Dysfunction of the right ventricle (RV) is a parameter of severity in acute pulmonary embolism (PE). Echocardiographic assessment is not always possible in accident and emergency, hence the need to predict the presence of RV dysfunction using easily measurable parameters.
To analyse the value of NT-proBNP and troponin T as markers of RV dysfunction in patients with acute PE. Secondarily, to assess the relationship between RV failure and clinical parameters related to PE.
Material and methodAnalytical, observational, cross-sectional and retrospective study comparing the values NT-proBNP, troponin T and presenting symptoms of PE among patients with and without RV dysfunction.
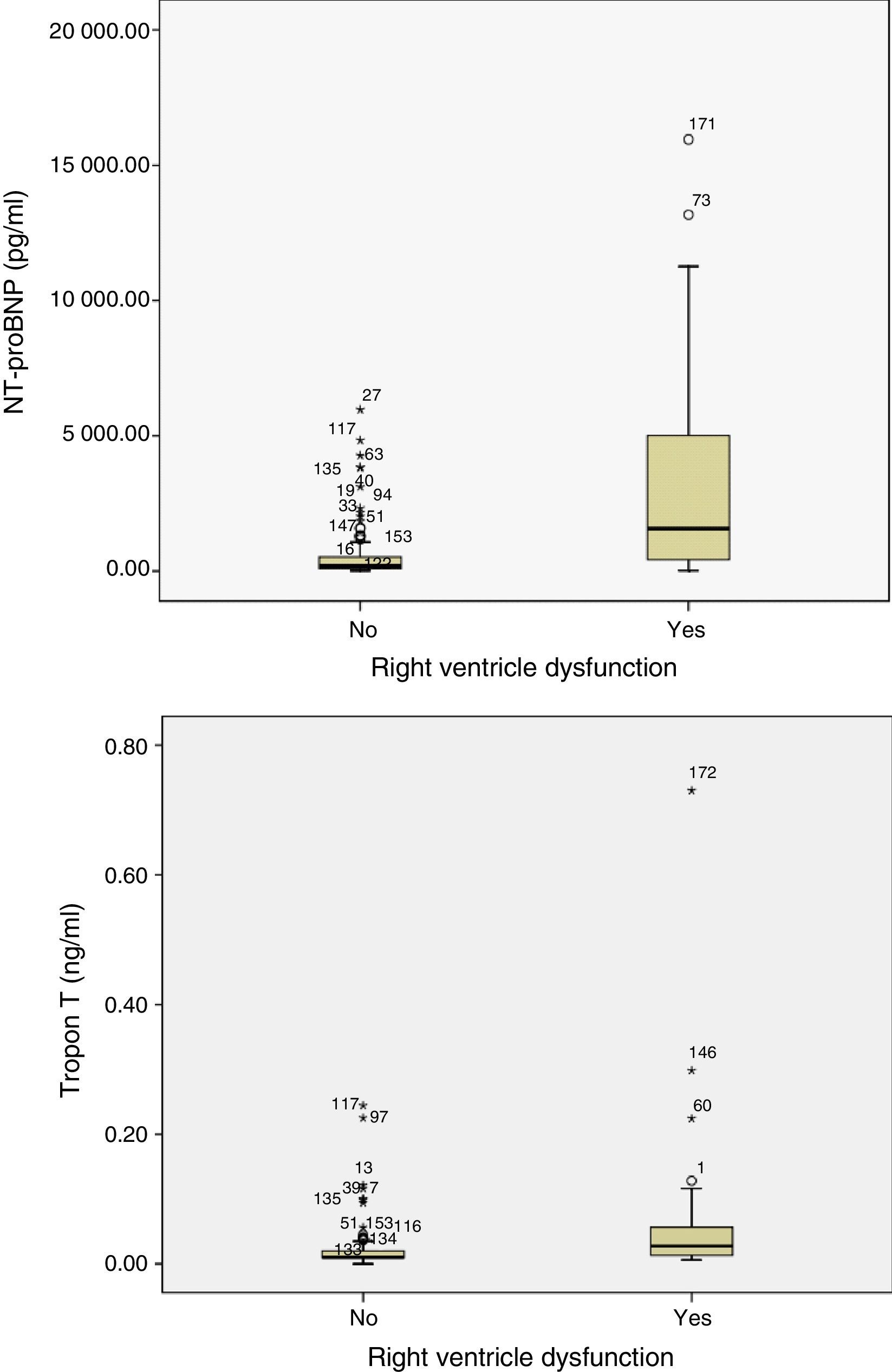
