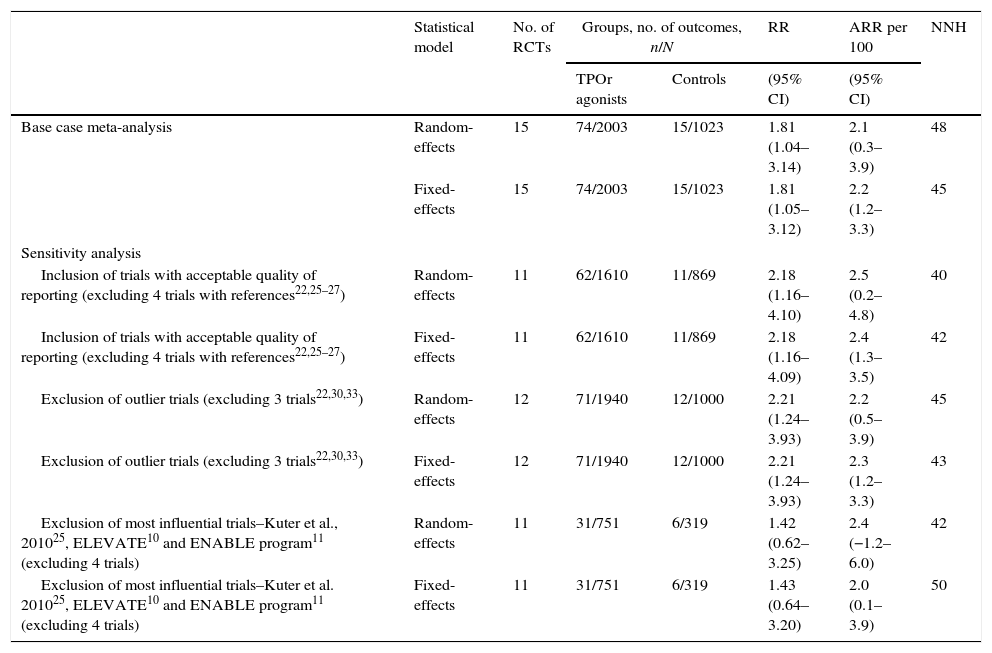
ResultsFifteen studies with 3026 adult thrombocytopenic patients were included. Estimated frequency of thromboembolism was 3.69% (95% CI: 2.95–4.61%) for TPOr agonists and 1.46% (95% CI: 0.89–2.40%) for controls. TPOr agonists were associated with a RR of thromboembolism of 1.81 (95% CI: 1.04–3.14) and an ARR of 2.10% (95% CI: 0.03–3.90%) meaning a NNH of 48. Overall, we did not find evidence of statistical heterogeneity (p=0.43; I2=1.60%).
ConclusionsOur updated meta-analysis suggested that TPOr agonists are associated with a higher risk of thromboemboembolic events compared with controls, and supports the current recommendations included in the European product information on this respect.
Los agonistas del receptor de la trombopoyetina (TPOr) (romiplostim y eltrombopag) promueven la diferenciación megacariocítica, la proliferación y la producción de plaquetas. En 2012, una revisión sistemática y metaanálisis informó de un aumento no estadísticamente significativo del riesgo tromboembólico para estos medicamentos, pero los análisis presentaban limitaciones por la falta de potencia estadística. El objetivo es actualizar el metaanálisis de 2012 examinando si los agonistas del TPOr afectan a la incidencia de tromboembolismos en los pacientes adultos con trombocitopenia.
Material y métodosSe llevó a cabo una revisión sistemática y metaanálisis de ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados (ECA). Se actualizaron búsquedas llevadas a cabo en PubMed, Cochrane Central, y registros públicos (hasta Diciembre de 2014). Se incluyeron ECA en los que se administrara romiplostim o eltrombopag en al menos uno de los grupos de pacientes tratados. Se calcularon los riesgos relativos (RR), la diferencia absoluta de riesgo (ARR, por sus siglas en inglés) y el número necesario de pacientes para dañar (NNH). Se examinó la heterogeneidad estadística mediante la Q de Cochran y el estadístico I2.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 15 estudios con 3026 pacientes adultos diagnosticados de trombocitopenia. Las frecuencias de acontecimientos tromboembólicos fueron de 3.69% ([intervalo de confianza] IC del 95%: 2,95–4,61%) para los agonistas del TPOr y de 1,46% (IC95%: 0,89–2,40%) para los controles. Los agonistas del TPOr se asociaron con un riesgo relativo de tromboembolismo de 1,81 (IC95%: 1,04–3,14) y una ARR del 2,10% (IC95%: 0,03–3,90%), que significa un NNH de 48. En general, no se encontró evidencia de heterogeneidad estadística (p=0,43; I2=1,60%).
ConclusionesEl metaanálisis actualizado sugiere que los agonistas del TPOr están asociados con un mayor riesgo de eventos thromboembólicos en comparación con los controles. Estos resultados apoyan las precauciones incluidas en la información del medicamento en la Unión Europea en relación con el riesgo tromboembólico.