Environmental pollution are one of the most relevant risk factors to atherosclerosis. To know awareness about the importance of urban air pollution as a trigger for hospital admission due to acute coronary syndrome (ACS), this study analyzed levels of different gaseous air pollutants in the air and its correlation with number of ACS.
MethodsEpidemiological data of patients admitted for ACS in five towns during the years 2006–2008 were recovered. Clinical data regarding admissions for ACS were obtained from the hospital admission services. Measures of seven air contaminants were recovered from the environmental stations. Mixed model including sex, age, location, and the average levels of air pollutants contaminants as fixed effects and its interaction were performed.
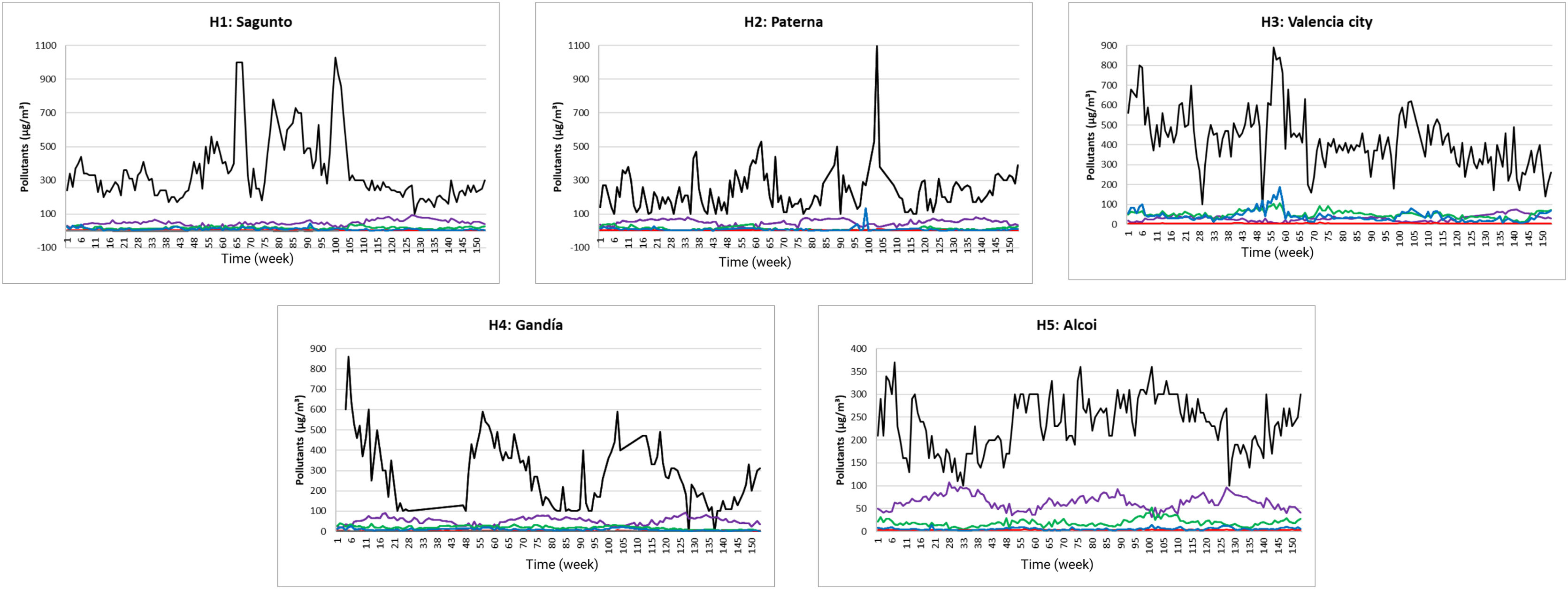
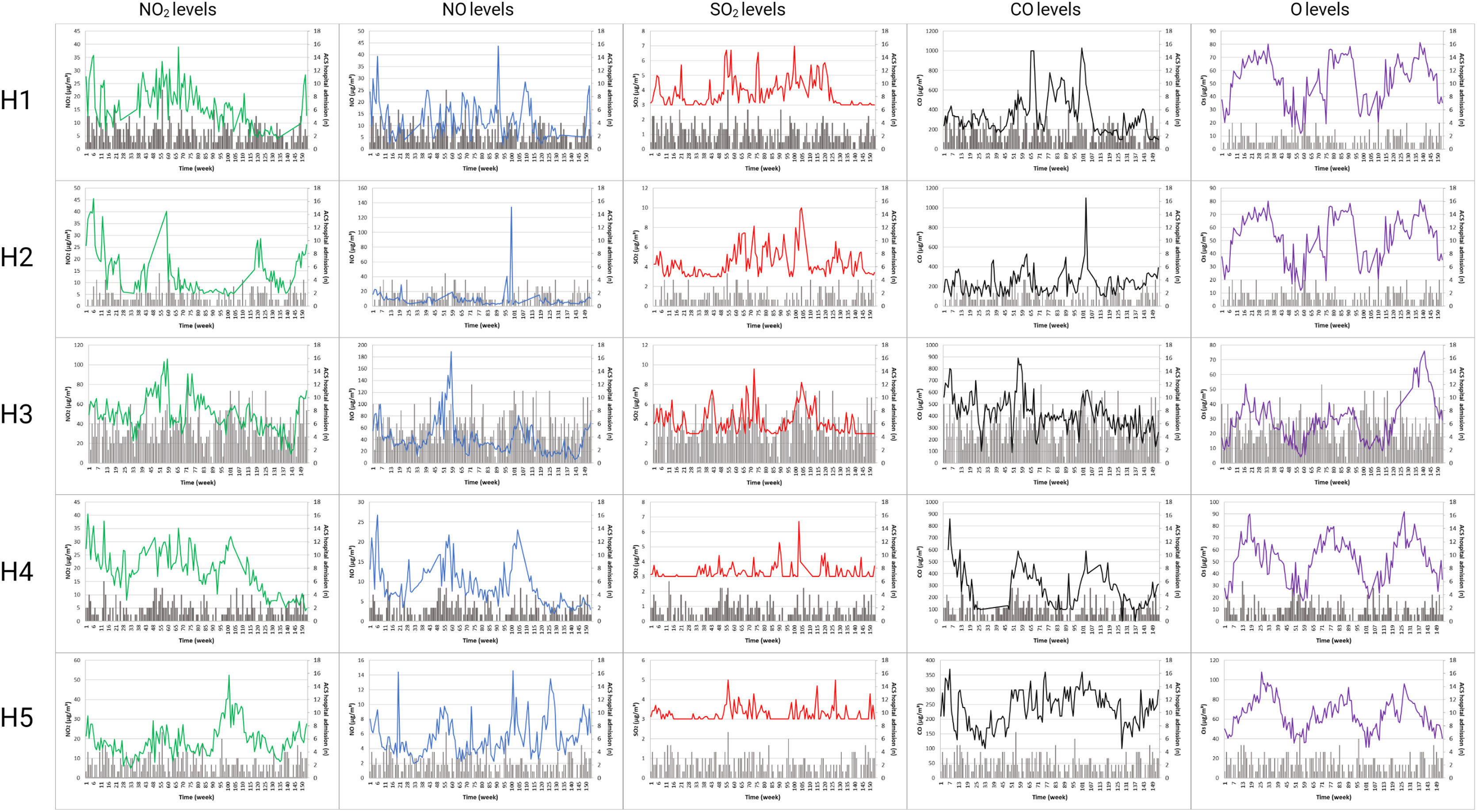
ResultsThe incidence rate of ACS is higher in man than woman, and higher in older people than young. The maximum ACS were in the last trimester of the year, was the most elevated levels of gaseous pollutants have been found. Levels of NO2, NO, and CO are positively correlated between them, and negatively correlated with O3 levels. All air pollutants analyzed increase the number of ACS hospital admission in the five locations evaluated.
ConclusionsLevels of gaseous pollutants are related between them, being the levels of NO2, NO, and CO, positively correlated, and negatively correlated with levels of O3. Number of ACS hospital admission increases with levels of five air gaseous pollutants studied.
