DNA hydroxymethylation may be induced by oxidative stress in lupus patients, so we investigated the association between DNA hydroxymethylation and demethylation with the antioxidant response.
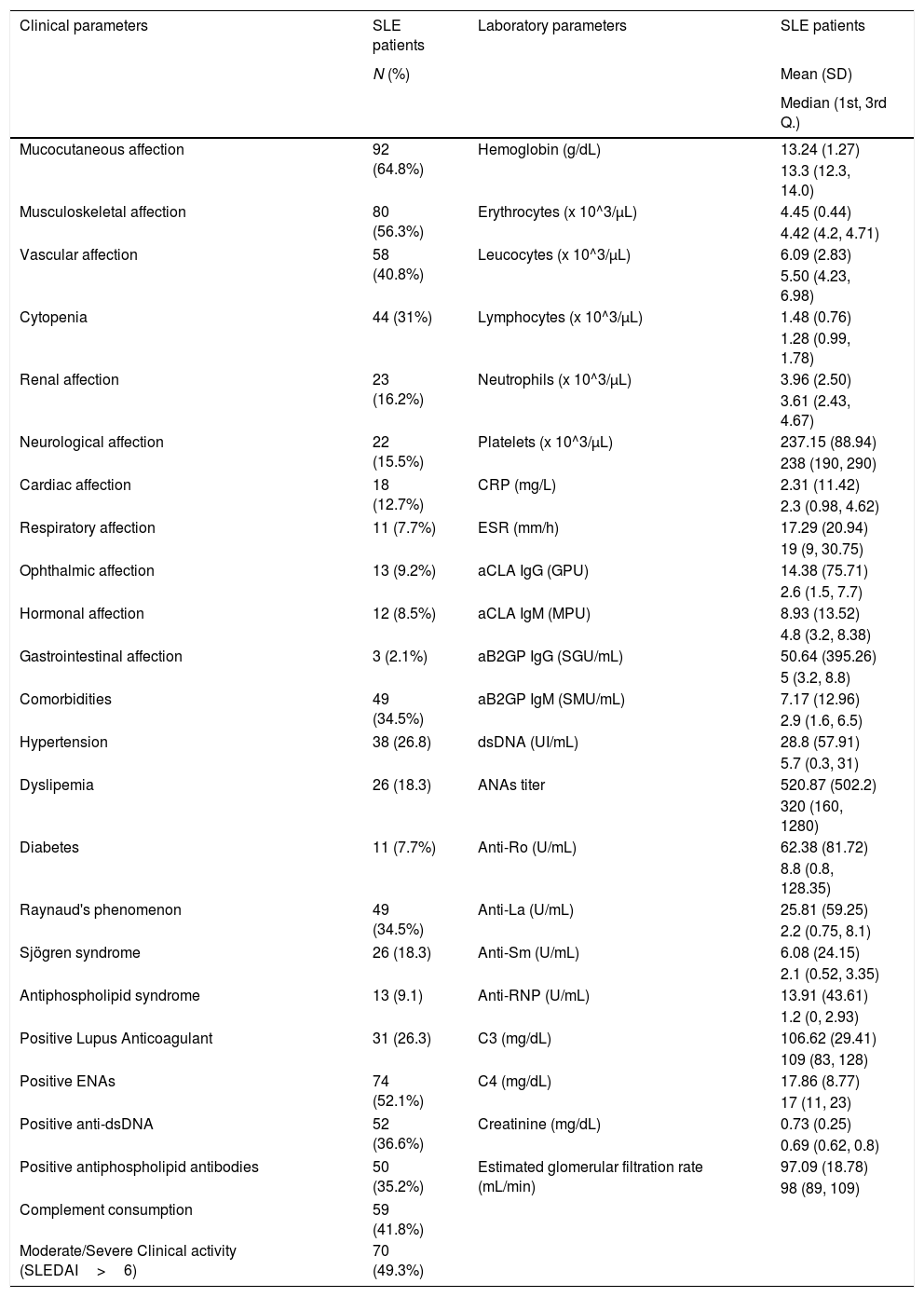
MethodsA case–control study was performed including lupus patients and matched healthy controls. Serum concentration of glutathione (GSH), glutathione disulphide (GSSG), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC), 5-mC and 5-hmC were determined.
