The objective of the study was to describe the trends of utilization, supply and prevalence of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in Spain during the period 2000–2014.
MethodsAnnual prevalence of HRT use including the 95% CI was calculated for women aged≥40 using individual data from the national population-based database BIFAP. Annual and total-period consumptions were expressed in defined daily doses (DDD) per 1000 inhabitants per day and were obtained from the databases of medications dispensed in community pharmacies and charged through official prescriptions to the Spanish National Health System.
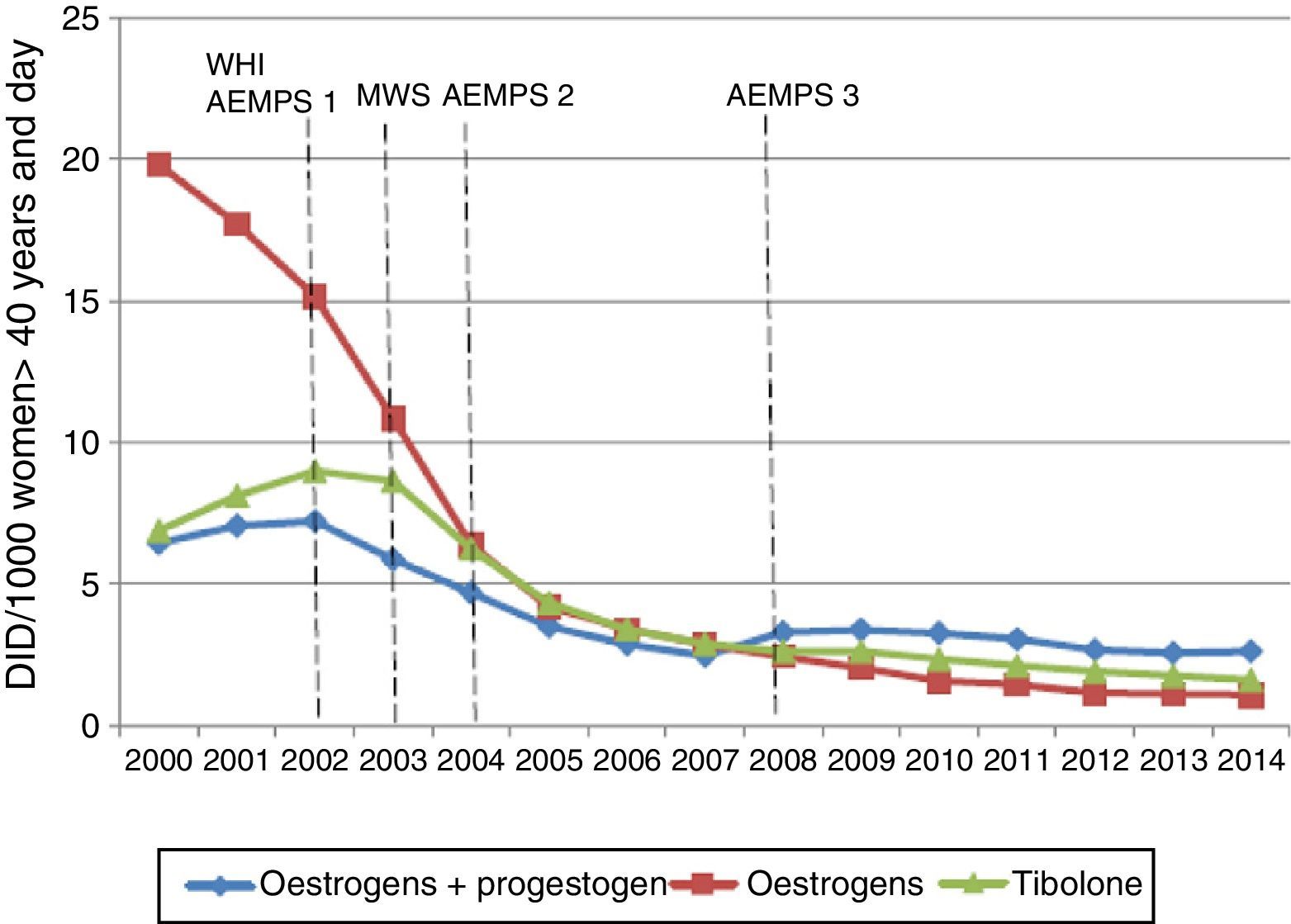
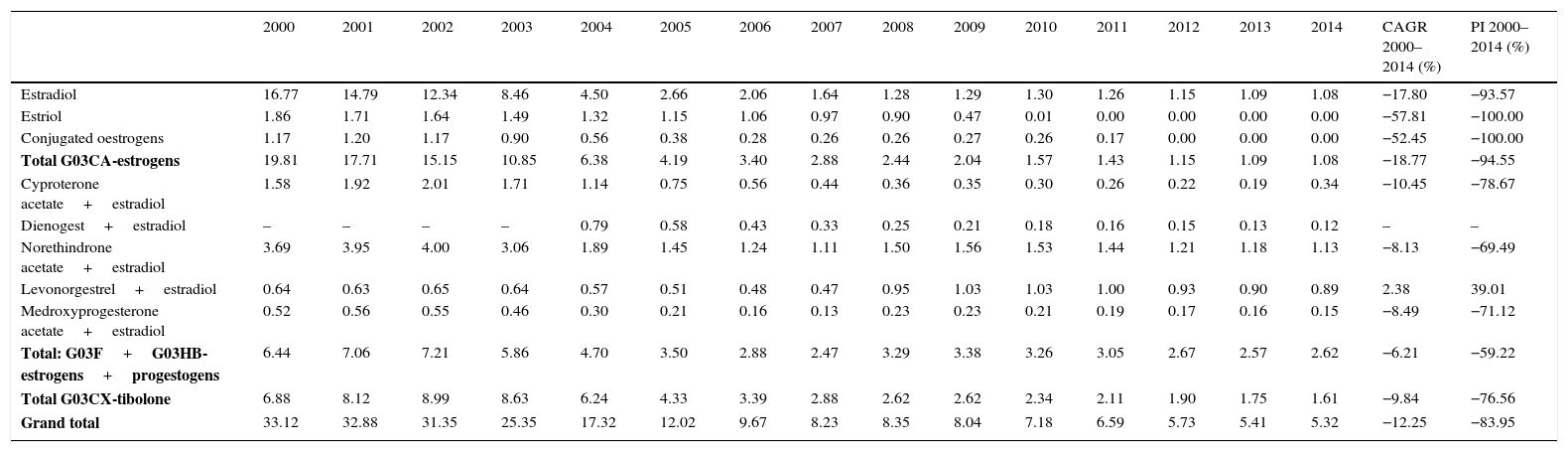
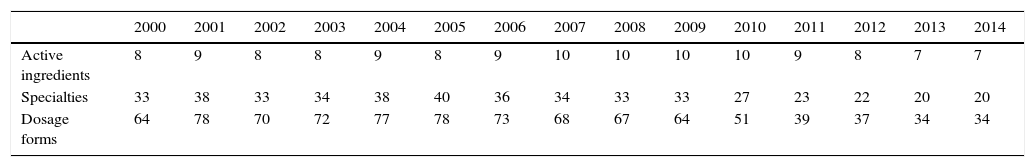
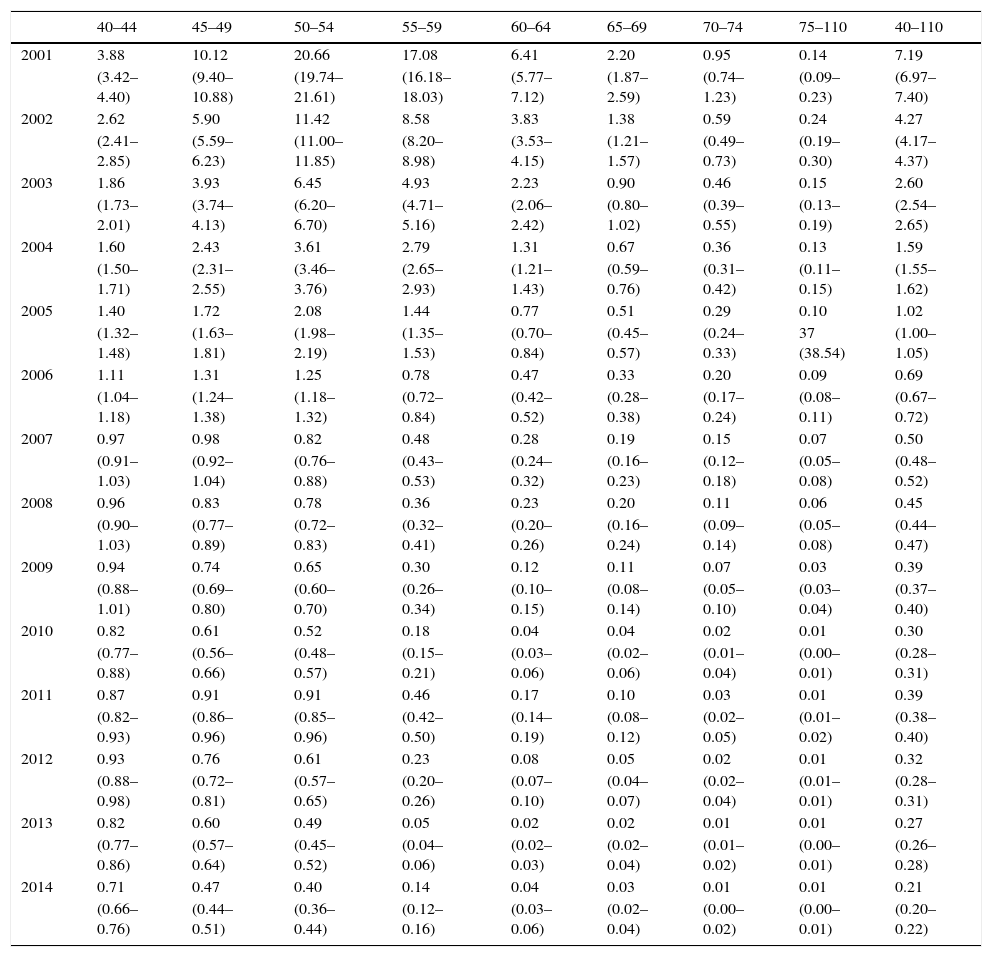
