Sudden cardiac death is an important cause of mortality in developed countries, most of them being consequence of acute ventricular arrhythmias. These arrhythmias, in some cases, owe to QT interval prolongation.
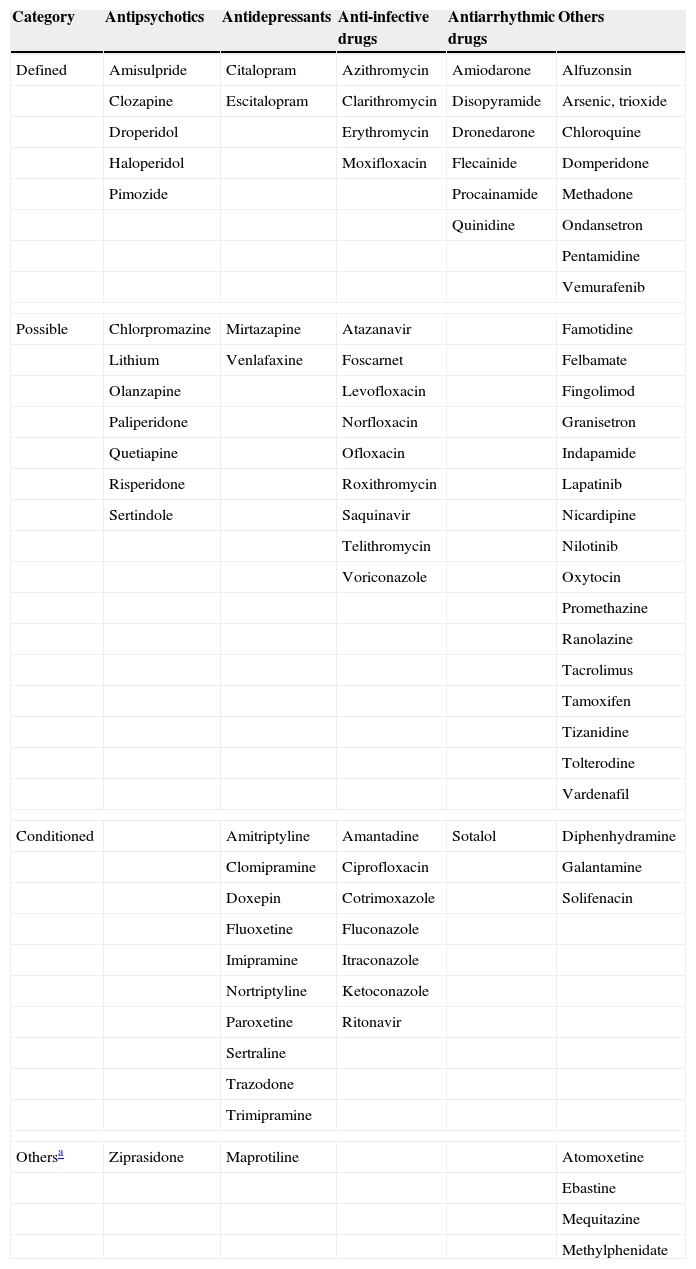
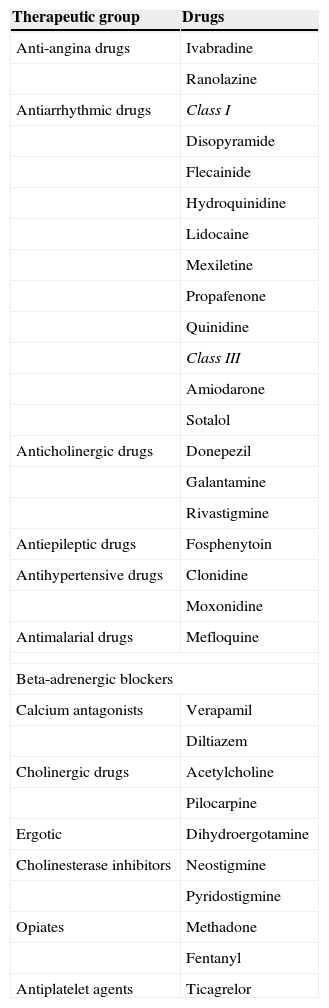
A major risk factor for this condition is the use of drugs that prolong the QT interval. In fact, in recent years, one of the most common reasons for drug withdrawal or usage restrictions has been drug induced QT interval prolongation that involves both cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular drugs.
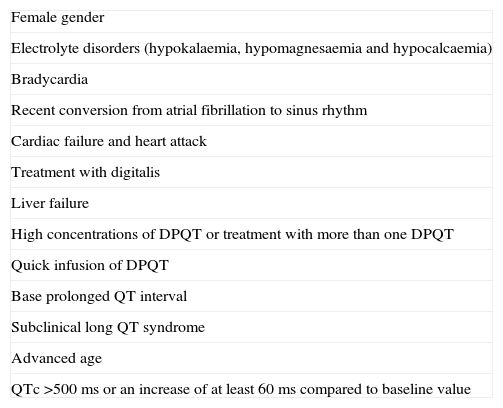
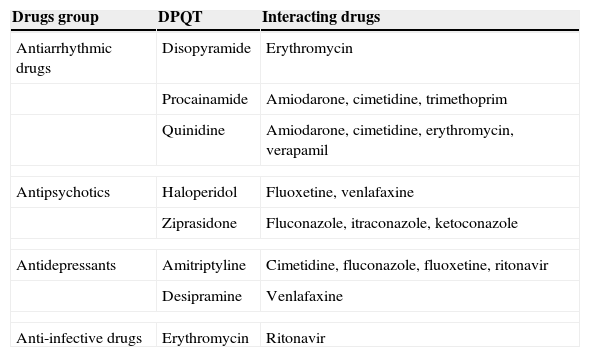
Taking into account the severity that the occurrence of such an event may have, it is important for clinicians to know the risks of these drugs in certain patients. In this review we analyse the drugs that prolong the QT interval, the risk factors that can enhance QT prolongation and the drug interactions that can increase these risks.
La muerte súbita cardiaca es una causa importante de mortalidad en los países desarrollados. La mayoría de ellas derivan de arritmias ventriculares agudas que, en algunas ocasiones, se producen como consecuencia de la prolongación del intervalo QT.
Un importante factor de riesgo para esta alteración es el uso de fármacos que prolongan este intervalo. De hecho, en los últimos años, uno de los motivos más frecuentes de retirada del mercado de medicamentos o de restricciones de uso ha sido la prolongación del intervalo QT, e implica tanto fármacos cardiovasculares como no cardiovasculares.
Dada la gravedad que puede conllevar la aparición de un suceso por esta causa, es importante que los clínicos conozcan los riegos del uso de estos fármacos en determinados pacientes. En esta revisión analizamos los fármacos que prolongan el intervalo QT, los factores de riesgo que pueden influir y las combinaciones de fármacos que pueden agravar esta situación.