To assess the interactions between weather and the impact of each individual meteorological parameters in the incidence of acute myocardial infarctions (AMI) in Galicia.
MethodsRetrospective study analyzing the number of AMI diagnosed and transferred to the hospital by the Emergencies Sanitary System of Galicia between 2002 and 2009. We included patients with clinical and ECG findings of AMI. The correlation between 10-minute meteorological variables (temperature, humidity, pressure, accumulated rainfall and wind speed) recorded by MeteoGalicia and the incidence of AMI was assessed.
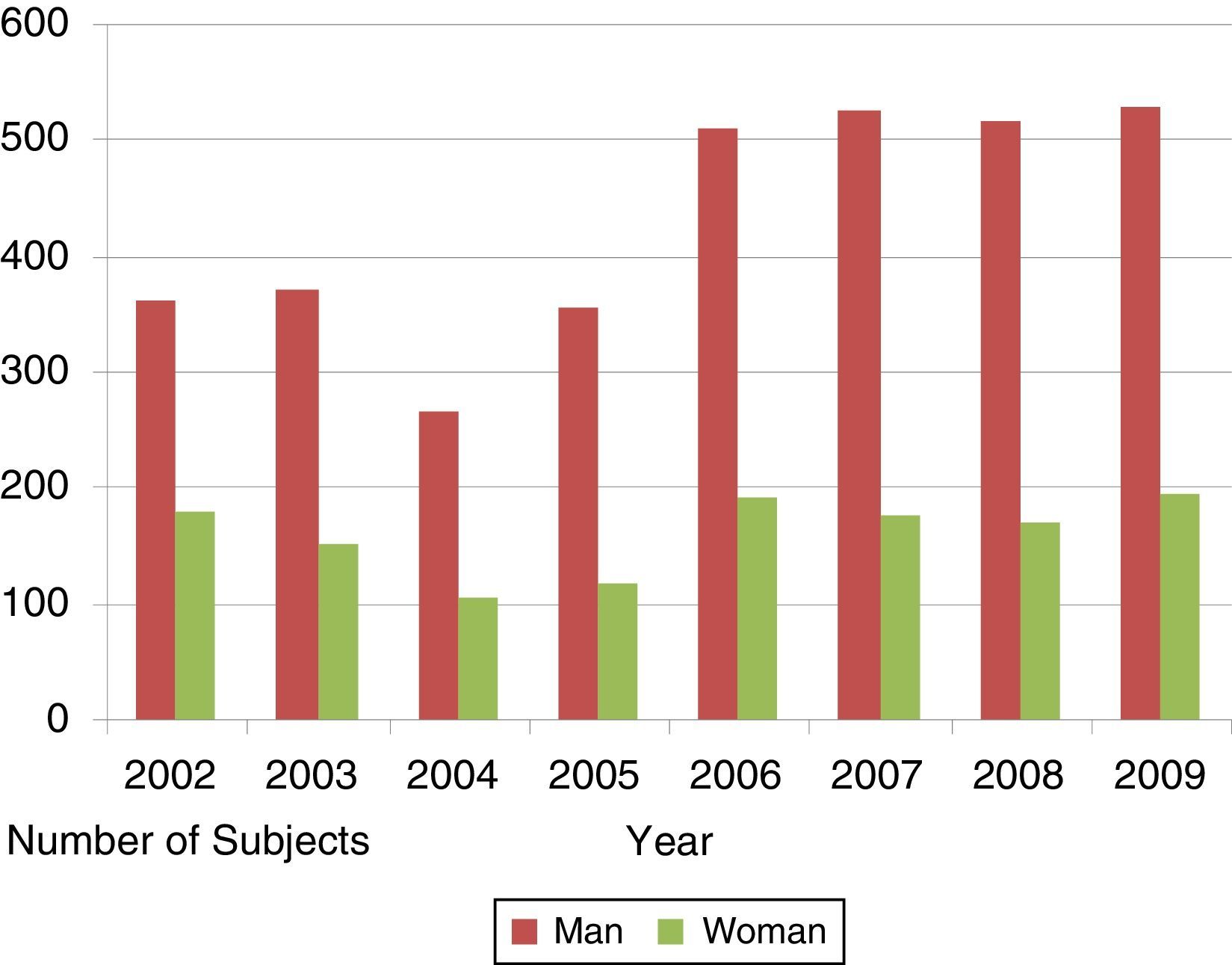
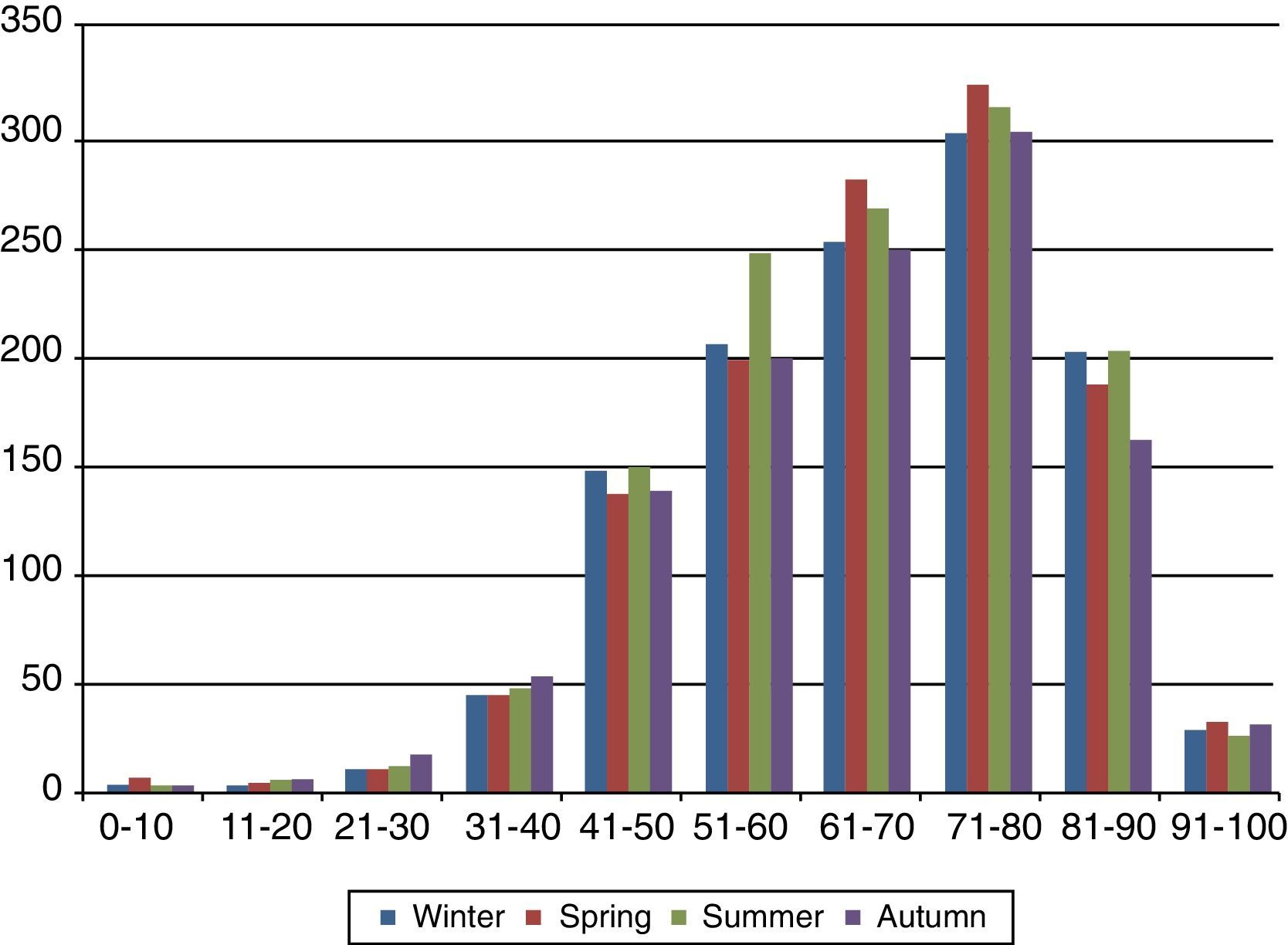
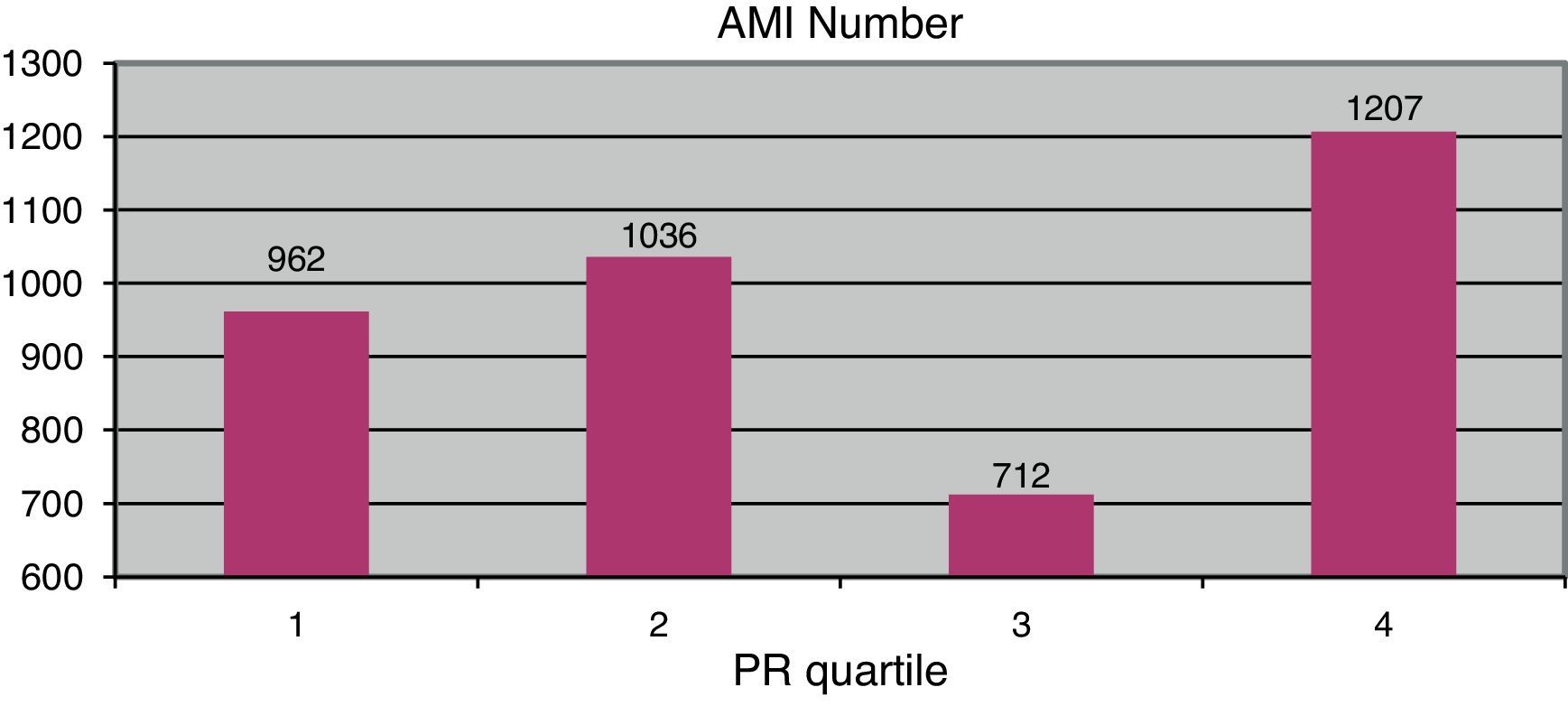
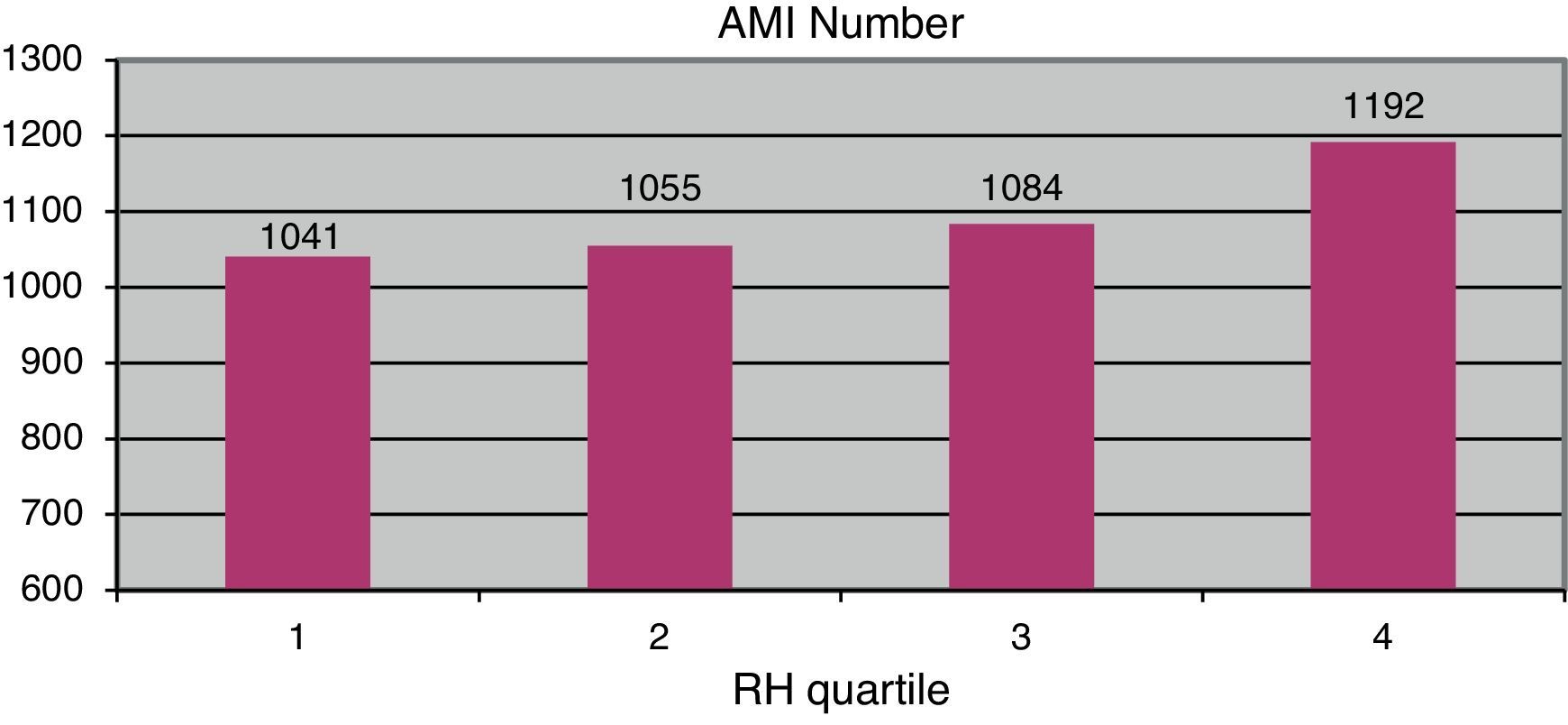
