In order to avoid the toxic effect of chemotherapy, it has been proposed to use GnRH agonist analogues (GnRHa) to inhibit the depletion of ovarian follicles. Nevertheless, there is controversy about its effectiveness. This clinical trial has been conducted with the aim to assess the protective effect of GnRH analogues on the reproductive capacity of women with malignancies or autoimmune diseases, which require chemotherapy.
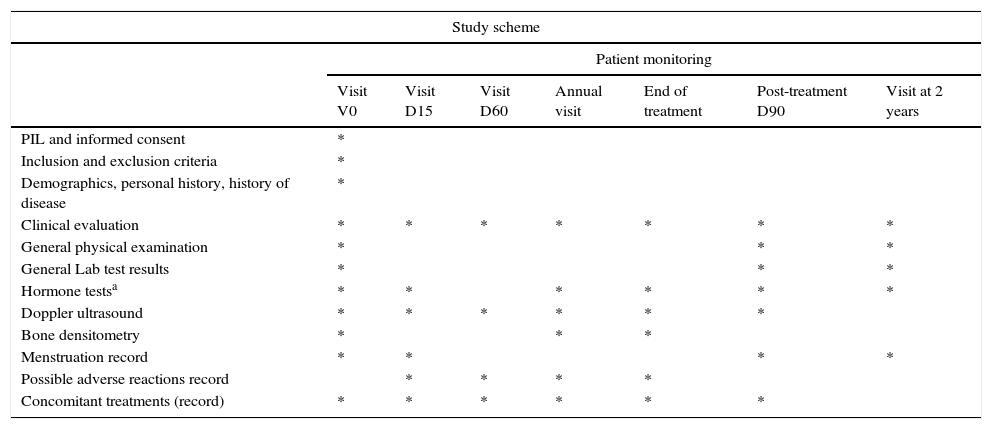
Patients and methodsOpen phase ii single-center clinical trial. During chemotherapy, a total of 5 doses of GnRH antagonist analogue at a dose interval of 3 days and/or a monthly dose of GnRHa were administered. Hormonal determinations prior to the start of the CT treatment were conducted during treatment and at the end of it.
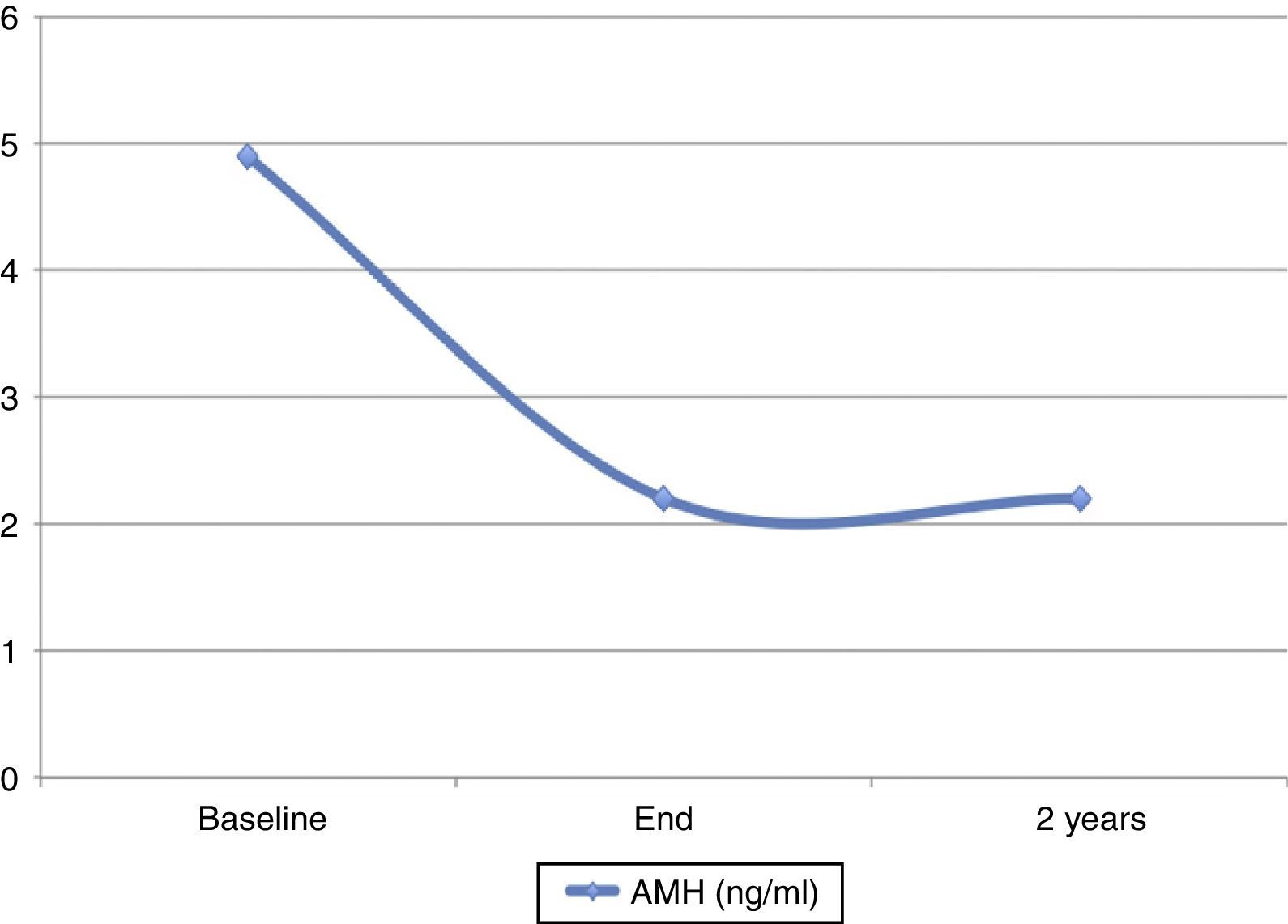