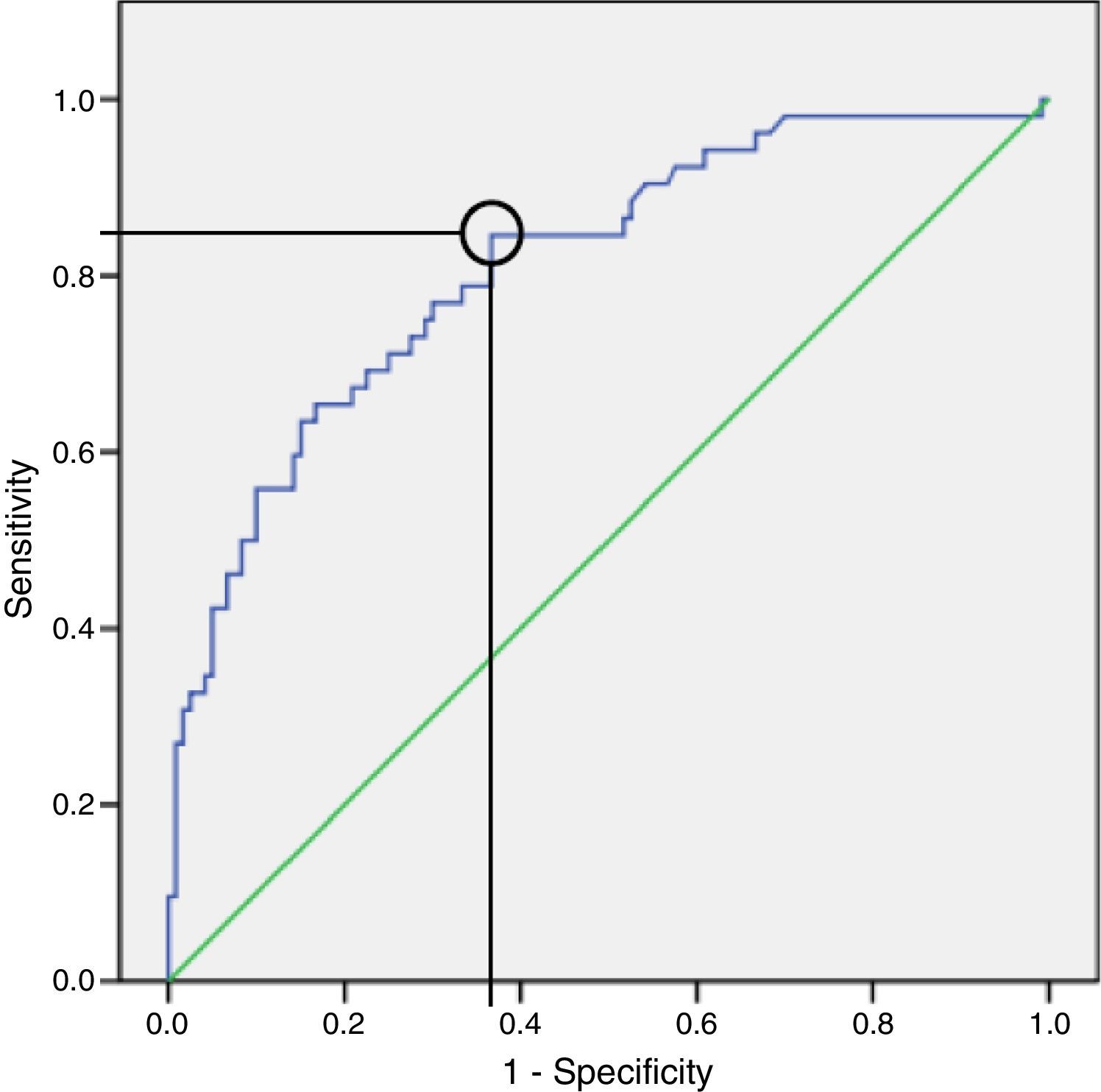
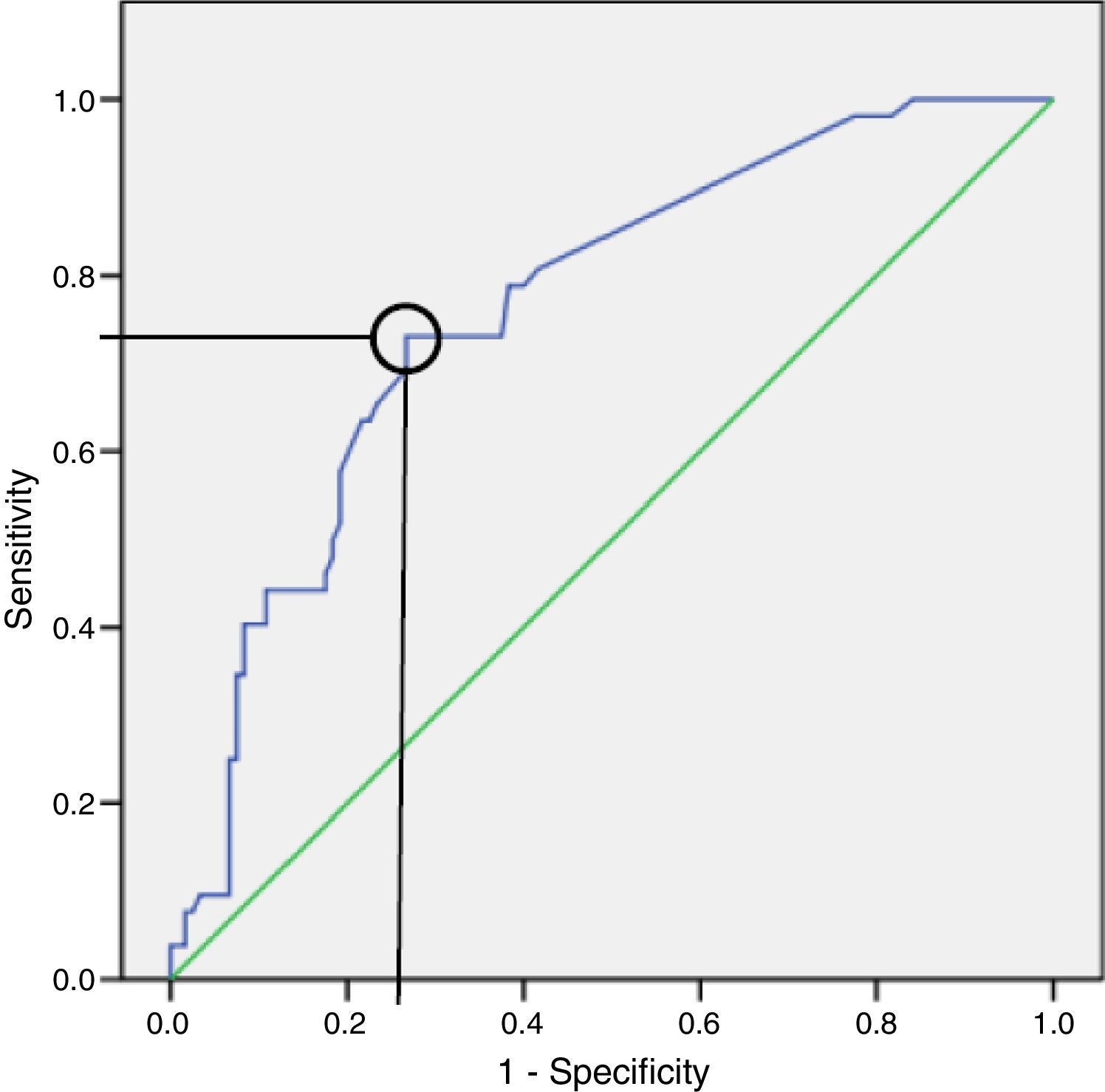
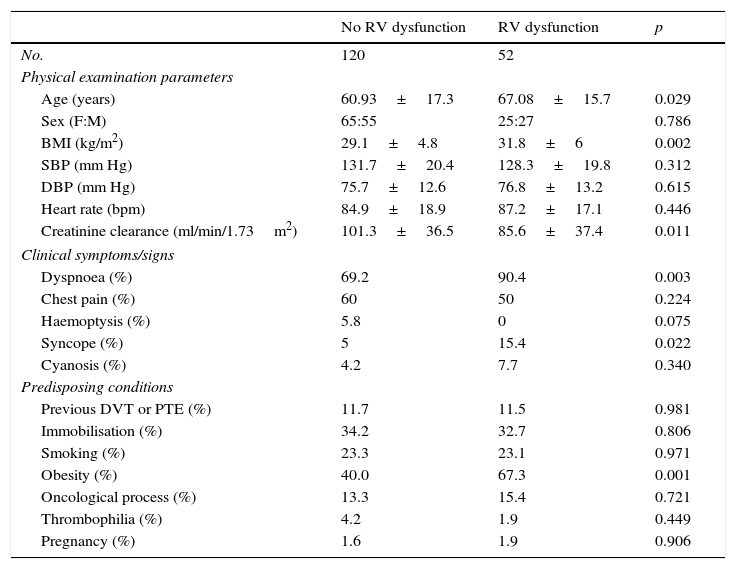
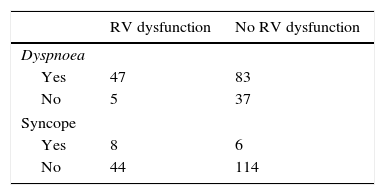
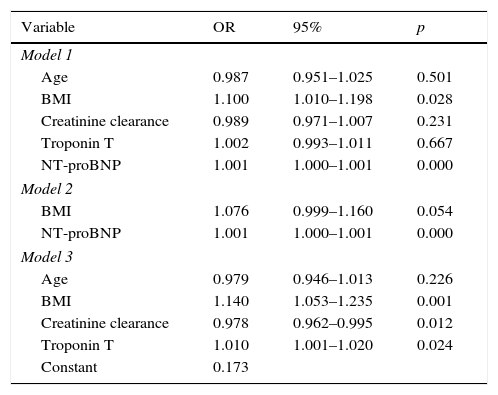
ResultsOne hundred seventy-two patients (52 with RV failure, 120 without) were included. All symptoms occurred with similar frequency between the 2 groups except dyspnoea and syncope (more common in the group with RV failure). Both NT-proBNP and troponin T had significantly higher values in the group of patients with RV dysfunction. However, in the multivariate analysis, NT-proBNP had a higher explanatory value for RV failure than troponin T.
