This study sought to evaluate the incidence, prognosis and treatment of heart rhythm disorders (TdR) in Tako-tsubo syndrome (STT).
BackgroundSTT is associated with TdR. The TdR prognostic value is not well characterized in STT yet.
MethodsThe TdR of patients included in the National Registry of Tako-tsubo syndrome (XXX1), admitted between 2002 and 2018 and coming from 38 hospitals throughout the country, was analyzed. We analyzed any heart rhythm disorder in patients presented before admission, at admission and in long-term follow-up.
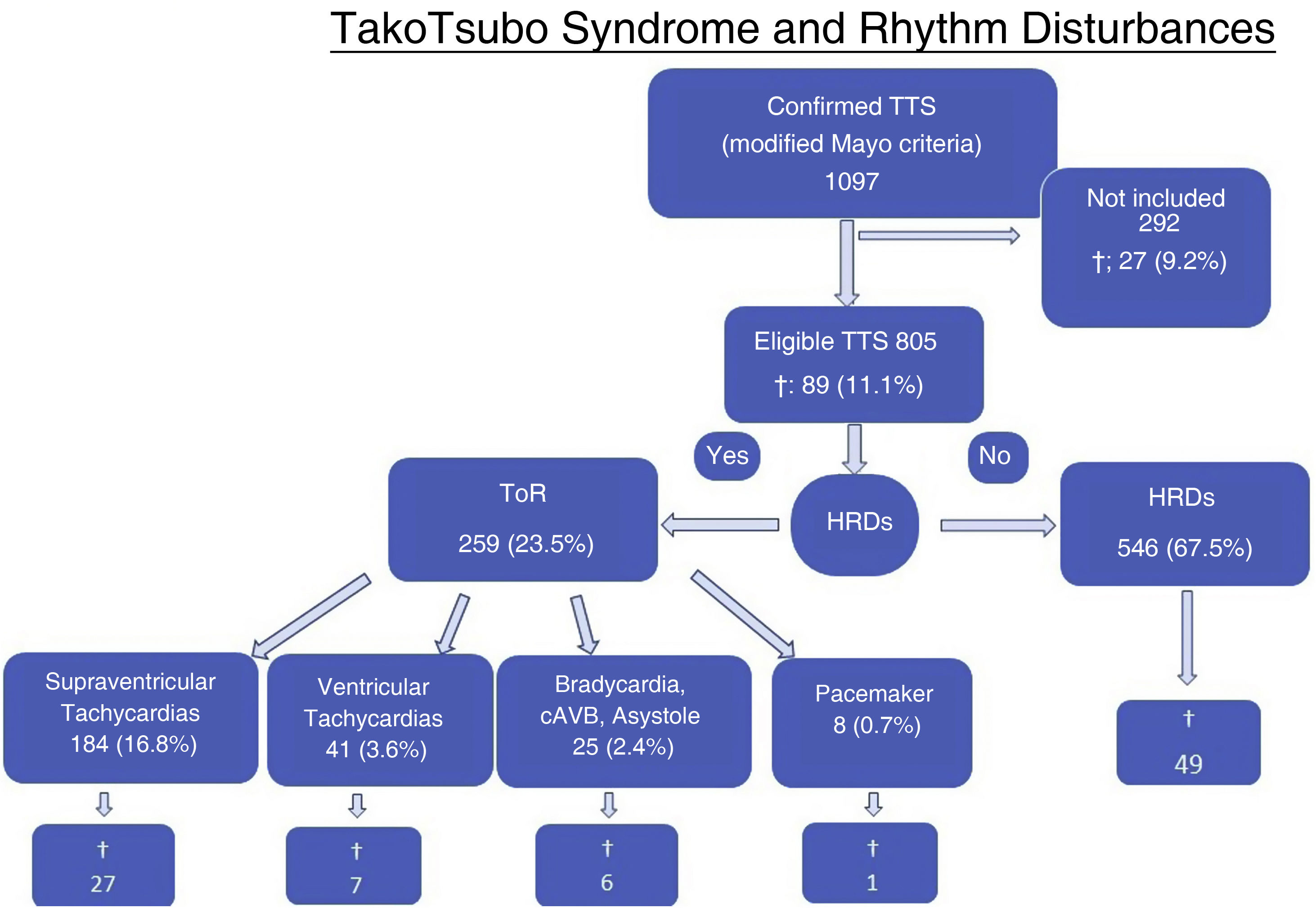
