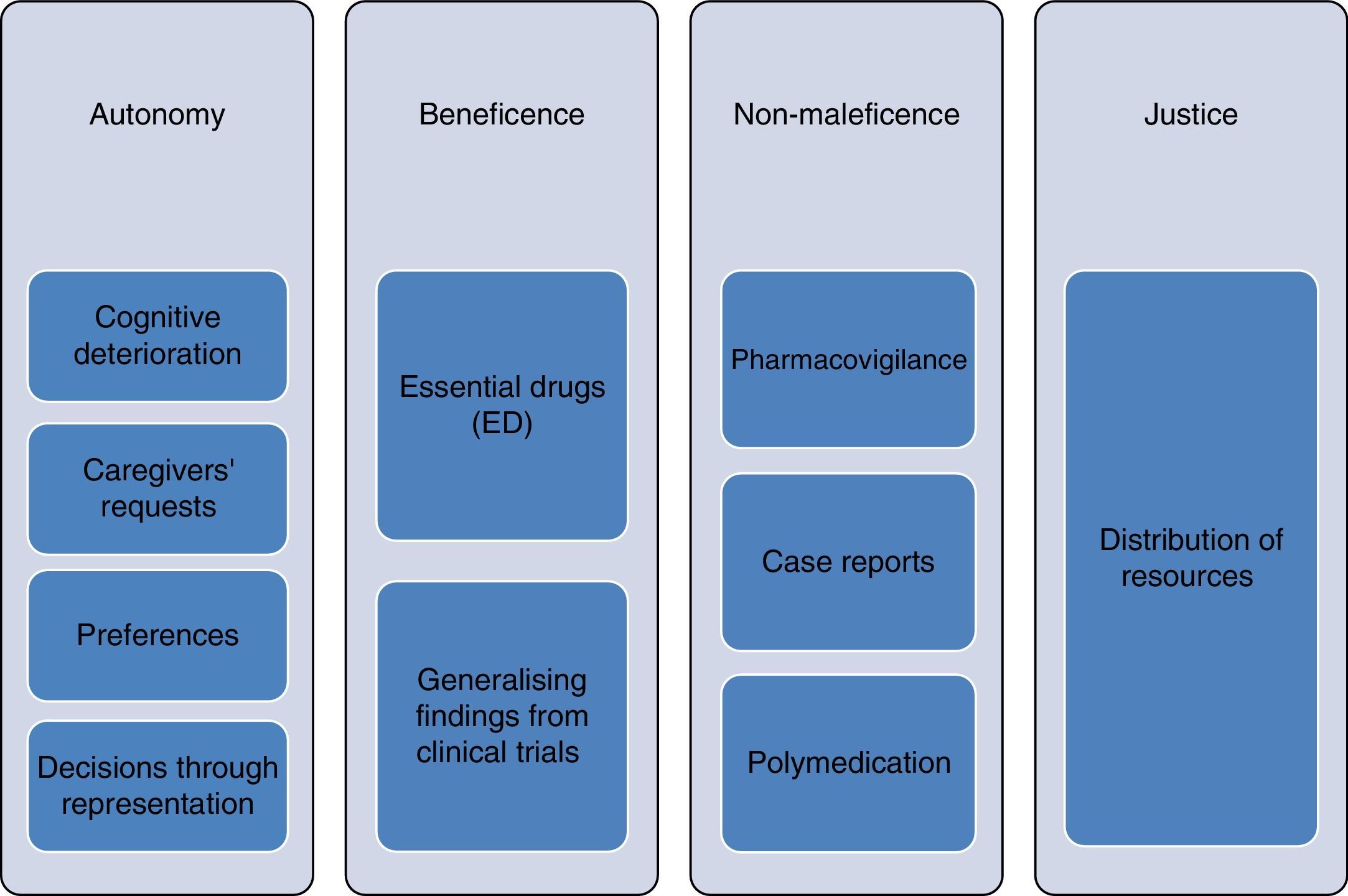
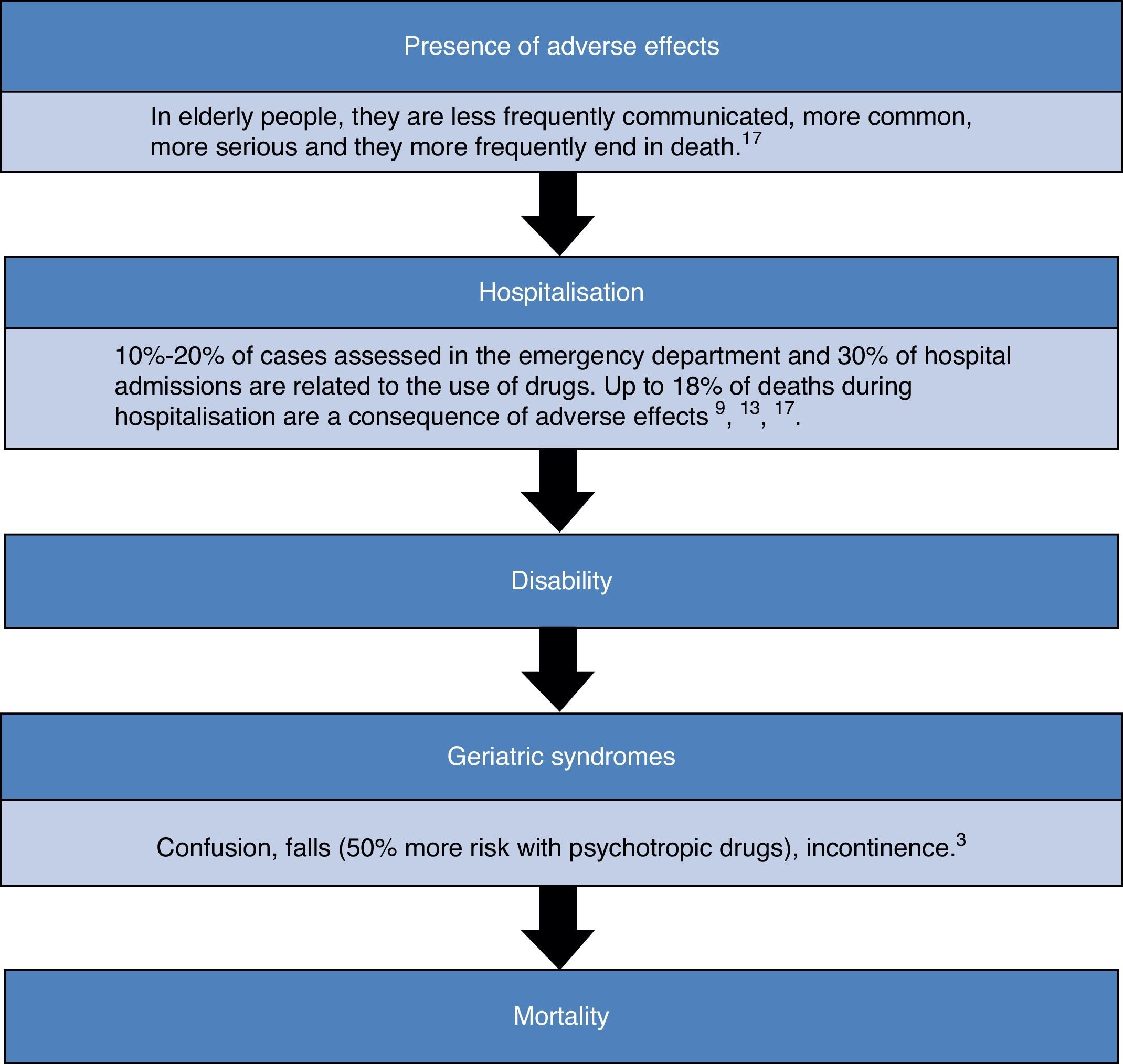
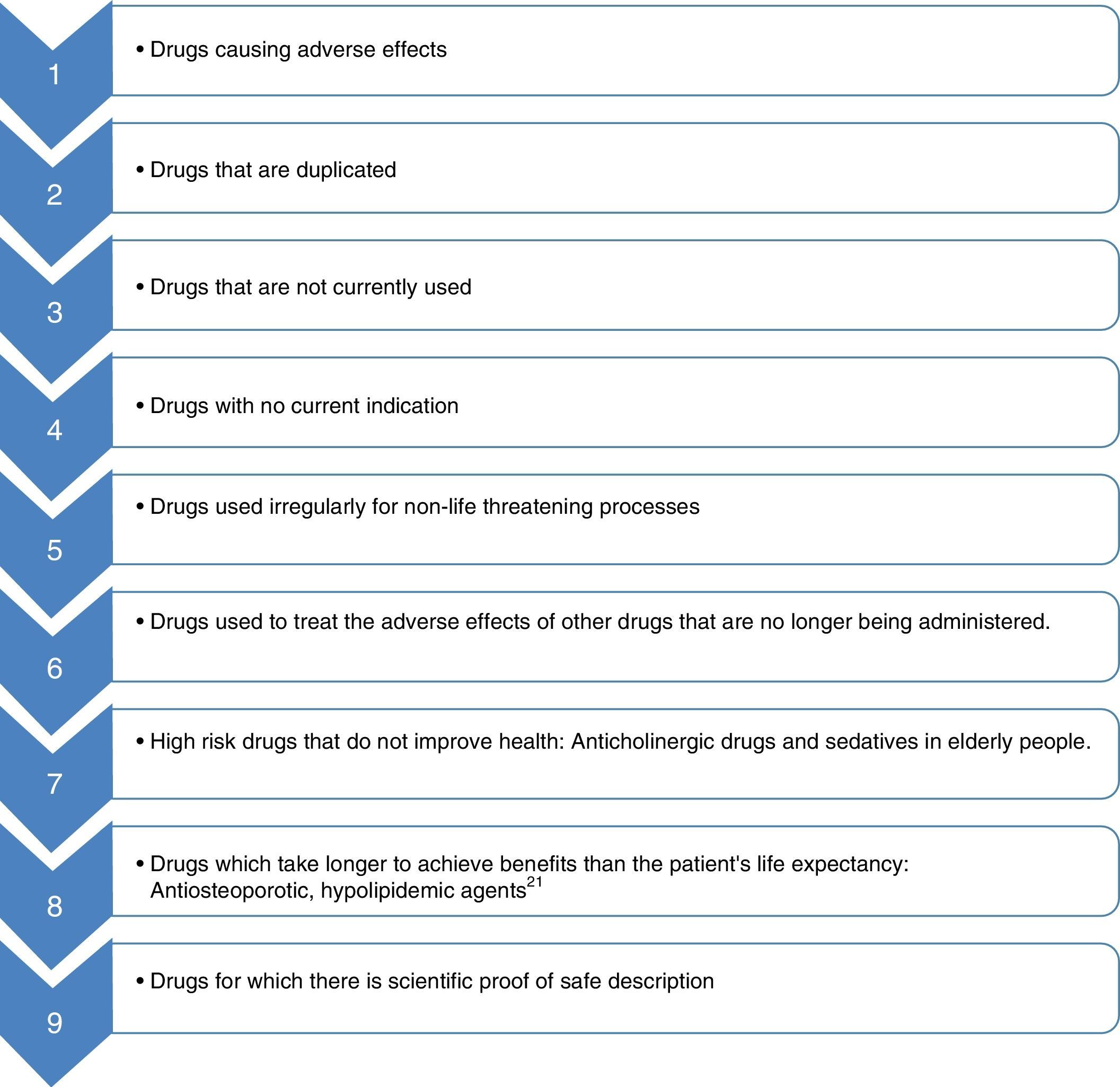
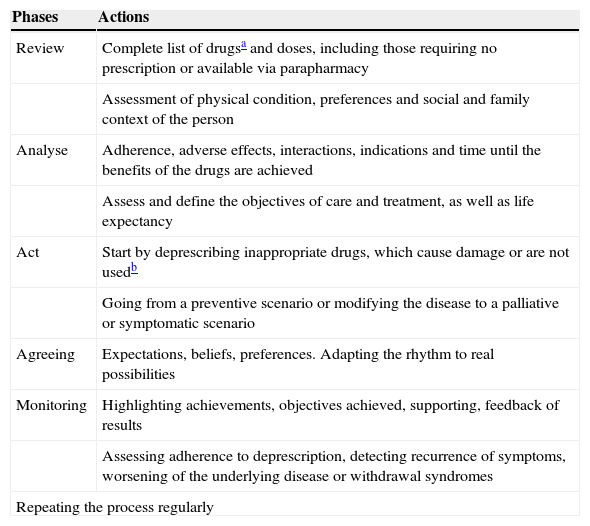
The therapeutic structure of health systems relies heavily on medical prescription, which generates a marked tendency to add drugs to a patient's medical history. There is an absence of incentives for professionals to reassess prescriptions and withdraw those with a negative or neutral risk/benefit. This can create a deviation of medical resources to the maintenance of useless or even harmful treatments. Deprescribing, a process of thoughtful medication withdrawal that complements moderate prescribing, is aimed to stop this unfair deviation of resources towards non-beneficial, if not maleficent, prescription.
La estructura terapéutica de los sistemas sanitarios descansa en gran medida sobre la prescripción, lo que genera una tendencia mantenida a sumar fármacos en la historia clínica del paciente. Por el lado contrario, destaca una ausencia significativa de estímulos sobre los profesionales para la reevaluación de prescripciones y la retirada de aquellas con un balance riesgo/beneficio negativo o neutro, lo que supone una desviación de recursos sanitarios hacia el mantenimiento de tratamientos inútiles, cuando no dañinos. La deprescripción, como la retirada meditada de medicación que complementa una prescripción prudente, está dirigida a frenar esta desviación injusta de recursos hacia prescripciones no beneficentes, cuando no maleficentes.