Although urine pneumococcal antigen is an useful test, it has false positives such as pneumococcal vaccination.
Material and methodsPositive urine pneumococcal antigen in Hospital de Denia (January–February/2015). We studied epidemiological, radiological and microbiological variables as well as previous pneumococcal vaccination (Pneumo-23 and/or Pneumo-13).
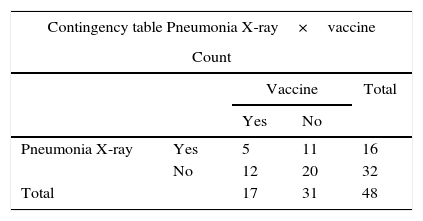
ResultsUrine pneumococcal antigen test was positive in 12.4% of 385 cases. Only 33.3% of positive cases had pneumonia in chest X-ray, and 35.4% of patients had previous pneumococcal vaccination. In most cases (87.5%), an antibiotic was prescribed.
ConclusionsPneumococcal vaccination can produce a false positive result in the urine pneumococcal antigen test in clinical practice, leading to an unnecessary prescription of antibiotics.
La detección del antígeno neumocócico en orina es una prueba útil pero puede presentar falsos positivos, entre ellos, la vacunación neumocócica.
Material y métodosDetección de las antigenurias positivas a neumococo en el Hospital de Denia (enero-febrero/2015). Se determinaron variables epidemiológicas, radiológicas, microbiológicas y antecedente de vacunación neumocócica (neumo-23 y/o neumo-13).
ResultadosLa antigenuria a neumococo mostró un resultado positivo en el 12,4% de 385 determinaciones. Solo en el 33,3% de los casos con antigenuria positiva se documentó infiltrado radiológico en la radiografía de tórax. En el 35,4% de los pacientes existía antecedente de vacunación neumocócica previa. En la mayor parte de los casos (87,5%) un antígeno neumocócico positivo supuso la prescripción de un tratamiento antibiótico.
ConclusionesLa vacunación neumocócica puede generar falsos positivos a la antigenuria por neumococo en la práctica clínica, con la consiguiente prescripción innecesaria de antibióticos en gran número de casos.