ResultsA total of 4717 AMI were registered (72.8% men, 27.2% women). No seasonal variations were found. No significant correlations were detected with regard to average daily temperature (P=.683) or wind speed (P=.895). Correlation between atmospheric pressure and incidence of AMI was significant (P<.005), as well as with the daily relative humidity average (P=.005).
ConclusionsOur study showed a statistical significant association with atmospheric pressure and with the daily relative humidity average. Since the local conditions of weather are widely variable, future studies should establish the relationship between weather patterns (including combinations of meteorological parameters), rather than seasonal variations, and the incidence of AMI.
Analizar la influencia del clima y el impacto de cada parámetro meteorológico sobre la incidencia del infarto agudo de miocardio (IAM) en Galicia.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo analizando el número de IAM diagnosticados y trasladados a hospitales por la Fundación Pública de Urgencias Sanitarias de Galicia-061 entre 2002 y 2009. Incluimos pacientes con criterios clínicos y electrocardiográficos de IAM, y analizamos su correlación con variables meteorológicas diezminutales (temperatura, humedad, presión, precipitaciones acumuladas y velocidad del viento) registradas por MeteoGalicia.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 4.717 infartos diagnosticados (72,8% varones y 27,2% mujeres), sin detectar variación estacional. La temperatura media diaria (p=0,683) y la velocidad media del viento (p=0,895) no mostraron relación significativa con la incidencia de IAM. La presión atmosférica presenta una asociación estadísticamente significativa con la incidencia de IAM (p<0,005), así como la humedad relativa, asociada a una mayor incidencia en el cuarto cuartil (p=0,005).
ConclusionesNuestro estudio muestra una asociación estadísticamente significativa entre la presión atmosférica y la humedad relativa media diaria con la incidencia de IAM en Galicia. Dado que las condiciones locales en las diferentes estaciones son muy variables, los futuros trabajos deberían dirigirse a establecer la relación entre patrones climáticos (definidos por combinaciones de parámetros meteorológicos individuales), en lugar de variaciones estacionales, y la incidencia de IAM.