ConclusionNT-proBNP is a diagnostic parameter of RV dysfunction with higher sensitivity in the context of acute PE.
La disfunción del ventrículo derecho (VD) es un parámetro de gravedad en la embolia pulmonar (EP) aguda. La valoración ecocardiográfica no siempre es posible en urgencias, de ahí la necesidad de predecir la presencia de disfunción de VD mediante parámetros de fácil medición.
Analizar el valor de NT-proBNP y troponina T como marcadores de disfunción del VD en los pacientes con EP aguda. Como objetivo secundario, valorar la relación entre fallo de VD y diferentes parámetros clínicos relacionados con la EP.
Material y métodoEstudio analítico, observacional, transversal y retrospectivo que compara los valores de NT-proBNP, troponina T y síntomas de presentación de EP entre pacientes con fallo de VD y sin fallo.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 172 pacientes (52 con fallo de VD, 120 sin fallo de VD). Todos los síntomas se presentaron con similar frecuencia entre ambos grupos, salvo la disnea y el síncope (más frecuentes en el grupo con fallo de VD). Tanto el NT-proBNP como la troponina T presentaron valores significativamente mayores en el grupo de pacientes con fallo de VD. Sin embargo, el valor explicativo de fallo de VD fue mayor para el NT-proBNP en al análisis multivariante.
ConclusiónEl NT-proBNP se muestra como un parámetro diagnóstico de fallo de VD con mayor sensibilidad en el contexto de EP aguda.