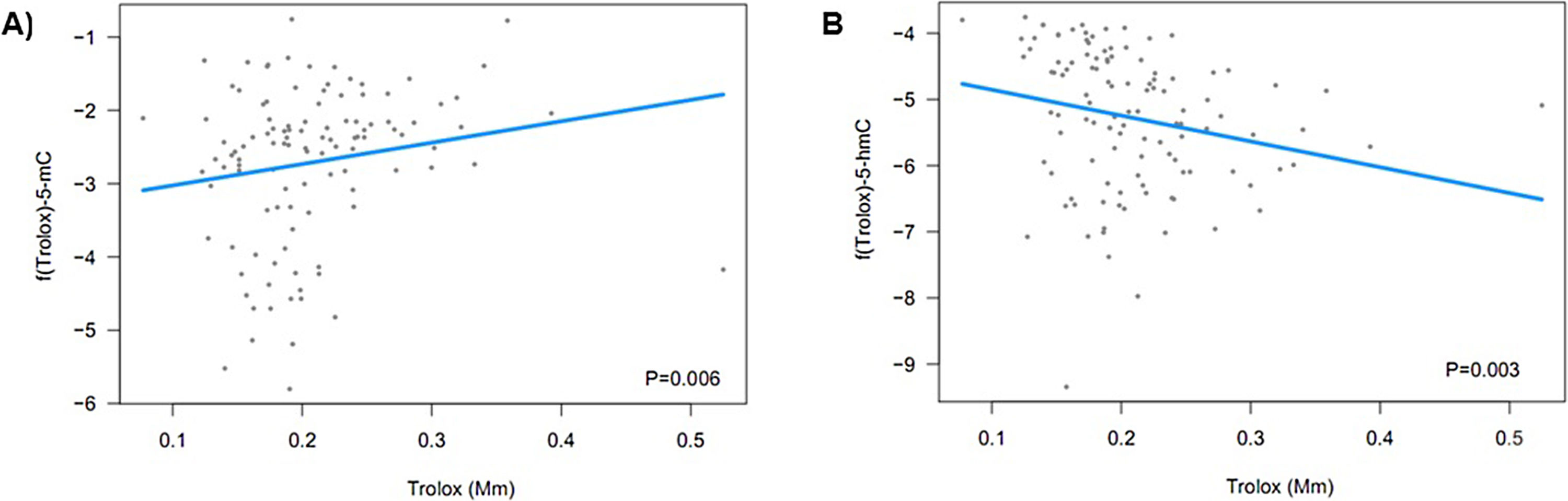
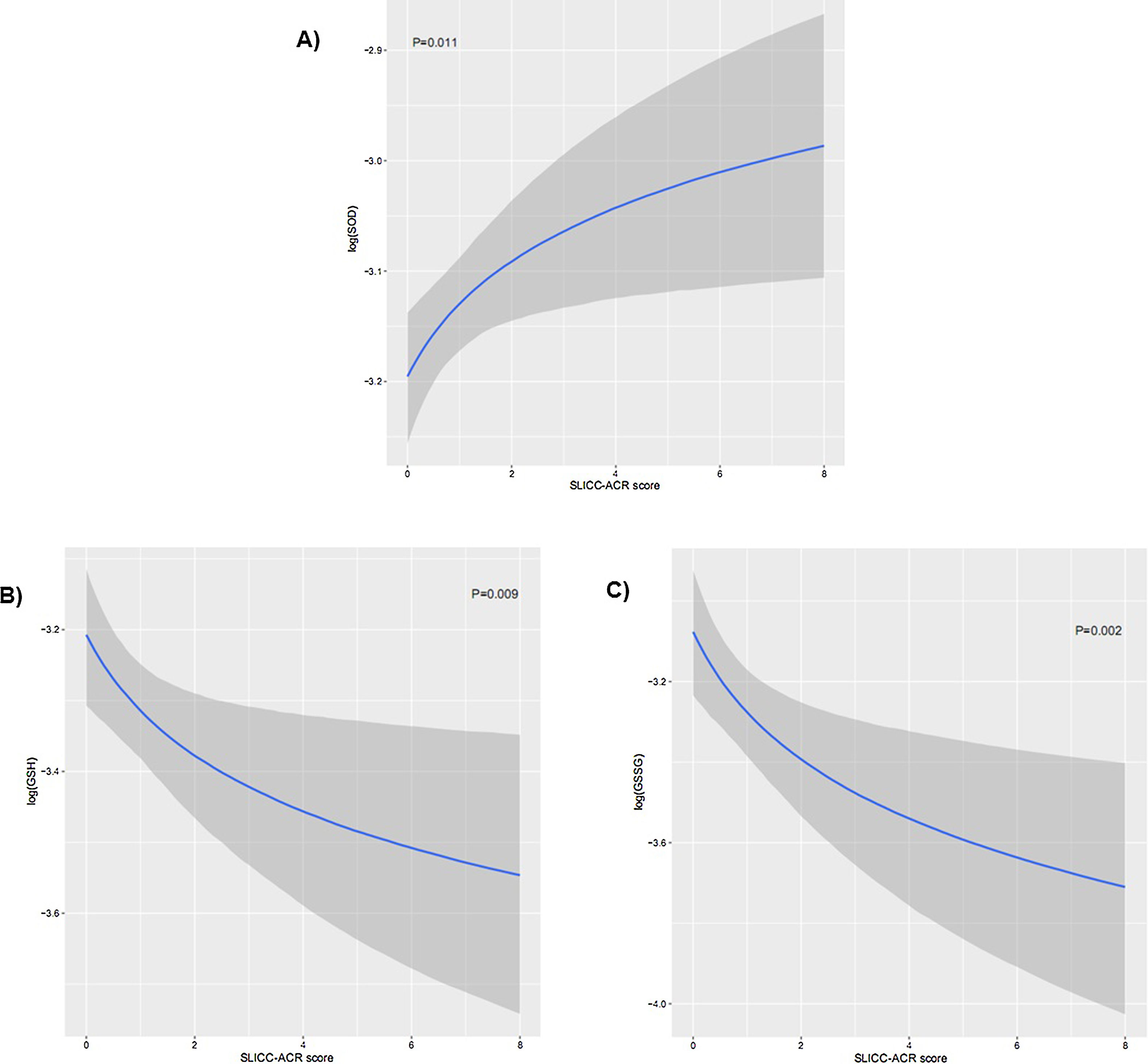
ResultsOne hundred and forty-two patients and 34 controls were included. 5-hmC levels were lower in SLE patients than in controls. GSH and GSSG values were lower in patients, while SOD levels were higher in patients. TAC did not show significant differences, but higher demethylation and lower hydroxydemethylation were associated to increased TAC values. Lower demethylation was associated with cytopenia and lower hydroxymethylation with longer course of the disease. Lower levels of GSH and GSSG and higher SOD values were associated with accumulated damage assessed by SLICC-ACR.
ConclusionsLower hydroxymethylation in patients than in controls was observed. Moreover, higher demethylation and lower hydroxymethylation leads to high TAC levels. DNA hydroxymethylation seems to be related to longer course of the disease.
La hidroximetilación del ADN puede estar inducida por el estrés oxidativo en pacientes de lupus, por lo que estudiamos la asociación entre hidroximetilación del ADN y desmetilación sin respuesta antioxidante.
