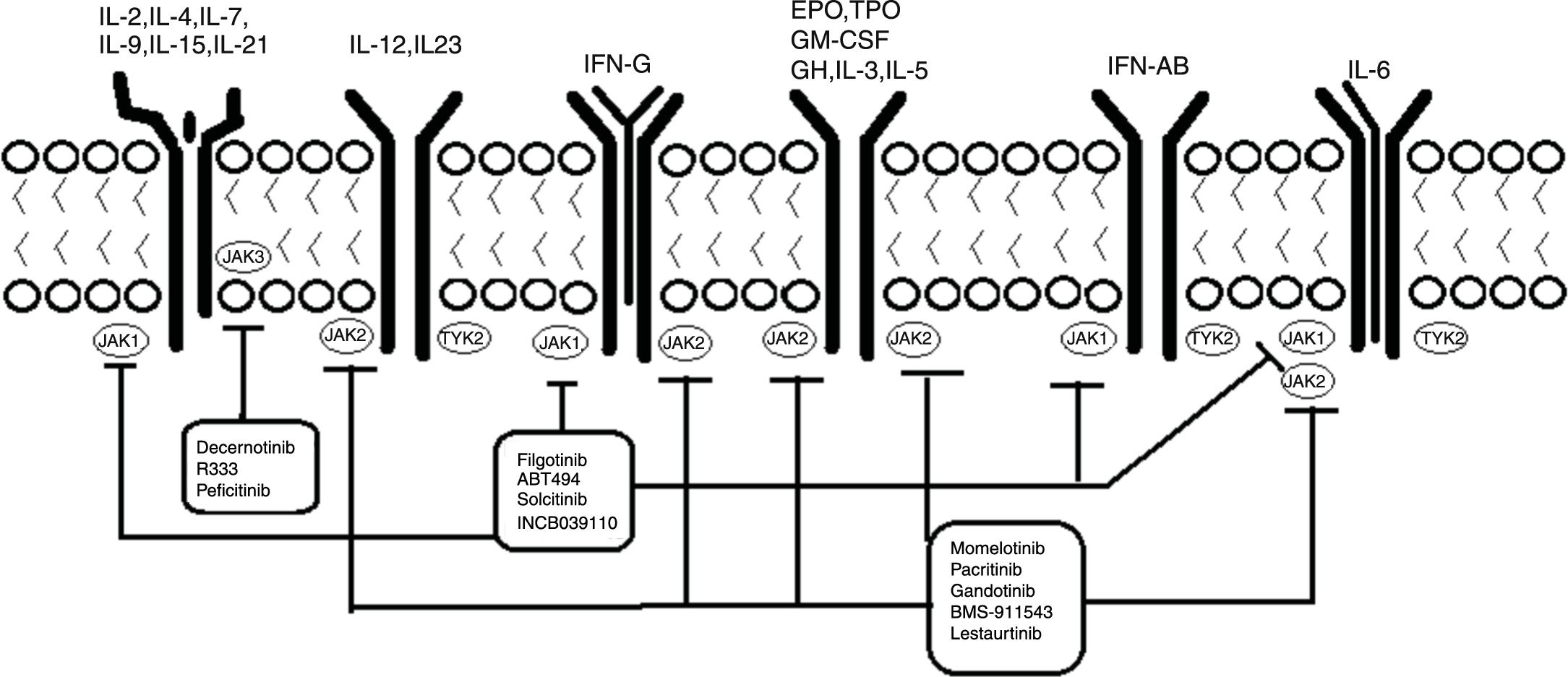
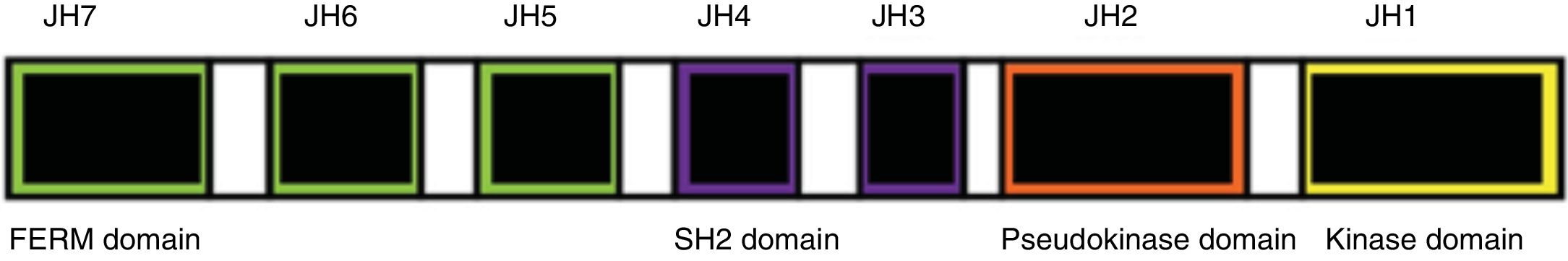
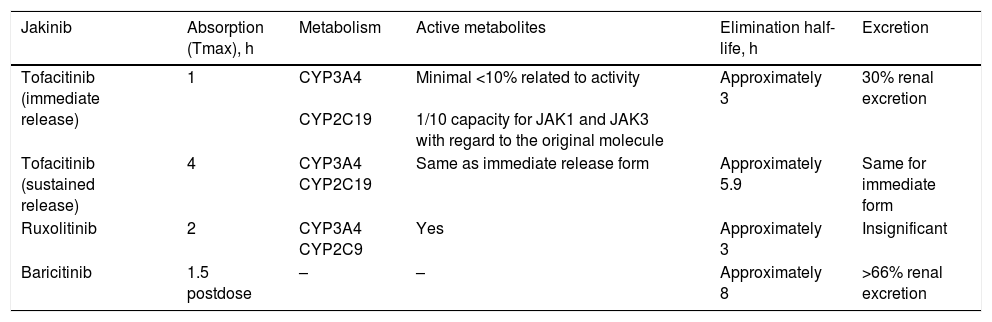
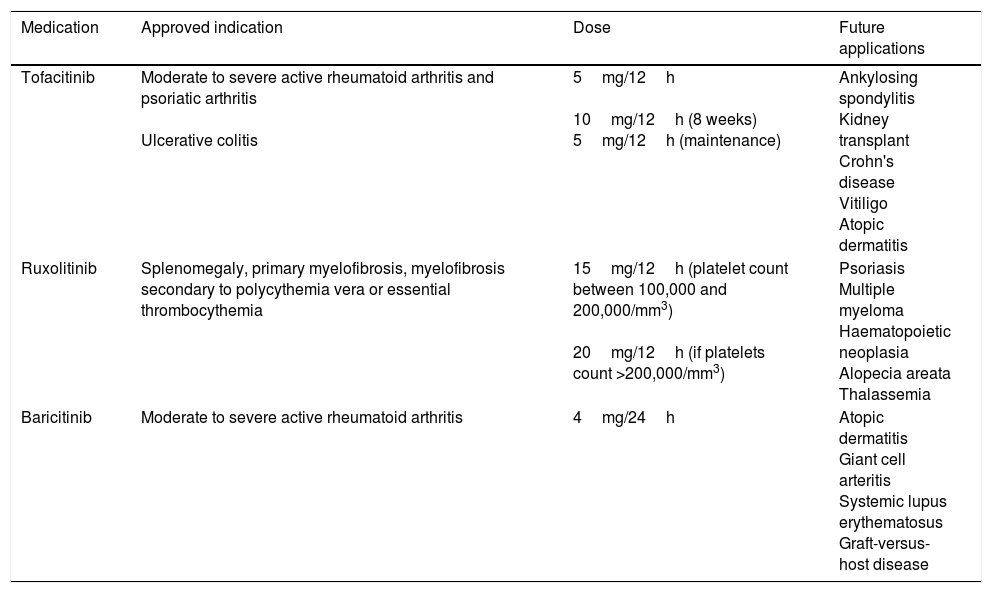
The Janus kinase (JAK) pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. There are a lot of proinflammatory cytokines involved in such diseases using this pathway to transduce intracellular signals. In the last years, JAK inhibitors (jakinibs) have appeared with a great success, showing that these kinds of drugs have a great applicability in clinical practice. Tofacitinib and baricitinib, the first jakinibs approved for the treatment of RA, are being investigated also for treating other autoimmune systemic diseases. Likewise, other jakinibs are in several phases of development. This review analyses the safety and clinical efficacy of the jakinibs, starting with the classics and continuing with next-generation jakinibs.
La ruta de señalización de las proteínas de la familia Janus cinasa (JAK) está implicada en la patogenia de muchas enfermedades inflamatorias y autoinmunitarias, como la artritis reumatoide (AR), la psoriasis y la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Una gran cantidad de citocinas implicadas en el desarrollo de estas enfermedades utilizan esta vía de señalización para transducir señales intracelulares. En los últimos años, la aparición de los inhibidores de las proteínas JAK (jakinibs) ha demostrado que los fármacos relacionados con esta ruta patogénica pueden tener gran aplicabilidad clínica. Tofacitinib y baricitinib, primeros jakinibs aprobados para el tratamiento de la AR, están en estudio para el tratamiento de otras enfermedades autoinmunitarias. Asimismo, otros jakinibs se encuentran en diferentes fases de desarrollo. En este trabajo se revisan los principales aspectos en cuanto a eficacia, interacciones farmacológicas y seguridad tanto de los jakinibs clásicos como de los de nueva generación.