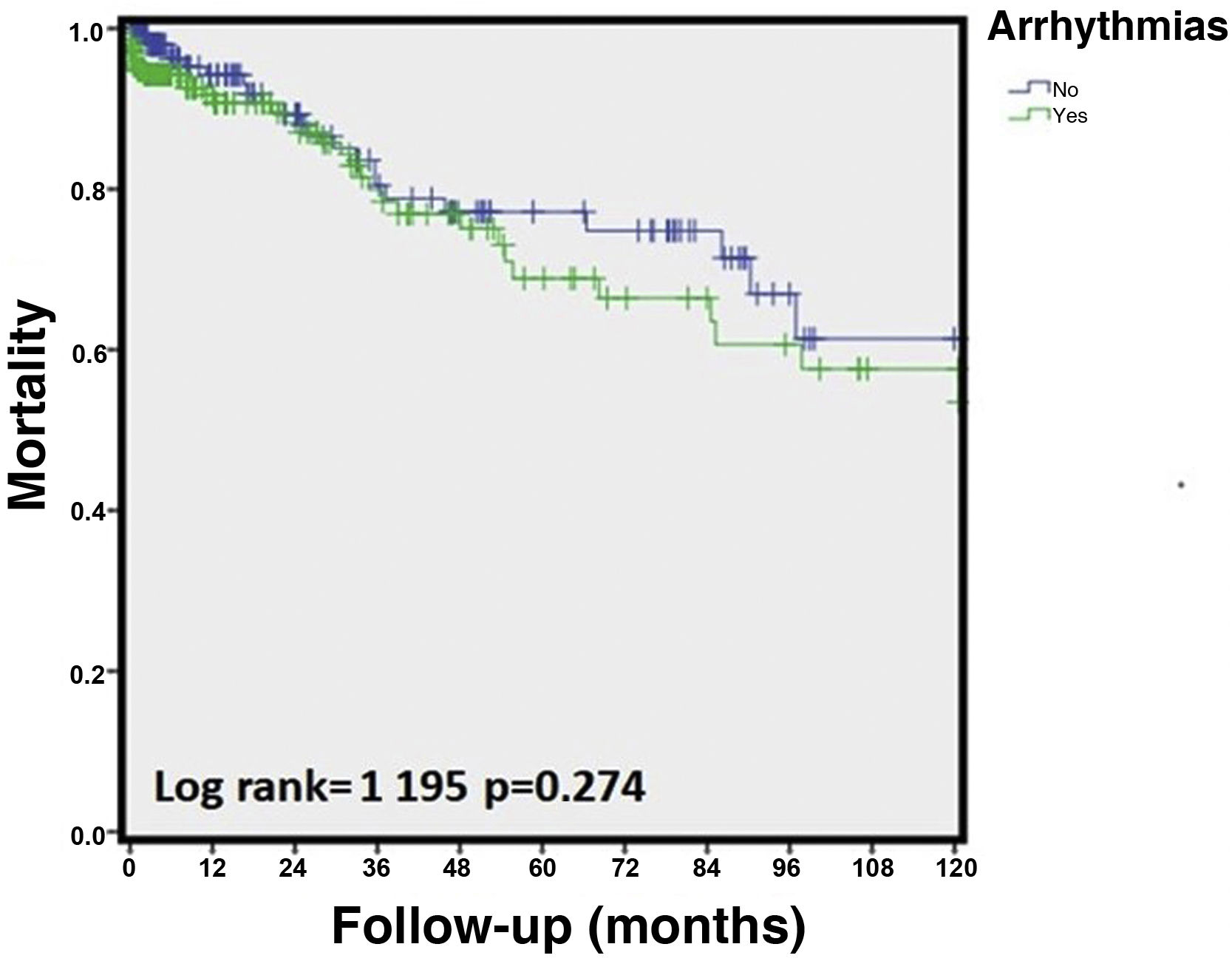
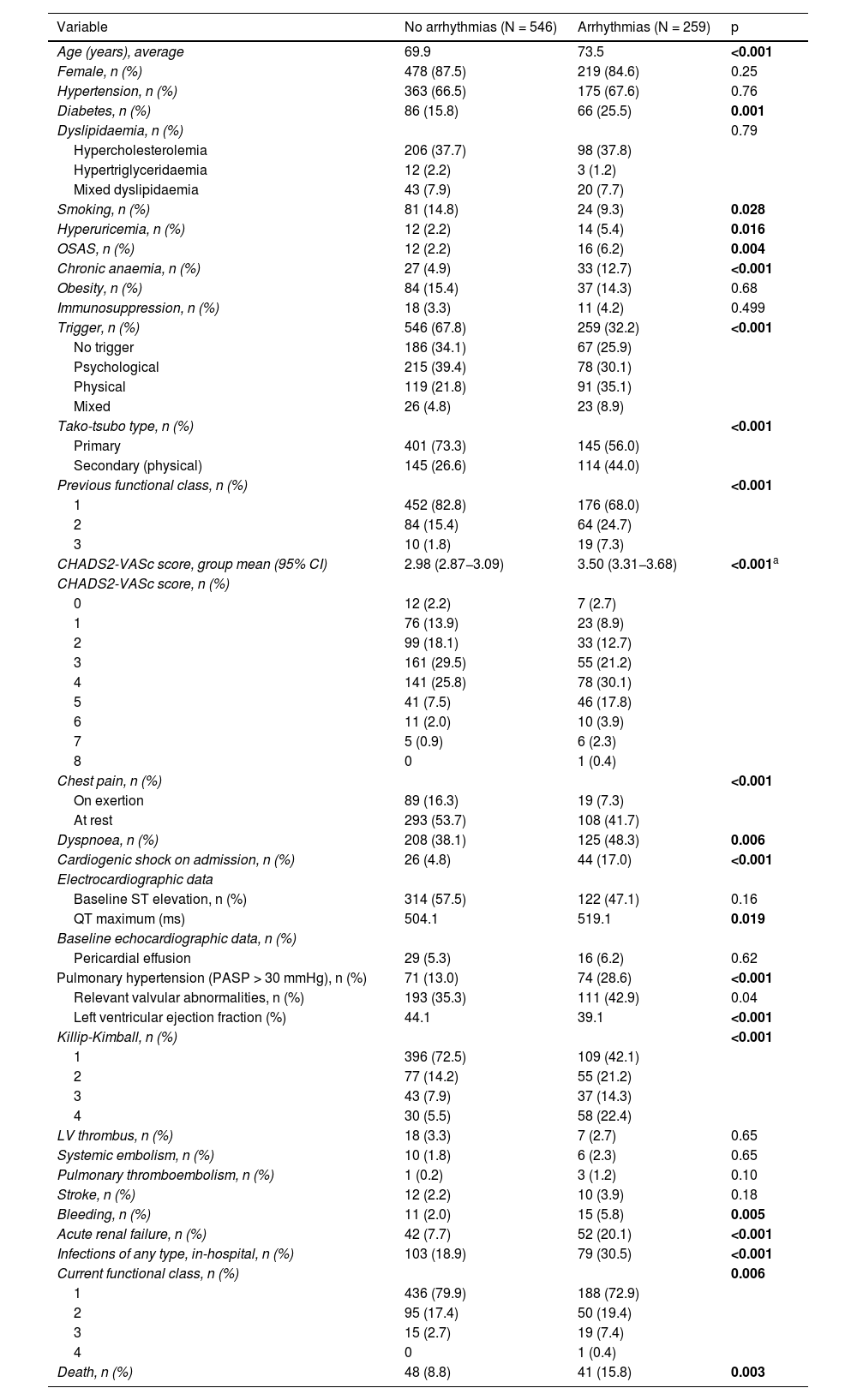
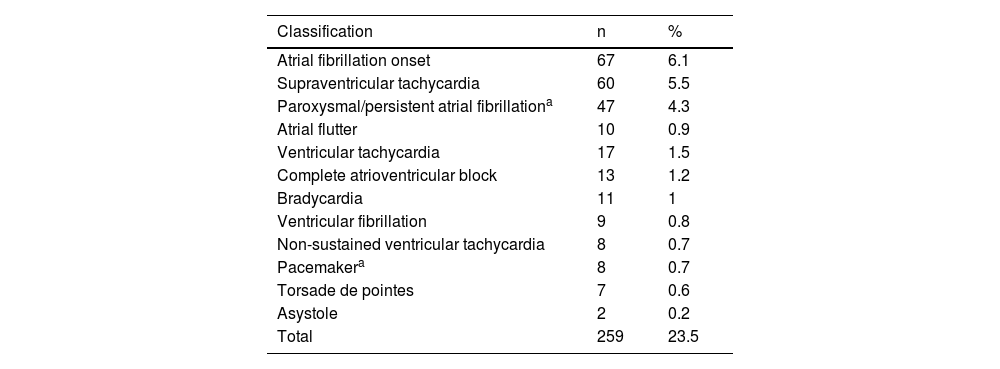
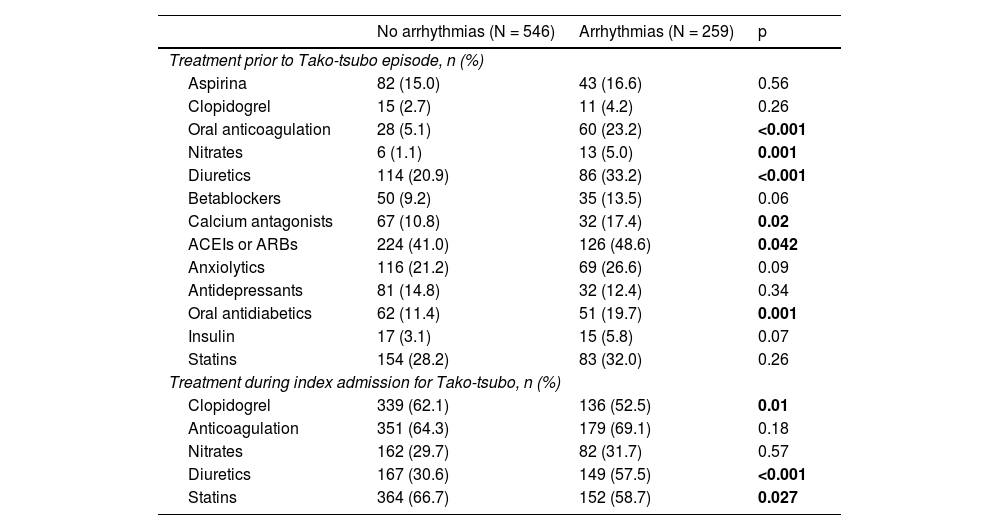
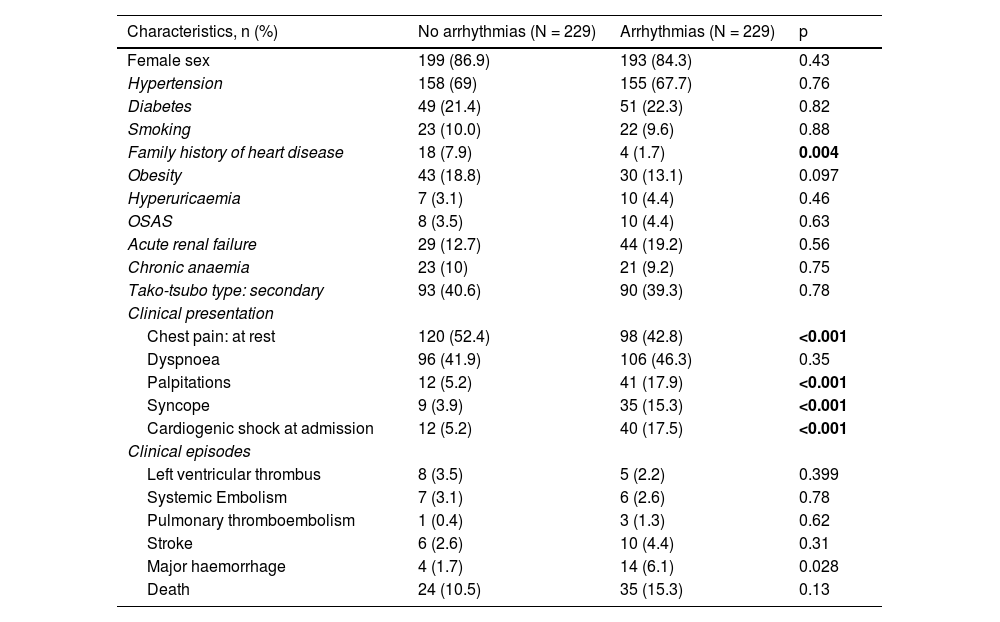
ResultsAll types of TdR were described in 259 (23.5%) cases, from a cohort of 1,097 consecutive patients with STT. TdR was more associated with Diabetes Mellitus, smoking, hyperuricemia, sleep apnea, anemia with a worse LVEF on admission. The most frequent TdR was a new onset of atrial fibrillation (FA). During hospitalization, patients with TdR showed more complications such as shock