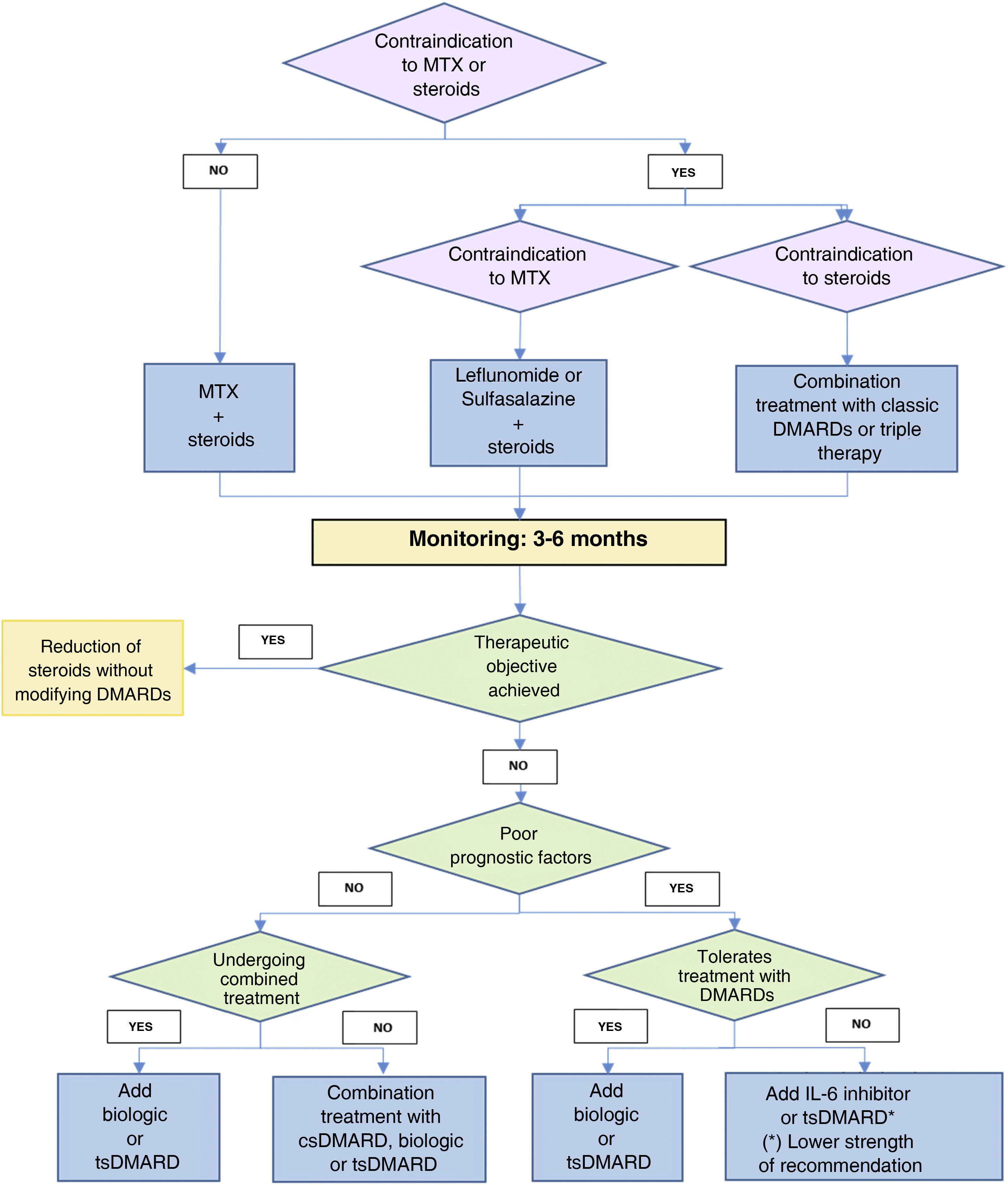
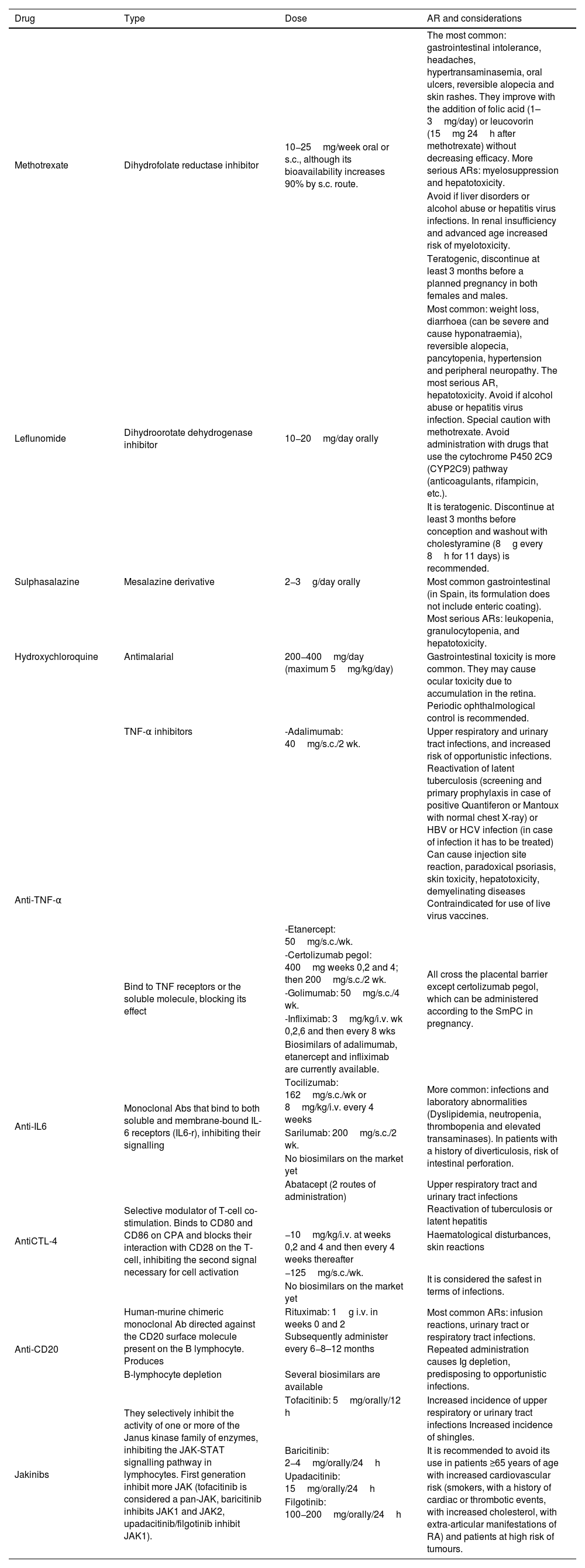
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory multisystemic disease of unknown etiology and autoimmune nature that predominantly affects peripheral joints in a symmetrical fashion. Although much progress has been made in understanding the pathophysiology of RA, its etiology remains unknown. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 play the important roles in the pathogenesis and maintenance of inflammation in RA. The presence of anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies aids in the diagnosis in patients with undifferentiated polyarthritis and is associated with a more aggressive RA. The natural history of RA causes joint deformity and disability, as well as reduced life expectancy, both due to increased cardiovascular risk, pulmonary involvement, infections, iatrogenesis or tumors. Early diagnosis and the use of targeted drugs to induce early remission have improved the RA prognosis.
La artritis reumatoide (AR) es una enfermedad inflamatoria crónica multisistémica de etiología desconocida y de naturaleza autoinmune que afecta predominantemente a las articulaciones periféricas de forma simétrica. Aunque se ha avanzado mucho en la comprensión de su fisiopatología, su etiología sigue siendo desconocida. El factor de necrosis tumoral (TNF)-α y la interleucina (IL)-6, juegan un papel importante en la patogénesis y la perpetuación de la inflamación en la AR. La presencia de anticuerpos antipéptidos citrulinados ayuda en el diagnóstico en pacientes con poliartritis indiferenciadas y se relaciona con una evolución más agresiva de la AR. La evolución natural de la AR causa deformidad articular y discapacidad, además de una reducción de la esperanza de vida, por aumento del riesgo cardiovascular, afectación pulmonar, infecciones, iatrogenia o tumores. El diagnóstico precoz y la utilización de fármacos dirigidos que buscan la remisión temprana han mejorado sustancialmente el pronóstico de la AR.