La contaminación ambiental es uno de los factores de riesgo más relevantes para la aterosclerosis. Para conocer la importancia de la contaminación del aire urbano como desencadenante del ingreso hospitalario por síndrome coronario agudo (SCA), este estudio analizó los niveles de diferentes contaminantes atmosféricos gaseosos en el aire y su correlación con el número de SCA.
MétodosSe recuperaron datos epidemiológicos de pacientes ingresados por SCA en 5 municipios durante los años 2006 a 2008. Los datos clínicos relativos a los ingresos por SCA se obtuvieron de los servicios de ingreso hospitalario. Se recuperaron medidas de 7 contaminantes del aire de las estaciones ambientales. Se realizó un modelo mixto que incluye sexo, edad, ubicación y los niveles promedio de contaminantes atmosféricos como efectos fijos y su interacción.
ResultadosLa tasa de incidencia de SCA es mayor en hombres que en mujeres, y mayor en personas mayores que en jóvenes. La mayoría de los SCA se dieron en el último trimestre del año, cuando se encontraron niveles más elevados de gases contaminantes. Los niveles de NO2, NO y CO se correlacionan positivamente entre ellos y negativamente con los niveles de O3. Todos los contaminantes atmosféricos analizados aumentan el número de ingresos hospitalarios por SCA en las 5 localidades evaluadas.
ConclusionesLos niveles de contaminantes gaseosos se relacionan entre sí, estando los niveles de NO2, NO y CO correlacionados positivamente entre sí y negativamente con los niveles de O3. El número de ingresos hospitalarios por SCA aumenta con los niveles de 5 contaminantes gaseosos del aire estudiados.