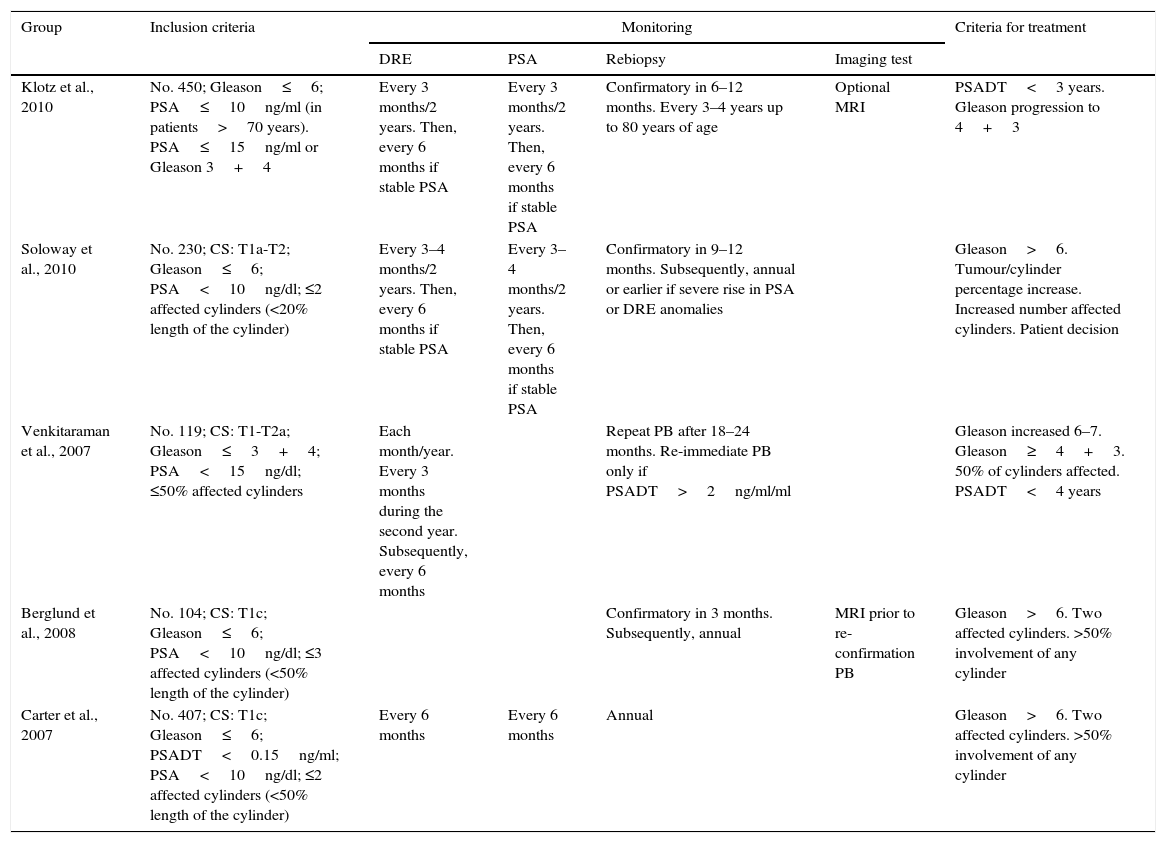
The Vall d’Hebron multidisciplinary prostate cancer (PC) team reviews recent advances in the management of this neoplasm. Screening studies with long follow-up show a reduction in mortality, whereas active surveillance is emerging as a therapeutic approach of non-aggressive cancers. New markers increase the specificity of PSA and also allow targeting suspected aggressive cancers. Multiparametric magnetic resonance (mMRI) has emerged as the most effective method in the selection of patients for biopsy and also for local tumour staging. The paradigm of random prostatic biopsy is changing through the fusion techniques that allow guiding ultrasonography-driven biopsy of suspicious areas detected in mMRI. Radical prostatectomy (RP) and radiotherapy (RT) are curative treatments of localized PC and both have experienced significant technological improvements. RP is highly effective and the incorporation of robotic surgery is reducing morbidity. Modern RT allows the possibility of high tumour dose with minimal adjacent dose reducing its toxicity.
