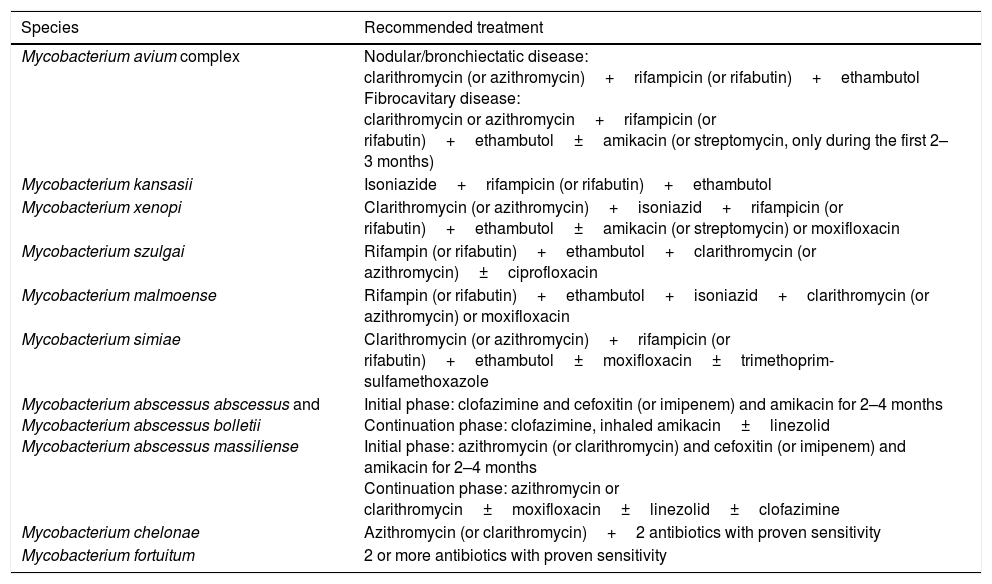
The most common infections caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are lung infections. The microorganisms causing these infections most frequently are Mycobacterium avium complex, Mycobacterium kansasii and Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Their incidence has increased in the last three decades.
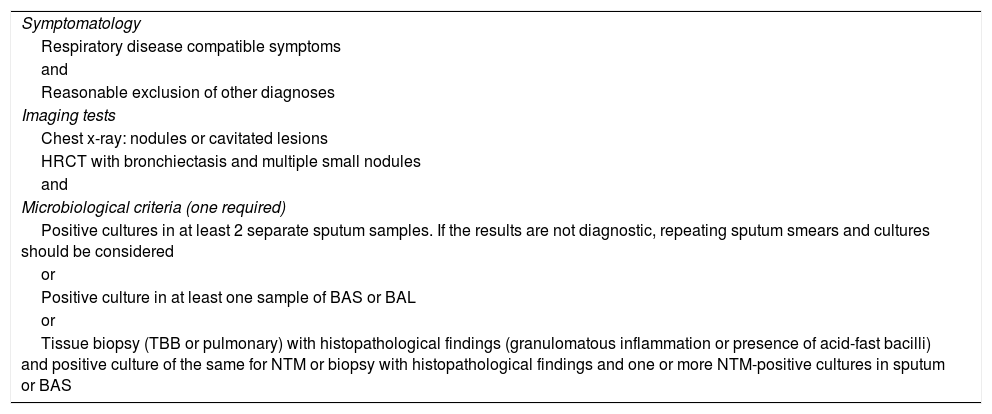
After identifying an NTM in the respiratory tract, clinical and radiological aspects must be considered to determine if isolations are clinically relevant. Predisposing conditions that could contribute to infection must also be investigated.
Pulmonary disease due to NTM is presented in three clinical forms: a) pneumonitis due to hypersensitivity; b) fibrocavitary form; and c) nodular-bronchiectasic.
The diagnosis of respiratory disease due to NTM does not make it obligatory to immediately initiate treatment. Before initiating the latter, other factors must be considered, such as age, comorbidities, life expectancy, due to the prolonged nature of treatments, with potential side effects and, in many cases, only a slight response to the treatment.
Las infecciones más frecuentes causadas por micobacterias no tuberculosas (MNT) son las pulmonares. Los microorganismos que causan con más frecuencia estas infecciones son Mycobacterium avium complex, Mycobacterium kansasii y Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Su incidencia ha aumentado en las 3 últimas décadas.
Tras la identificación de una MNT en el tracto respiratorio, deben considerarse aspectos clínicos y radiológicos para determinar si los aislamientos son clínicamente relevantes. También deben investigarse las condiciones predisponentes que pudieran favorecer la infección.
La enfermedad pulmonar por MNT se presenta de 3 formas clínicas: a) neumonitis por hipersensibilidad; b) forma fibrocavitaria, y c) forma nodular-bronquiectásica.
El diagnóstico de enfermedad respiratoria por MNT no obliga a iniciar el tratamiento inmediatamente. Antes de iniciar el mismo deben considerarse otros factores, tales como edad, comorbilidades, esperanza de vida, debido a que los tratamientos son prolongados, con potenciales efectos secundarios y, en muchos casos, con escasa respuesta a los mismos.