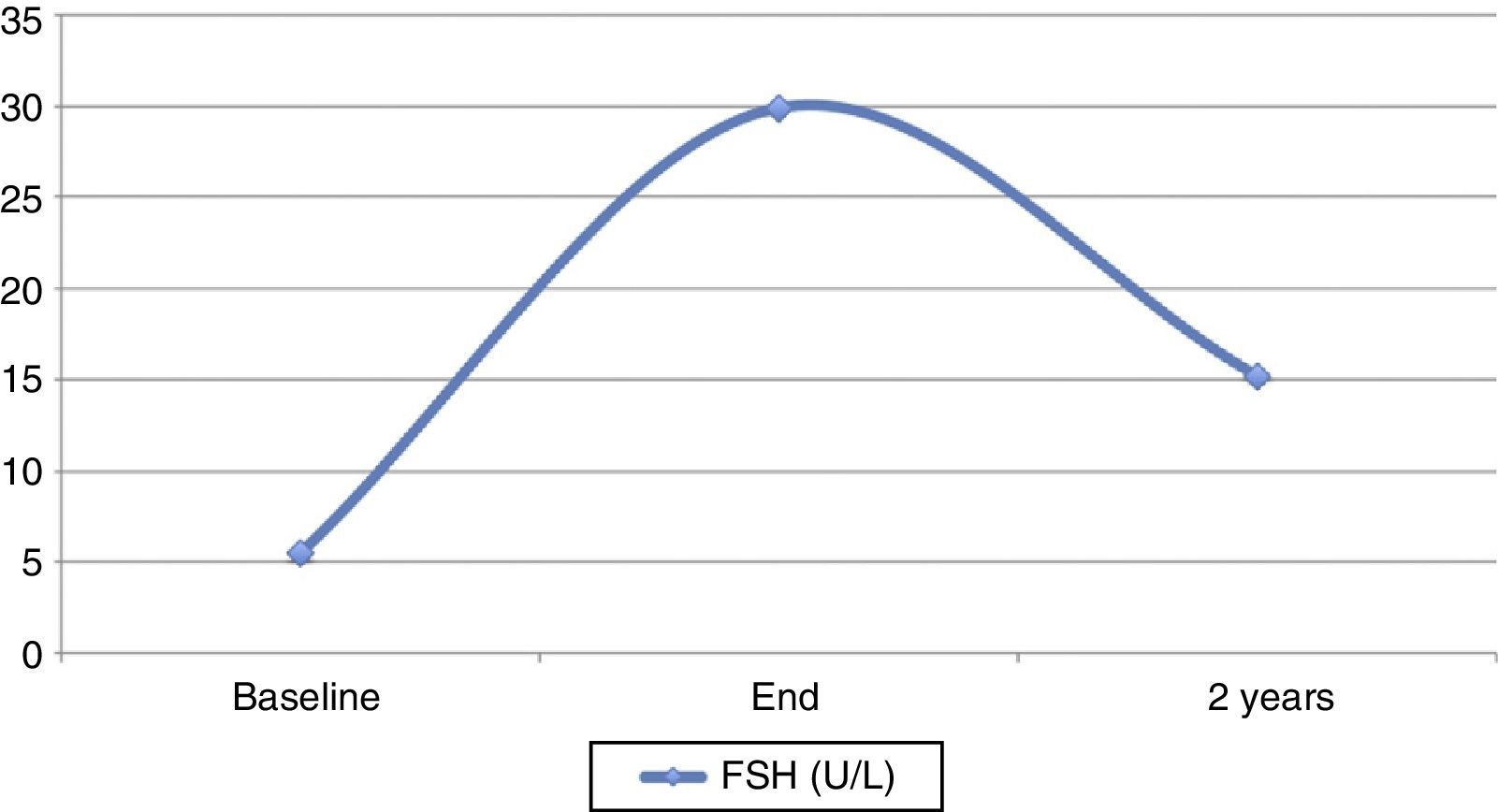
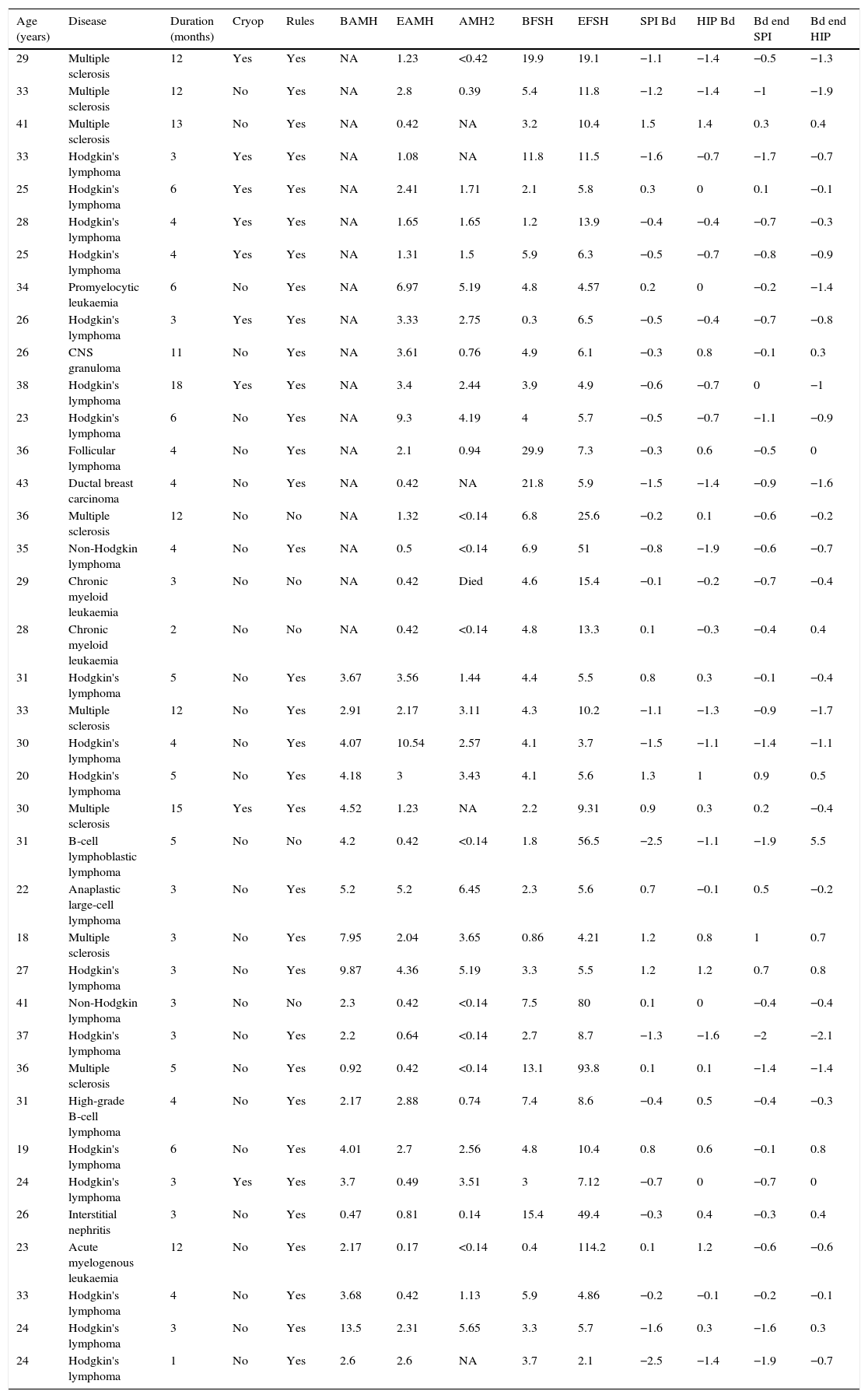
ResultsThe inclusion of patients was prematurely concluded when incorporating the determination of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) as a parameter for assessing the ovarian reserve. Out of 38 patients, 23 (60.5%, 95%CI 43.4–76.0) had AMH values below normal following completion of treatment. An intermediate analysis was carried out observing that while most patients were recovering the menstrual cycle (86.6% 95%CI 71.9–95.6), they had reduced levels of AMH.
ConclusionAlthough most patients recovered their menstrual cycles, the ovarian reserve, assessed by the concentration of AMH, decreased in many patients. Therefore, we can conclude that the concomitant treatment of chemotherapy and GnRH analogues does not preserve the loss of follicular ovarian reserve.