MétodosSe realizó un control de casos que incluyó a pacientes de lupus pareados con controles sanos. Se calcularon la concentración sérica de glutatión (GSH), glutatión disulfuro (GSSG), superóxido dismutasa (SOD), capacidad antioxidante total (CAT), 5-mC y 5-hmC.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 142 pacientes y 34 controles. Los niveles de 5-hmC fueron menores en el grupo de pacientes de LES que en el de controles. Los valores de GSH y GSSG fueron menores en el grupo de pacientes, mientras que los valores de SOD fueron superiores en el grupo de pacientes. La CAT no reflejó diferencias significativas, pero el incremento de desmetilación y la disminución de hidroximetilación estuvieron asociados al incremento de los valores de la CAT. La disminución de la desmetilación estuvo asociada a citopenia, y la disminución de la hidroximetilación a un curso más corto de la enfermedad. Los niveles menores de GSH y GSSG, y los valores superiores de SOD estuvieron asociados a una acumulación del daño, según lo evaluado mediante SLICC-ACR.
ConclusionesSe observó menor hidroximetilación en los pacientes que en los controles. Además, el incremento de la desmetilación y la disminución de la hidroximetilación conllevan unos altos niveles de CAT. La hidroximetilación del ADN parece estar relacionada con un curso más largo de la enfermedad.