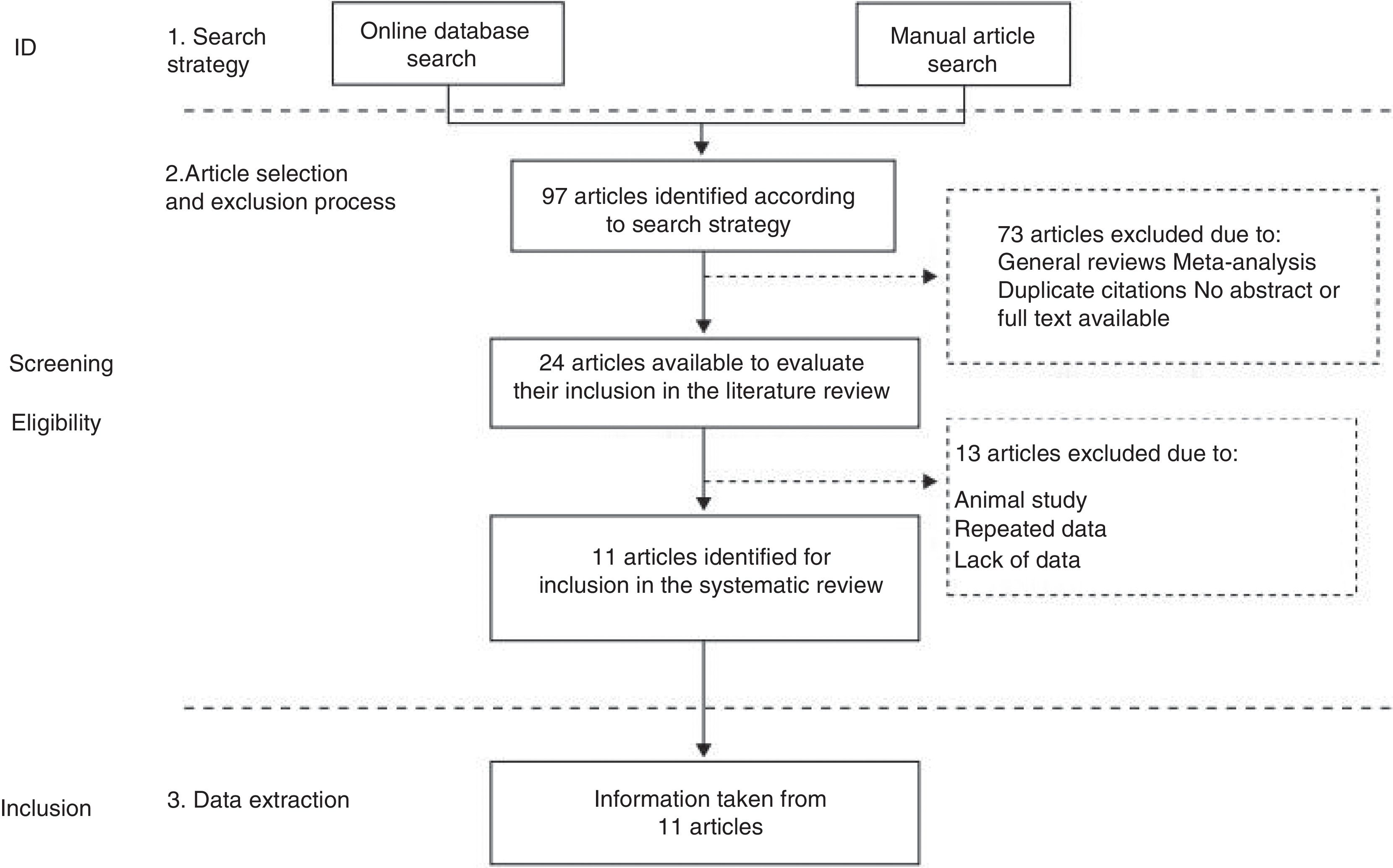
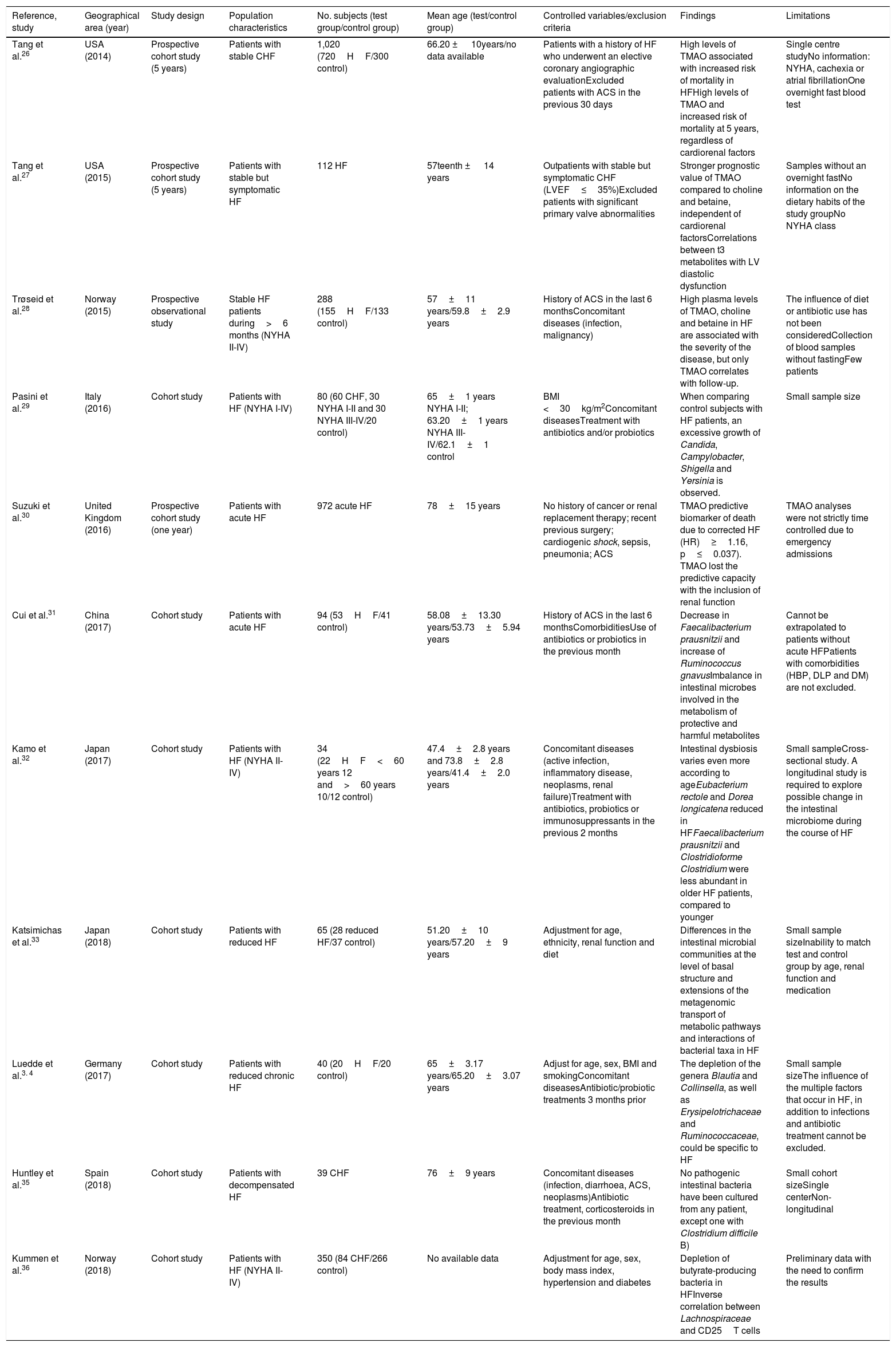
Heart failure (HF) is a chronic disease with significant morbidity and mortality. Substantial haemodynamic changes such as hypoperfusion and intestinal congestion can alter the composition of the intestinal microbiota in patients with HF. The aim of this systematic review is to evaluate the influence of bowel function in patients with HF and the possible role of the intestinal microbiota in the development and evolution of the latter. Eleven studies were included in the review. These studies seem to confirm that HF patients present with substantial abnormalities in the composition of their intestinal microbiota. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is identified as a key mediator between the alterations in the intestinal microbiota and HF and correlates with worse prognosis in HF patients. In conclusion, patients with HF present with frequent abnormalities in the characteristics of their intestinal microbiota, which may play a role in the prognosis of the disease.
La insuficiencia cardiaca (IC) es una enfermedad crónica con importante morbimortalidad asociada. Los pacientes con IC experimentan cambios hemodinámicos sustanciales, generadores de hipoperfusión y congestión esplácnica, que pueden alterar la composición de su microbiota intestinal. El objetivo de esta revisión sistemática es evaluar la influencia de la función intestinal en el paciente con IC, examinando el posible rol de la microbiota intestinal. Se incluyeron en la revisión 11 estudios. Los estudios evaluados ponen de manifiesto la existencia de alteraciones en la composición de la microbiota intestinal en pacientes con IC. El N-óxido de trimetilamina (TMAO) parece actuar como un mediador clave entre estas alteraciones en la microbiota intestinal y la IC; asimismo, su presencia en concentraciones anormales se correlaciona con un peor pronóstico en los pacientes con IC. En conclusión, los pacientes con IC sufren alteraciones en la microbiota intestinal que parecen incidir en el pronóstico de la enfermedad.