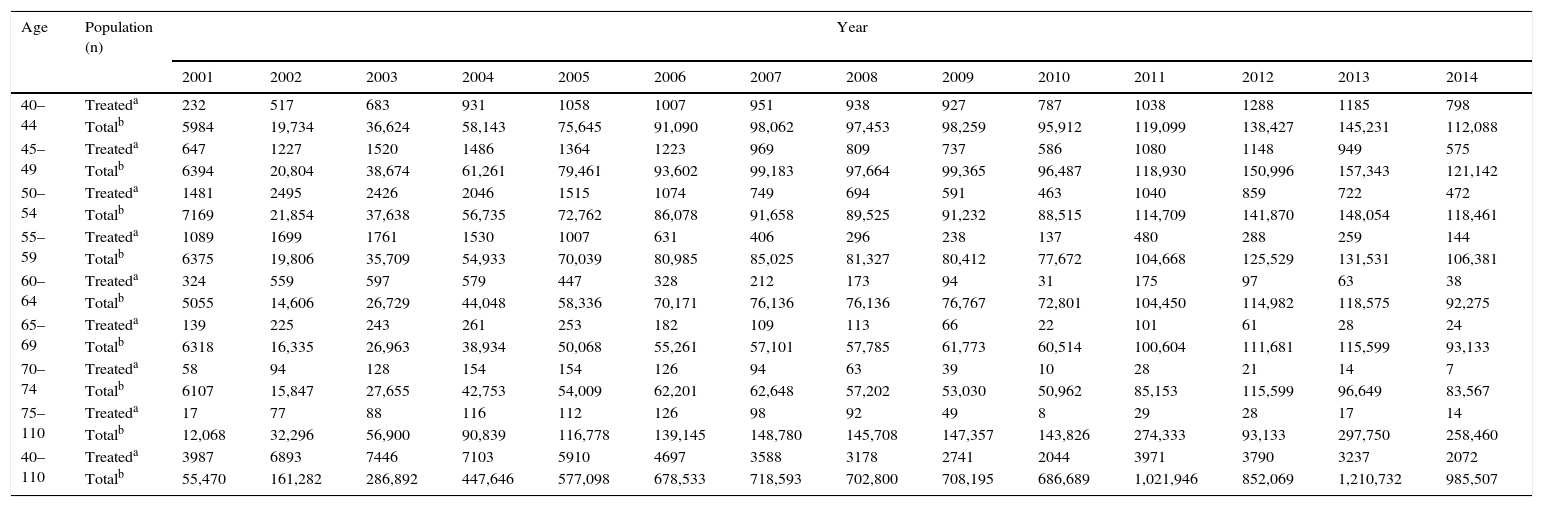
ResultsIn the year 2000, overall HRT consumption was 33.12 DDDs/1000 inhabitants/day: 19.81 for oestrogen only, 6.88 for tibolone and 6.44 for combined oestrogen and progestagen. In 2014 overall HRT consumption was 5.32 DDDs/1000 inhabitants/day: 1.08 for oestrogen only, 1.61 for tibolone and 2.62 for combinations of oestrogen and progestagen. The marketed presentations of HRT decreased by 46.9%. Prevalence of HRT use in women aged≥40 in BIFAP was 7.19% (95% CI 6.97–7.40) in 2001 and 0.21% (95% CI 0.20–0.22) in 2014. Women aged 40–45 registered the highest prevalence of use in 2014: 0.71% (95% CI 0.66–0.76).
ConclusionsA sharp decline in the consumption and prevalence of HRT has been observed in Spain since the publication of the Women's Health Initiative and Million