Arterial oxygen saturation (AOS) predicts altitude sickness. Objectives: To estimate the AOS values with relation to altitude. Furthermore, make a graph to use during activity which assesses the AOS for each altitude and the normal range.
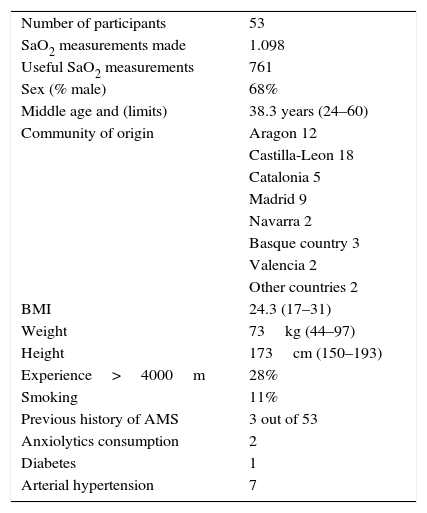
Patients and methodValues of AOS were assessed during eight high mountain activities in the Alps, Himalaya, Caucasus and Andes; 53 mountaineers participated, 17 of them in more than one activity; 761 measurements of AOS were registered.
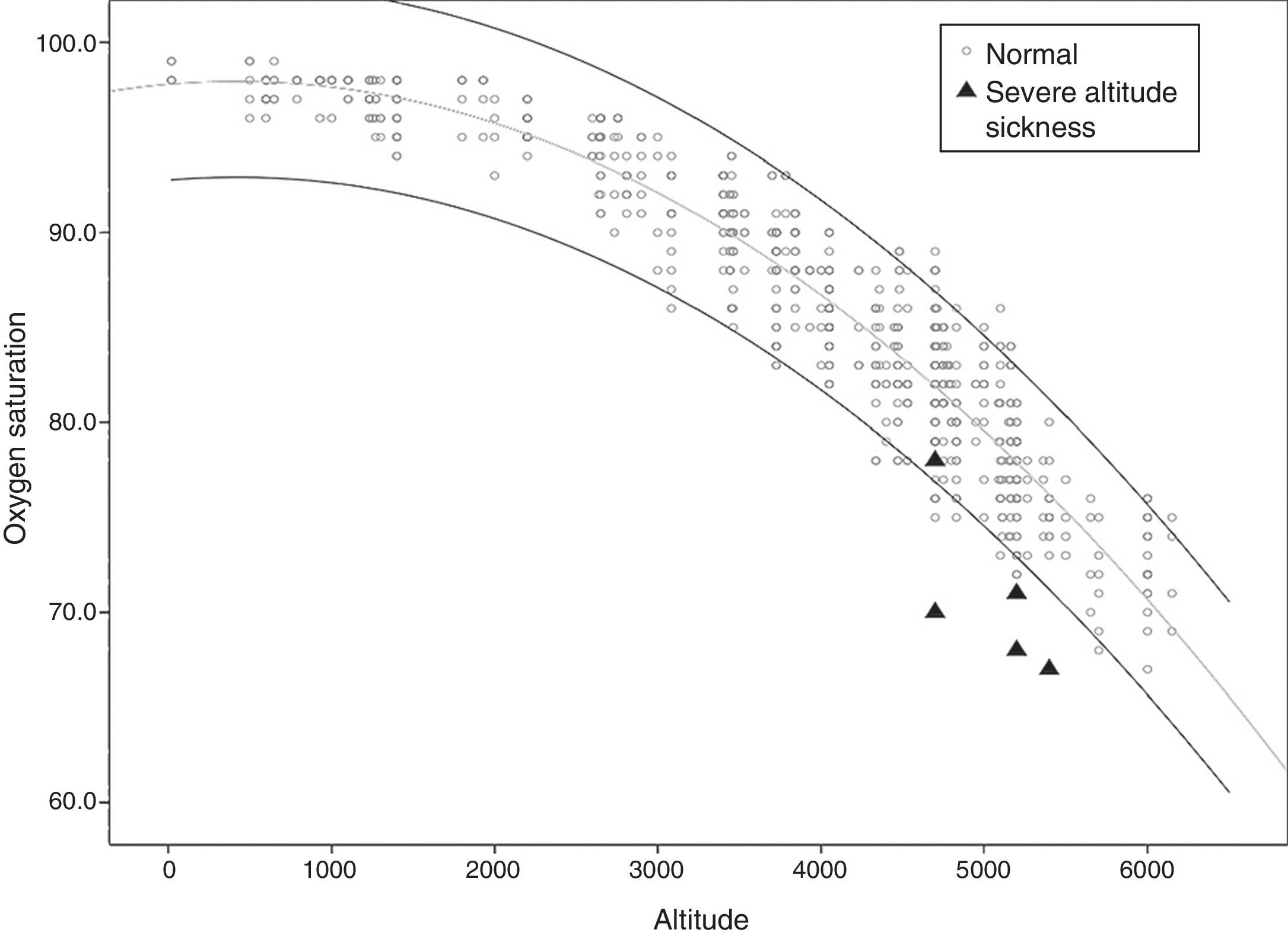
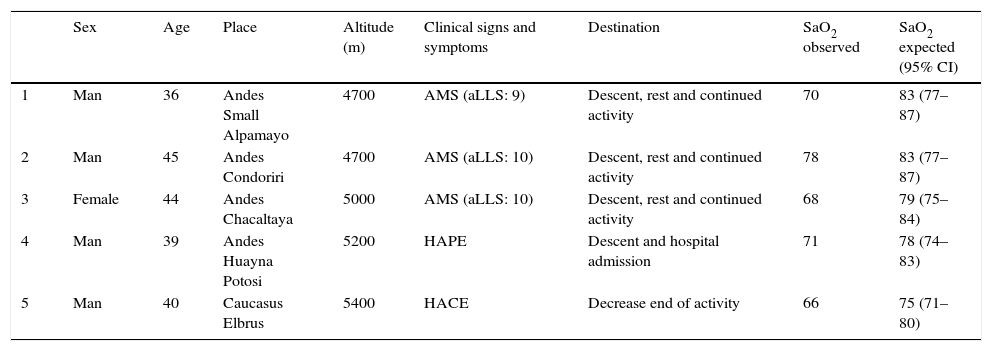
ResultsA Logistic Regression Model was made to estimate the AOS values dependent on altitude, adjusted to possible related factors. A strong lineal relationship exists between altitude and AOS (R2=0.83, p<0.001); 0.7 points more in women. The AOS in a particular altitude is not related to age, weight, height, smoking, heart rate, or even with previous experiences in mountains.
