Factor XI (FXI) deficiency is a mild bleeding disorder, common among Ashkenazis, that may be underestimated in Caucasians. Management of FXI deficiency in women is a challenge, due to its unpredictable bleeding tendency and the little evidence available on this issue.
ObjectiveTo describe gynaecological/obstetrical bleeding complications and to analyze the effectiveness and safety of the antihaemorrhagic treatment among women with FXI deficiency.
Material and methodsA retrospective, observational study of 214 Caucasian subjects with FXI deficiency collected during 20 years (1994–2014) without clinical selection.
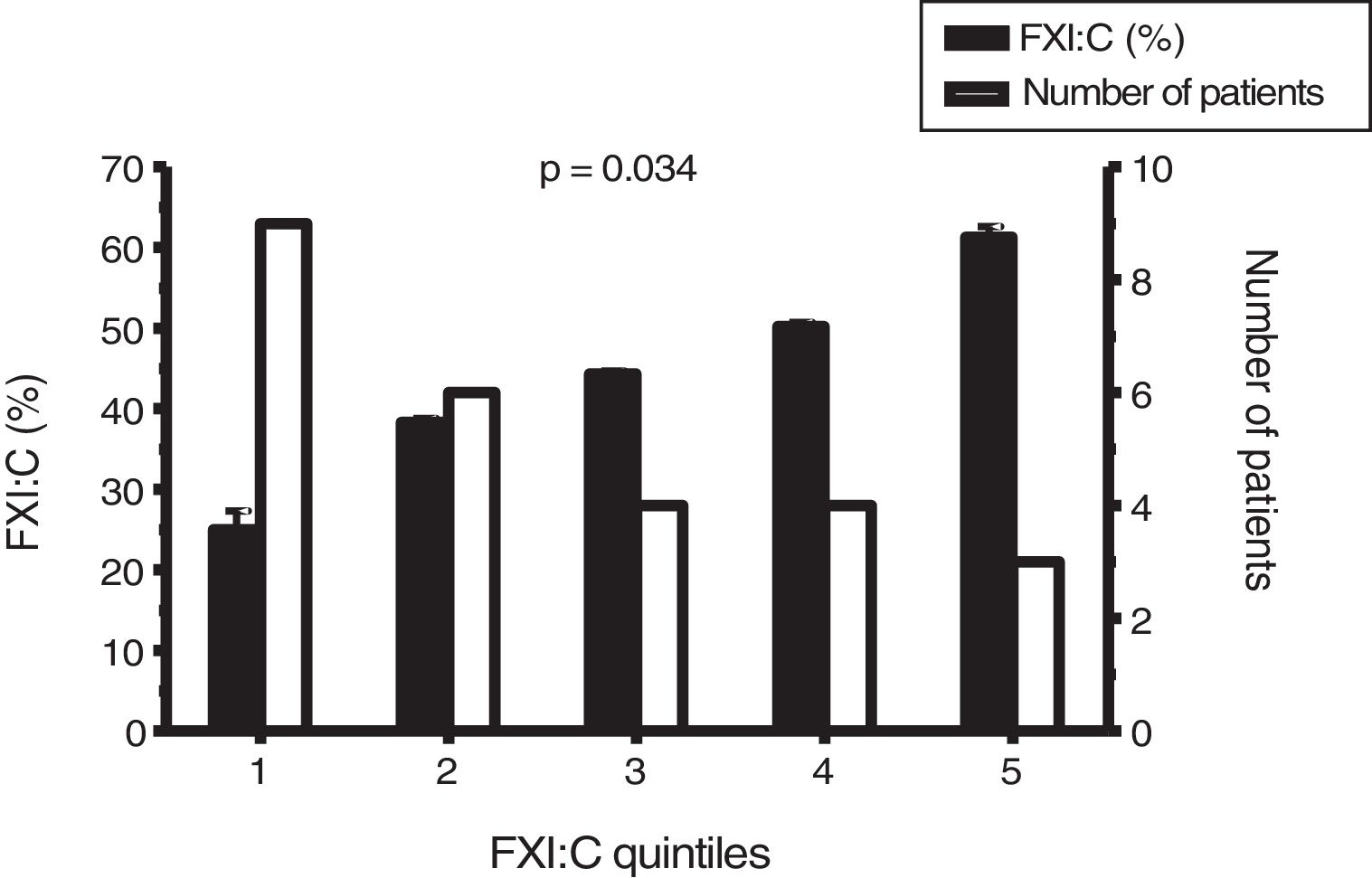
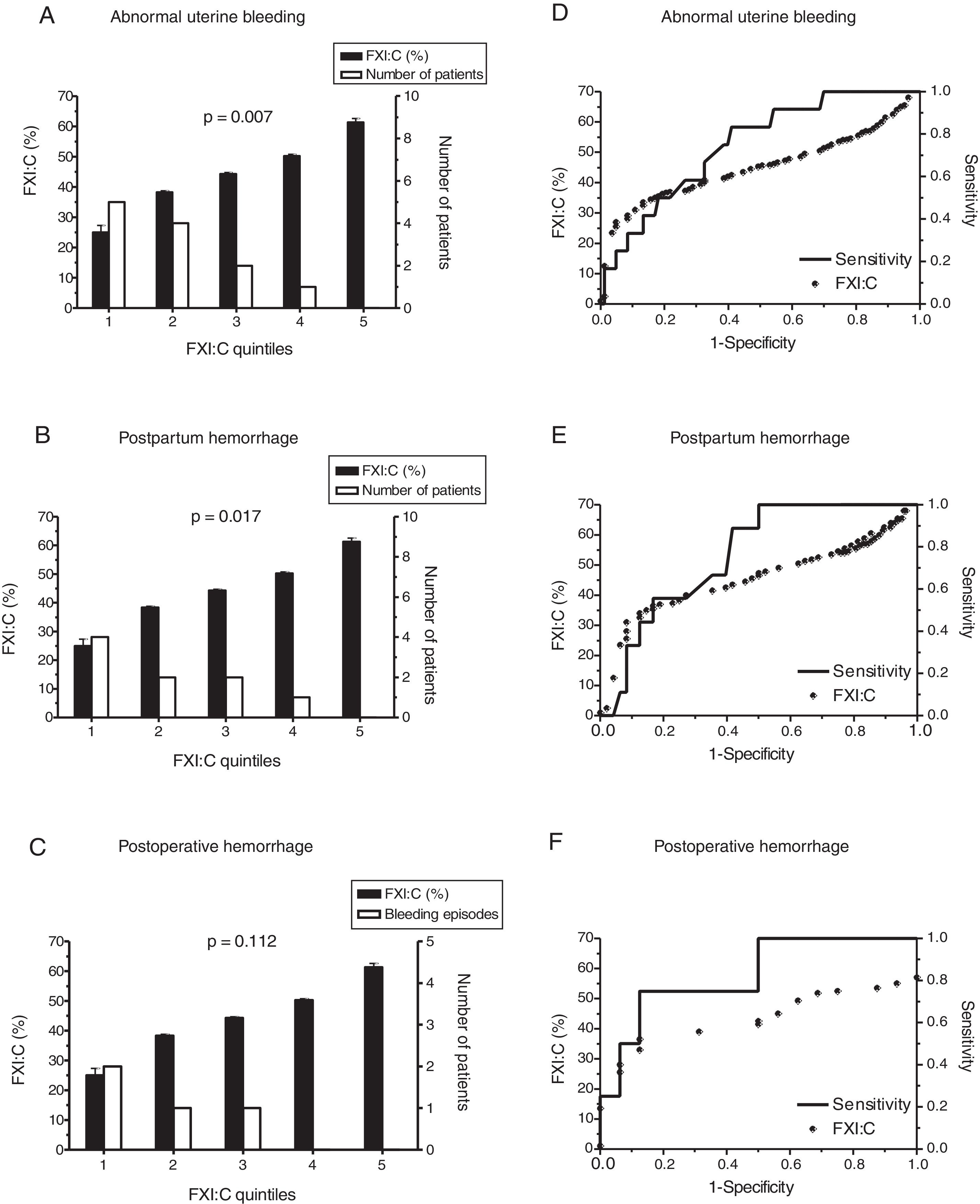
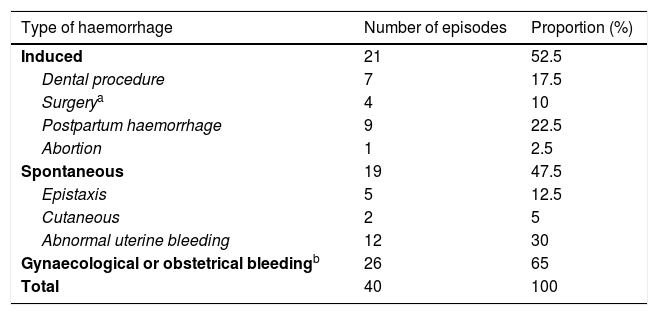
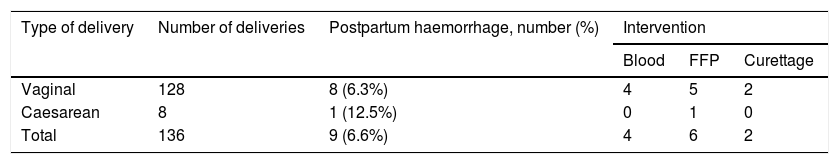
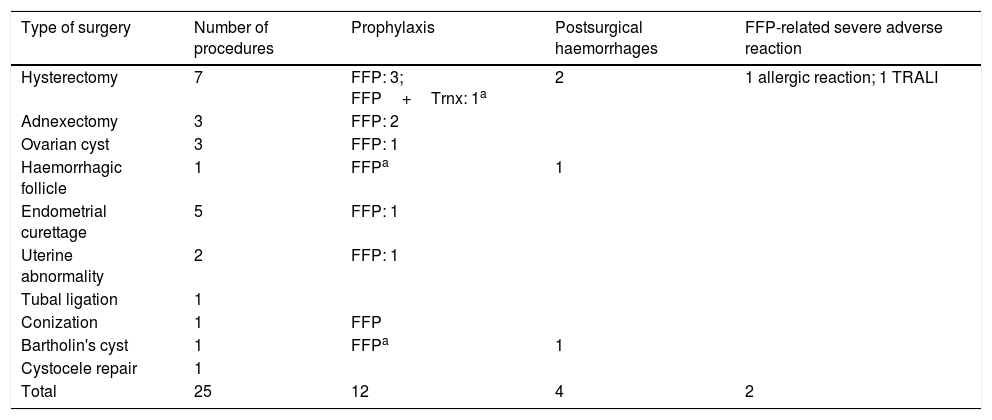
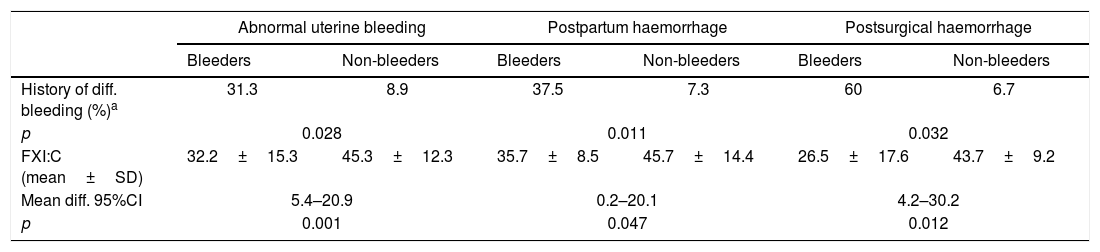
ResultsWe identified 95 women with FXI deficiency. Any haemorrhagic event was communicated by 26/95 (27.4%), being abnormal uterine bleeding the most frequently found (12/95, 12.6%). Nine postpartum haemorrhages were recorded from 136 deliveries (6.6%) in 57 women. Four postsurgical bleeding complications were registered among 25 