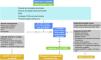
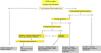
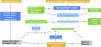
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a histopathologic definition associated with enlargement of the prostate gland that causes obstruction of the lower urinary tract and manifests clinically with characteristic symptoms that are what bring patients for consultation.
Urinary tract symptoms are common, especially in an increasingly aging population. Diagnosis and the decision on when and how to treat depend on the patient's quality of life and objective clinical parameters.
An individualized, risk-based approach is necessary to guide conservative, pharmacologic, or surgical treatment.
La hiperplasia benigna de próstata (HBP) es una definición histopatológica asociada al crecimiento de la glándula prostática, que genera obstrucción del tracto urinario inferior y se manifiesta clínicamente con síntomas característicos que son los que conducen a los pacientes a la consulta.
Los síntomas del tracto urinario son frecuentes, especialmente en una población cada vez más envejecida. Diagnosticarlos y decidir cuándo y cómo tratarlos depende de la afectación de la calidad de vida del paciente, junto con parámetros objetivos clínicos.
Es necesario un enfoque individualizado basado en el riesgo para orientar a un tratamiento conservador, farmacológico o quirúrgico.