Women Study and the regulatory measures taken restricting conditions of use, showing a similar trend to that of other western countries.
El objetivo de este trabajo fue describir la evolución del consumo, la oferta y la prevalencia de uso del tratamiento hormonal sustitutivo (THS) en España durante el período 2000-2014.
MétodosLa prevalencia de uso anual bruta en mujeres≥40 años se estimó a partir de datos individuales procedentes de las historias clínicas anonimizadas de la base de datos BIFAP. Para el cálculo del consumo se utilizaron datos agregados de dispensación. El consumo de THS se expresó en dosis diarias definidas dispensadas por cada 1.000 mujeres≥40 años y día (DHD).
ResultadosEn el año 2000 el consumo de THS fue de 33,12 DHD: estrógenos (19,81 DHD), tibolona (6,88 DHD) y estrógenos asociados a progestágenos (6,44 DHD). En 2014 el consumo de THS fue de 5,32 DHD: estrógenos (1,08 DHD), tibolona (1,61 DHD) y estrógenos combinados con progestágenos (2,62 DHD). Las presentaciones comercializadas se redujeron un 46,9%. La prevalencia de uso de THS en mujeres≥40 años registradas en la base de datos BIFAP ha pasado de un 7,19% (IC 95% 6,97-7,40) en el año 2001 a un 0,21% (IC 95% 0,20-0,22) en 2014. Las mujeres de 40-45 años registraron la mayor prevalencia de uso en 2014: 0,71% (IC 95% 0,66-0,76).
ConclusionesEl consumo y la prevalencia de uso de THS ha descendido de manera notable a partir de la publicación de los estudios Women's Health Iniciative, Million Women Study y las medidas reguladoras, siguiendo una tendencia similar a la observada en otros países occidentales.