gynaecological surgeries (16%) in 20 women. Abnormal uterine bleeding, postpartum and postsurgical haemorrhages were related to both a positive bleeding history and FXI:C values ≤43.5%. Prophylaxis with fresh frozen plasma, used in 12/25 (48%) gynaecological surgeries, did not prevent from postoperative bleeding in three cases, but two developed severe adverse reactions.
ConclusionWomen with FXI deficiency, especially those with a positive history of bleeding or FXI:C ≤43.5%, are at risk of developing gynaecological/obstetrical haemorrhages, most of them mild/moderate. Systematic prophylaxis has questionable effectiveness, but might cause severe side effects.
La deficiencia del factor XI (FXI) es un trastorno hemorrágico leve, común entre los asquenazíes, que puede subestimarse en los caucásicos. El manejo de la deficiencia de FXI en las mujeres es un desafío, debido a la dificultad para predecir la tendencia hemorrágica y la poca evidencia disponible sobre este tema.
ObjetivoDescribir las complicaciones hemorrágicas ginecológicas/obstétricas y analizar la efectividad y la seguridad del tratamiento antihemorrágico en mujeres con deficiencia de FXI.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de 214 sujetos caucásicos con deficiencia de FXI recogidos durante 20 años (1994-2014) sin selección clínica.
ResultadosSe identificaron 95 mujeres con deficiencia de FXI. Cualquier evento hemorrágico fue comunicado por 26/95 (27.4%), siendo la hemorragia uterina anormal el más frecuente (12/95, 12.6%). Se registraron nueve hemorragias posparto de 136 partos (6,6%) en 57 mujeres. Se registraron cuatro complicaciones hemorrágicas posquirúrgicas en 25 cirugías ginecológicas (16%) en 20 mujeres. La hemorragia uterina anormal y las hemorragias postparto y posquirúrgicas se relacionaron con una historia positiva para hemorragia y valores de FXI:C ≤ 43.5%. La profilaxis con plasma fresco congelado, utilizado en 12/25 (48%) cirugías ginecológicas, no evitó la hemorragia postoperatoria en tres casos, pero dos desarrollaron reacciones adversas graves.
ConclusiónLas mujeres con deficiencia de FXI, especialmente aquellas con una historia positiva para hemorragia o FXI:C ≤ 43.5%, están en riesgo de desarrollar hemorragias ginecológicas/obstétricas, la mayoría de ellas leves/moderadas. La profilaxis sistemática tiene una efectividad cuestionable, pero puede causar efectos secundarios graves.