The COVID-19 pandemic has had a great effect on the management of chronic diseases, by limiting the access to primary care and to diagnostic procedures, causing a decline in the incidence of most diseases. Our aim was to analyze the impact of the pandemic on primary care new diagnoses of respiratory diseases.
MethodsObservational retrospective study performed to describe the effect of COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of respiratory diseases according to primary care codification. Incidence rate ratio between pre-pandemic and pandemic period was calculated.
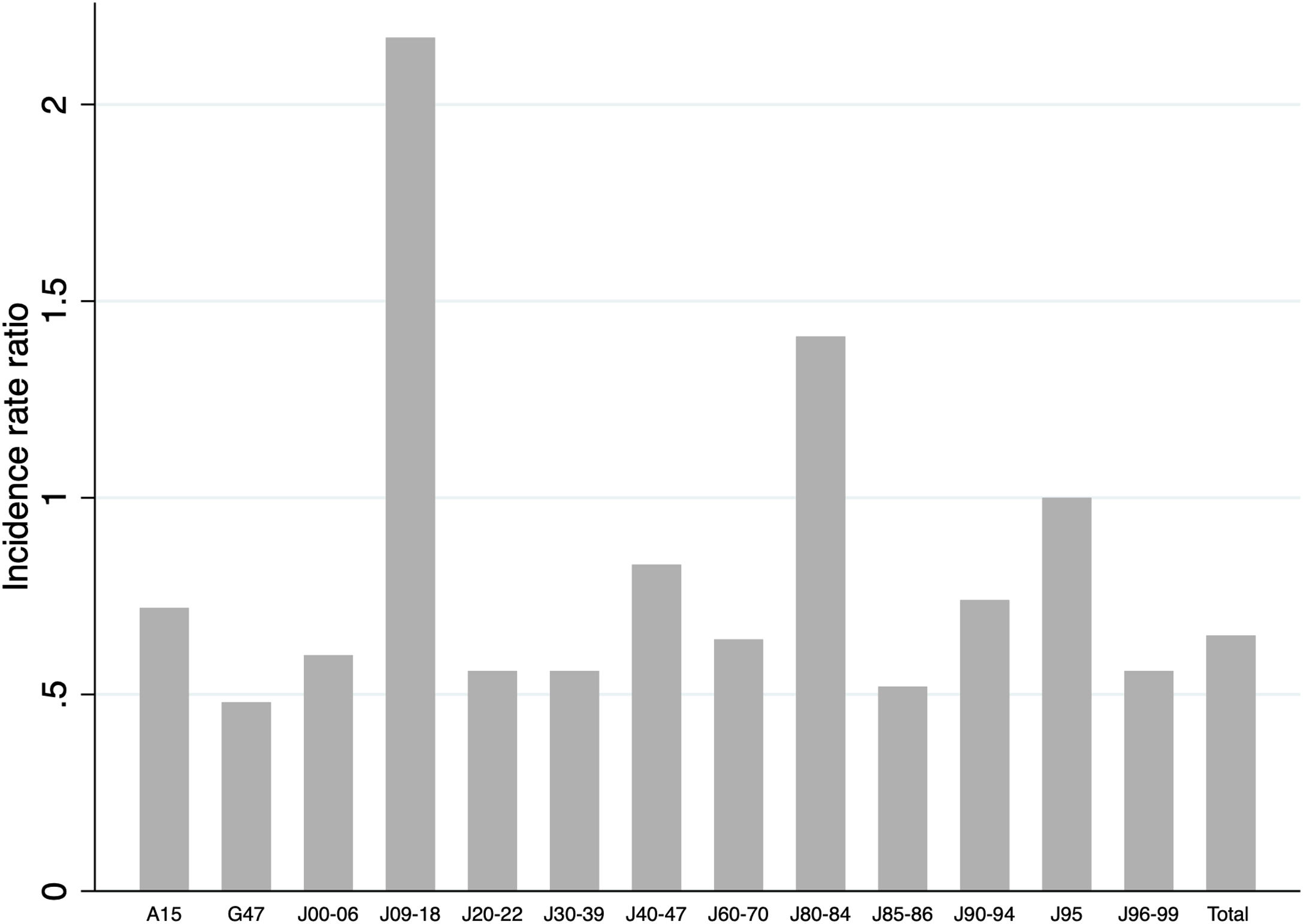
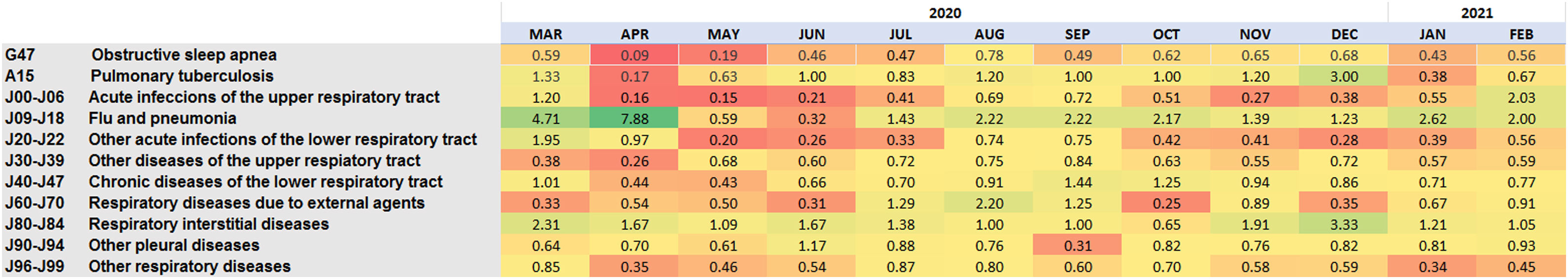
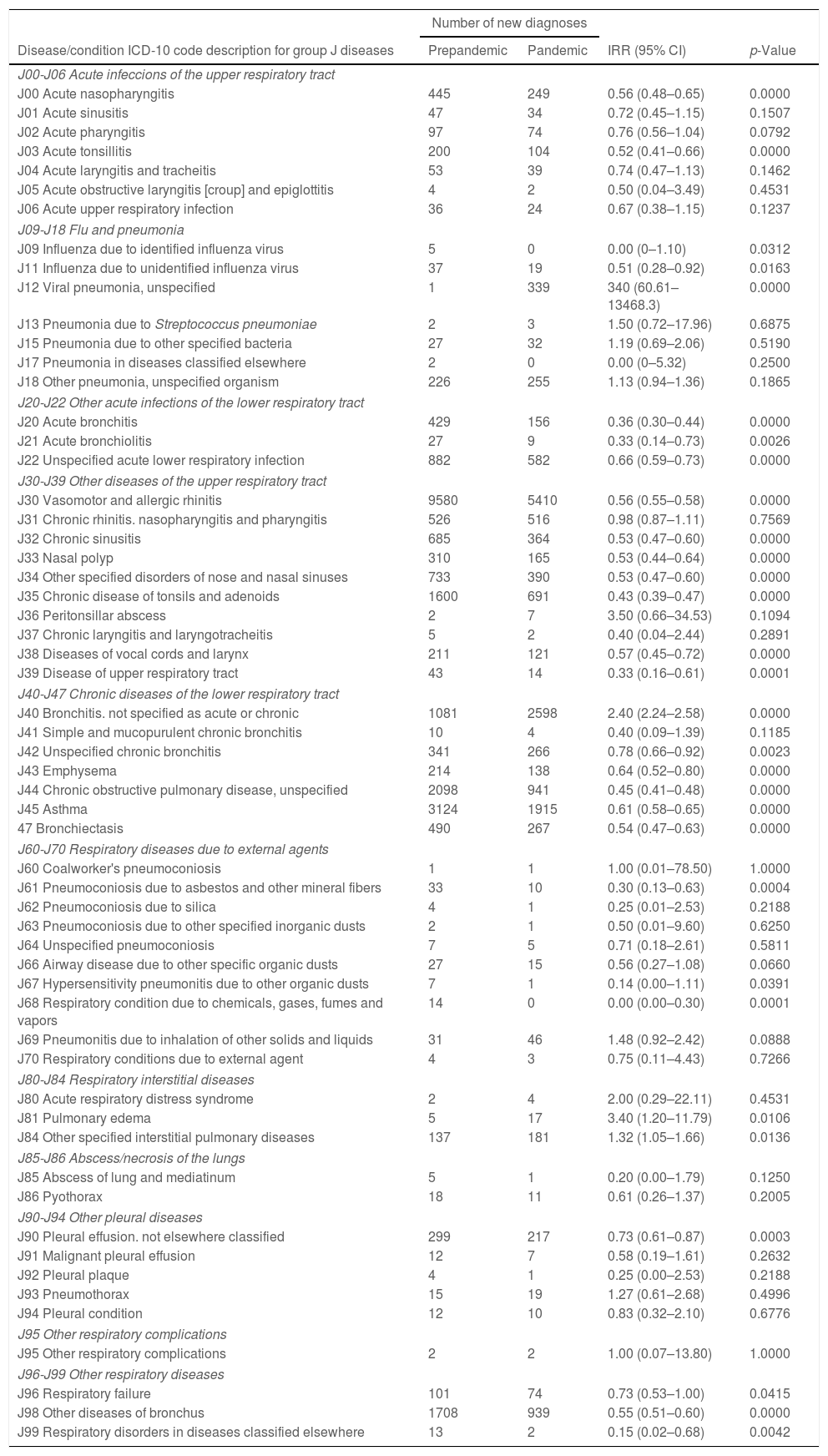
ResultsWe found a decrease in the incidence of respiratory conditions (IRR 0.65) during the pandemic period. When we compared the different groups of diseases according to ICD-10, we found a significant decrease in the number of new cases during the pandemic period, except in the case of pulmonary tuberculosis, abscesses or necrosis of the lungs and other respiratory complications (J95). Instead, we found increases in flu and pneumonia (IRR 2.17) and respiratory interstitial diseases (IRR 1.41).
ConclusionThere has been a decrease in new diagnosis of most respiratory diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic.
La pandemia de COVID-19 ha tenido efecto sobre el seguimiento de las enfermedades crónicas. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar el impacto de la pandemia por COVID-19 en los nuevos diagnósticos respiratorios en atención primaria.
MetodologíaEstudio observacional retrospectivo realizado para describir el impacto de la COVID-19 sobre la incidencia de diagnósticos respiratorios en atención primaria. Se ha calculado la tasa relativa de incidencia entre el periodo prepandémico y el pandémico.
ResultadosHallamos una reducción en la incidencia de patología respiratoria (IRR 0,65) durante la pandemia. Al comparar los distintos grupos de enfermedades (CIE-10), encontramos una reducción significativa en el número de nuevos casos durante la pandemia, excepto en el caso de tuberculosis pulmonar, abscesos o necrosis pulmonar y otras complicaciones respiratorias. Por otro lado, se detectaron incrementos en nuevos diagnósticos de gripe y neumonía (IRR 2,17) y enfermedades respiratorias intersticiales (IRR 1,41).
ConclusiónSe ha producido un descenso en el número de nuevos diagnósticos de la mayoría de las enfermedades respiratorias durante la pandemia por COVID-19.