on admission, major bleeding, acute renal failure, and combined infections. At follow-up, they presented higher mortality and more MACE, but with a non-significant correlation.
ConclusionsThe incidence of TdR in patients with STT is not infrequent. STT, when associated with TdR, presents more complications and a worse prognosis both in hospital and in the long term.
El presente estudio pretende evaluar la incidencia, pronóstico y tratamiento de los trastornos del ritmo (TdR) en el síndrome de Tako-tsubo (STT).
AntecedentesEl STT se asocia frecuentemente a TdR. El valor pronóstico de estos TdR aún no está bien caracterizado en el STT.
Material y métodosSe analizaron los TdR de los pacientes incluidos en el REgistro nacional de síndrome de Tako-tsubo (XXX1), ingresados entre 2002 y 2018, aportados por 38 hospitales de todo el país. Analizamos en los pacientes TdR previos, en el ingreso y en el seguimiento a largo plazo.
ResultadosSe describió cualquier tipo de TdR en 259 (23,5%) casos, de una cohorte de 1.097 pacientes consecutivos con STT. Los TdR se presentan más en pacientes con diabetes mellitus, tabaquismo, hiperuricemia, apnea del sueño y anemia, además de con una FEVI menor al ingreso. El TdR más frecuente fue el debut de fibrilación auricular (FA). Durante el ingreso hospitalario, los pacientes con TdR mostraron más complicaciones, como shock al ingreso, sangrado mayor, insuficiencia renal aguda y el combinado de infecciones. En el seguimiento, presentaron mayor mortalidad y numéricamente más eventos adversos combinados.
ConclusionesLos trastornos del ritmo no son infrecuentes en fase aguda del síndrome de Tako-tsubo. El STT asociado a TdR se presenta con más complicaciones y peor pronóstico tanto hospitalario como a largo plazo.