The calculation of the AOS responds to the follow equation: Blood Oxygen Saturation=103.3−(altitude×0.0047)+(Z), being Z=0.7 in men and 1.4 in women.
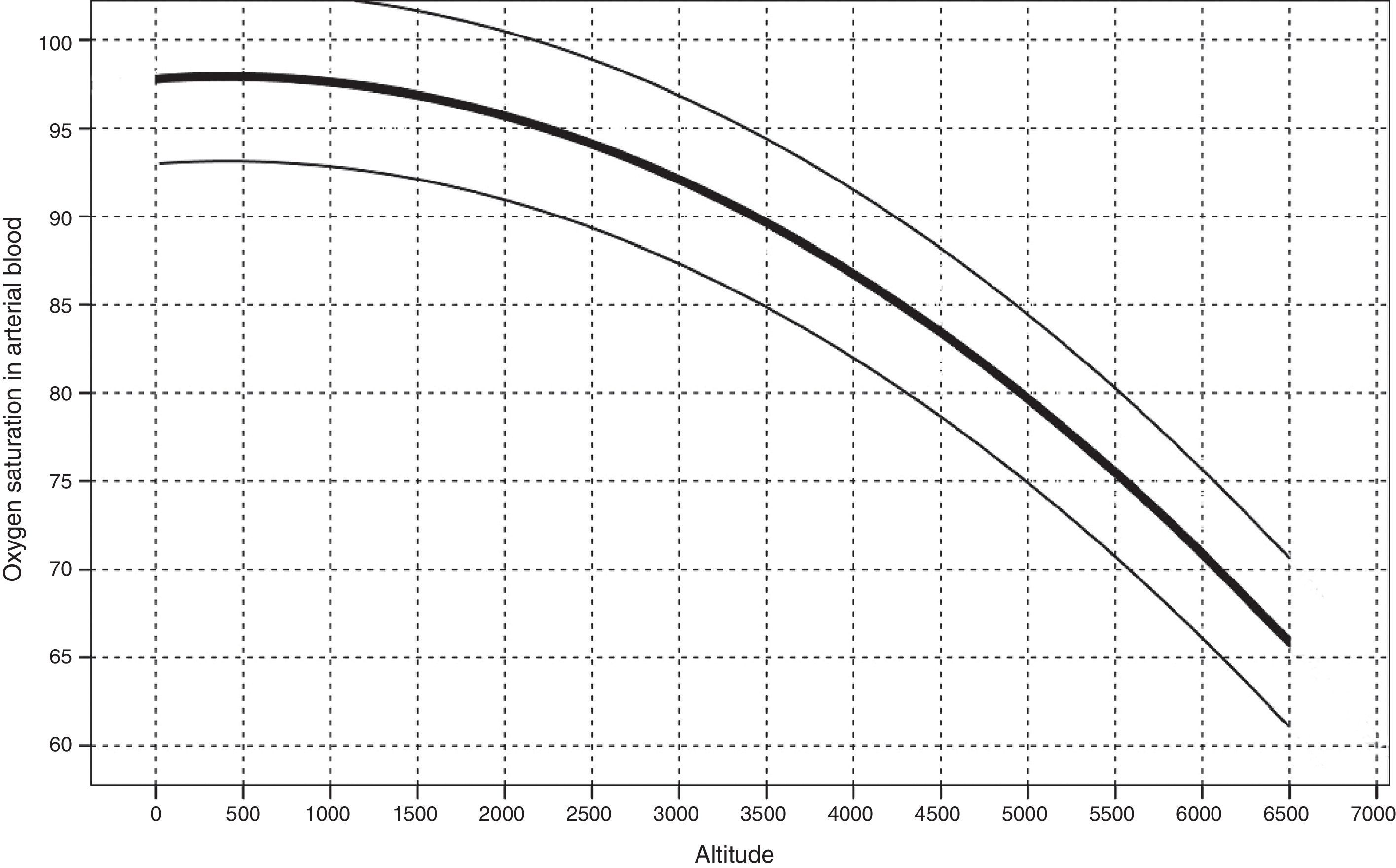
A scatter plot was made to relate the estimated altitude with the AOS, with their normal limits values: percentiles 2.5 and 97.5.
ConclusionsThe simple calculation of the AOS estimated for a particular altitude with the proposed graphic can help in the early decision-making onsite.
La saturación arterial de oxígeno (SAO) es capaz de predecir el desarrollo de mal de altura. Objetivos: estimar los valores de SAO en función de la altitud y, adicionalmente, diseñar un gráfico para usar sobre el terreno que muestre la saturación esperada para cada altitud y sus límites de normalidad.
Pacientes y métodoSe registraron valores de SAO a los participantes de 8 actividades de alta montaña en los Alpes, el Himalaya, el Cáucaso y los Andes. Participaron 53 montañeros; 17 de ellos repitieron en más de una actividad. Se registraron 761 mediciones de SAO.
ResultadosSe diseñó un modelo de regresión lineal múltiple para estimar los valores de SAO en función de la altitud, ajustados por distintos posibles factores relacionados. Existe una fuerte relación lineal entre altitud y SAO (R2=0,83, p<0,001), dando valores 0,7 puntos mayores en mujeres. La SAO a una determinada altitud no se relaciona con la edad, el peso, la talla, el tabaquismo, la frecuencia cardíaca ni con la experiencia previa en montaña.
El cálculo de la estimación de la SAO responde a la siguiente ecuación: SAO=103,3−(altitud×0,0047)+(Z), siendo Z=0,7 en hombres y 1,4 en mujeres.
Se ha diseñado una gráfica de coordenadas que relaciona la altitud con los valores estimados de SAO con sus límites de normalidad: percentiles 2,5 y 97,5.
ConclusionesLa sencillez en el cálculo de la SAO estimada para una determinada altitud mediante la gráfica propuesta ayudará en la toma de decisiones precoces sobre el terreno.