Para evitar el efecto tóxico quimioterápico se ha propuesto la utilización de análogos agonistas de la GnRH (aGnRH) para inhibir la depleción de folículos ováricos. Existen controversias sobre su eficacia, por lo que se ha realizado un ensayo clínico para valorar el efecto protector de los análogos de la GnRH en mujeres afectadas de cáncer y enfermedades autoinmunitarias tratadas con fármacos citotóxicos.
Pacientes y métodosEnsayo clínico, de fase ii, unicéntrico y abierto. Durante el tratamiento quimioterápico se administraron 5 dosis de análogo antagonista de la GnRH en intervalos de 3 días y/o una dosis mensual de aGnRH. Se realizaron determinaciones hormonales previamente al inicio del tratamiento quimioterápico y al finalizar este.
ResultadosLa inclusión de las pacientes se concluyó precozmente al introducir como parámetro de evaluación de la reserva ovárica la determinación de hormona antimulleriana (HAM). De las 38 pacientes seguidas, 23 (60,5%, IC95% 43,4-76,0) presentaron valores de AMH por debajo de la normalidad tras la conclusión del tratamiento. Se realizó un análisis intermedio en el que se observó que el 86,6% (IC95% 71,9-95,6) de las pacientes recuperaban el ciclo menstrual, pero estas presentaban una reducción de los niveles de HAM.
ConclusiónAunque la mayoría de las pacientes presentaron recuperación de los ciclos menstruales, la reserva ovárica disminuyó en la mayoría de ellas, por lo que podemos concluir que la administración concomitante al tratamiento quimioterápico de análogos de la GnRH no preserva de la pérdida de la población folicular ovárica.