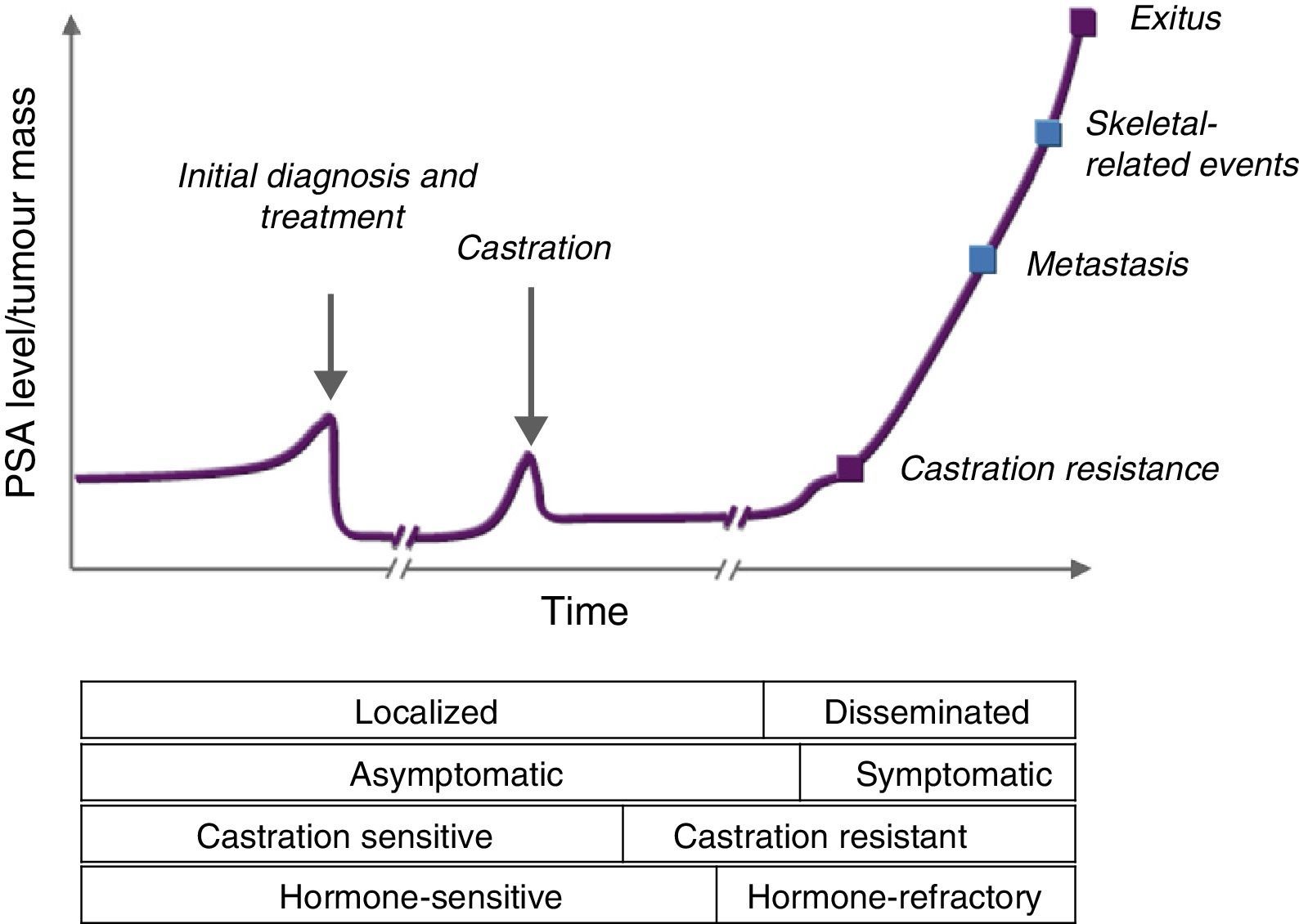
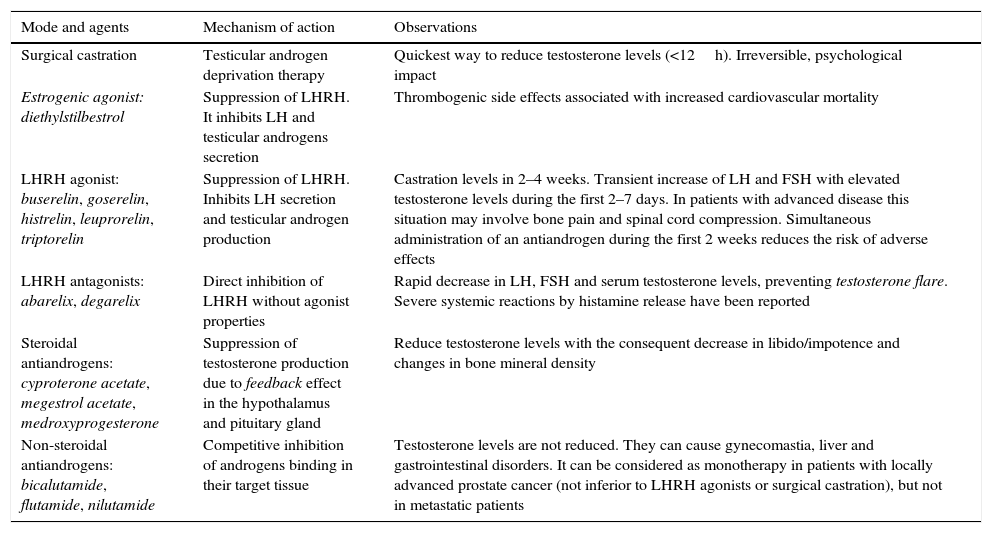
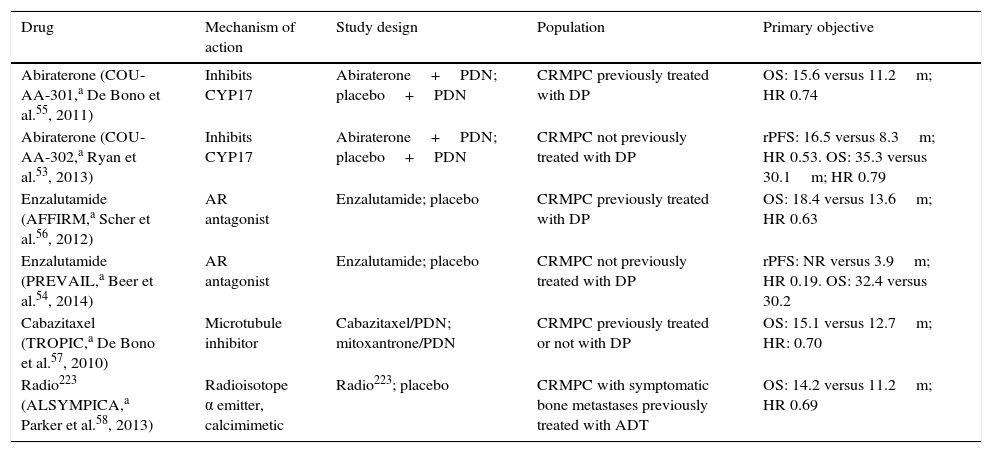
Androgen deprivation therapy with LHRH analogues remains the treatment of choice for advanced PC, but should be limited to this indication. The loss of bone mass and adverse metabolic effects increases the frequency of fractures and cardiovascular morbimortality. After castration resistance in metastatic disease, new hormone-based drugs have demonstrated efficacy even after chemotherapy resistance.
El equipo multidisciplinario de cáncer de próstata (CP) del Hospital Universitario Vall d’Hebron revisa los avances recientes en el tratamiento de esta neoplasia. Estudios de cribado y largo seguimiento ponen de manifiesto una reducción de la mortalidad, mientras la vigilancia activa emerge como una actitud terapéutica frente al diagnóstico de cánceres no agresivos. Nuevos marcadores incrementan la especificidad del PSA y, además, permiten focalizar la sospecha de cánceres con comportamiento agresivo. La resonancia magnética multiparamétrica (RMm) se ha posicionado como el método más eficaz en la selección de pacientes para biopsia y también para estadificar el tumour a nivel local. El paradigma de biopsia aleatoria ecodirigida está cambiando, y a través de la fusión de imágenes entre RMm y ecografía se está convirtiendo en una biopsia guiada a zonas sospechosas. La prostatectomía radical (PR) y la radioterapia (RT) son los tratamientos curativos del CP localizado y en ambas se han experimentado mejorías tecnológicas notables. La PR es altamente eficaz y la incorporación de la cirugía robótica está reduciendo su morbilidad. La moderna RT permite administrar mayores dosis en el tumour y mínimas dosis adyacentes, reduciéndose significativamente su toxicidad.
La supresión androgénica con análogos de la LHRH sigue siendo el tratamiento de elección del CP avanzado, pero debe limitarse a esta indicación. La pérdida de masa ósea y los efectos metabólicos adversos incrementan la frecuencia de fracturas y morbimortalidad cardiovascular. En la fase de resistencia a la castración con diseminación metastásica nuevos fármacos de base hormonal han demostrado eficacia incluso después de resistencia a quimioterapia.