To analyse the association between interferon-1α (INF1α), interleukin-10 (IL-10) and BLyS concentrations and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional, observational study of 142 SLE patients and 34 healthy controls was performed, through a complete blood and urine test and review of their medical history. Serum concentration of INF1α, IL-10 and BLyS was determined by colorimetric methods. A biostatistical analysis was performed with R (3.3.2).
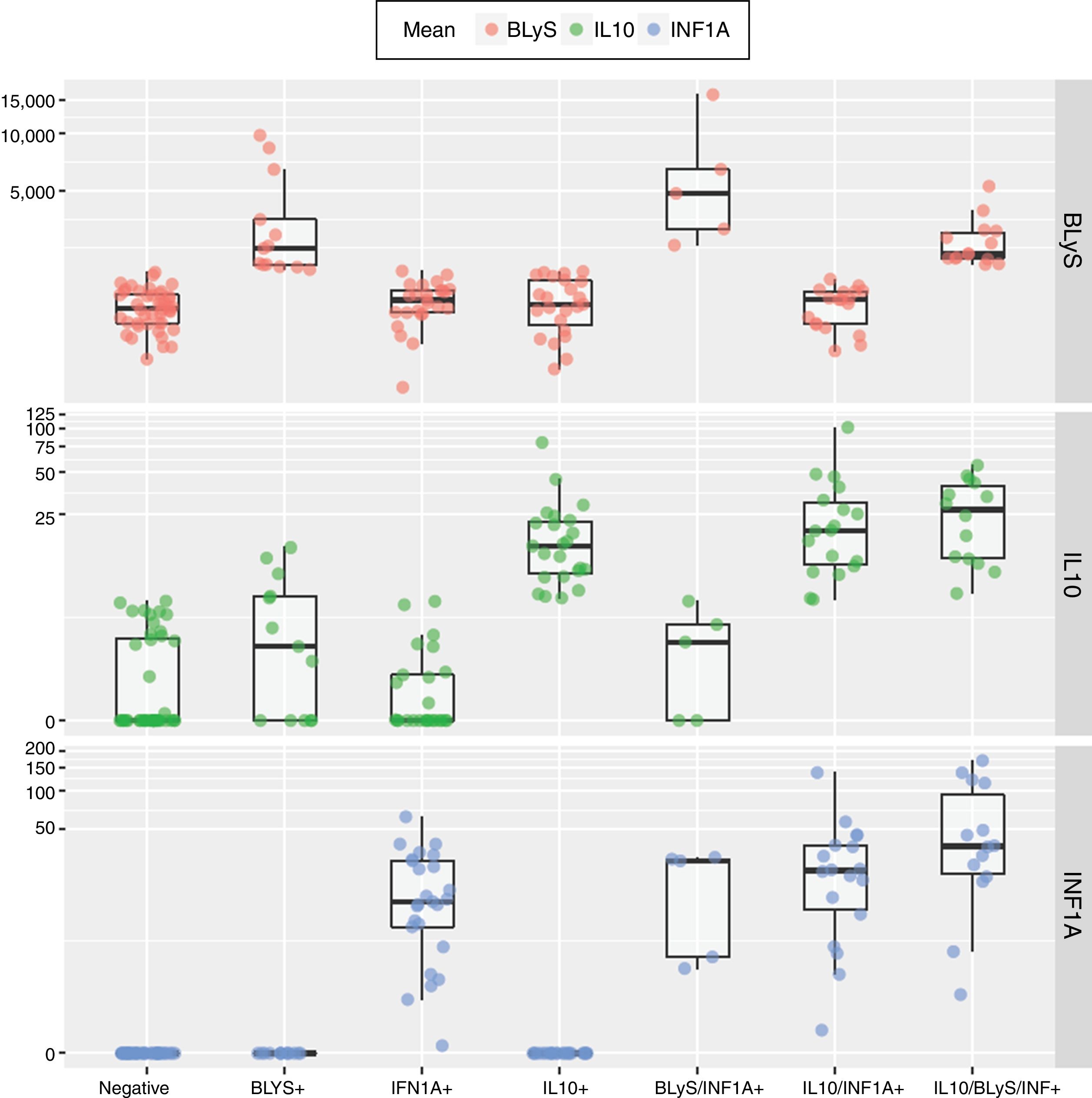
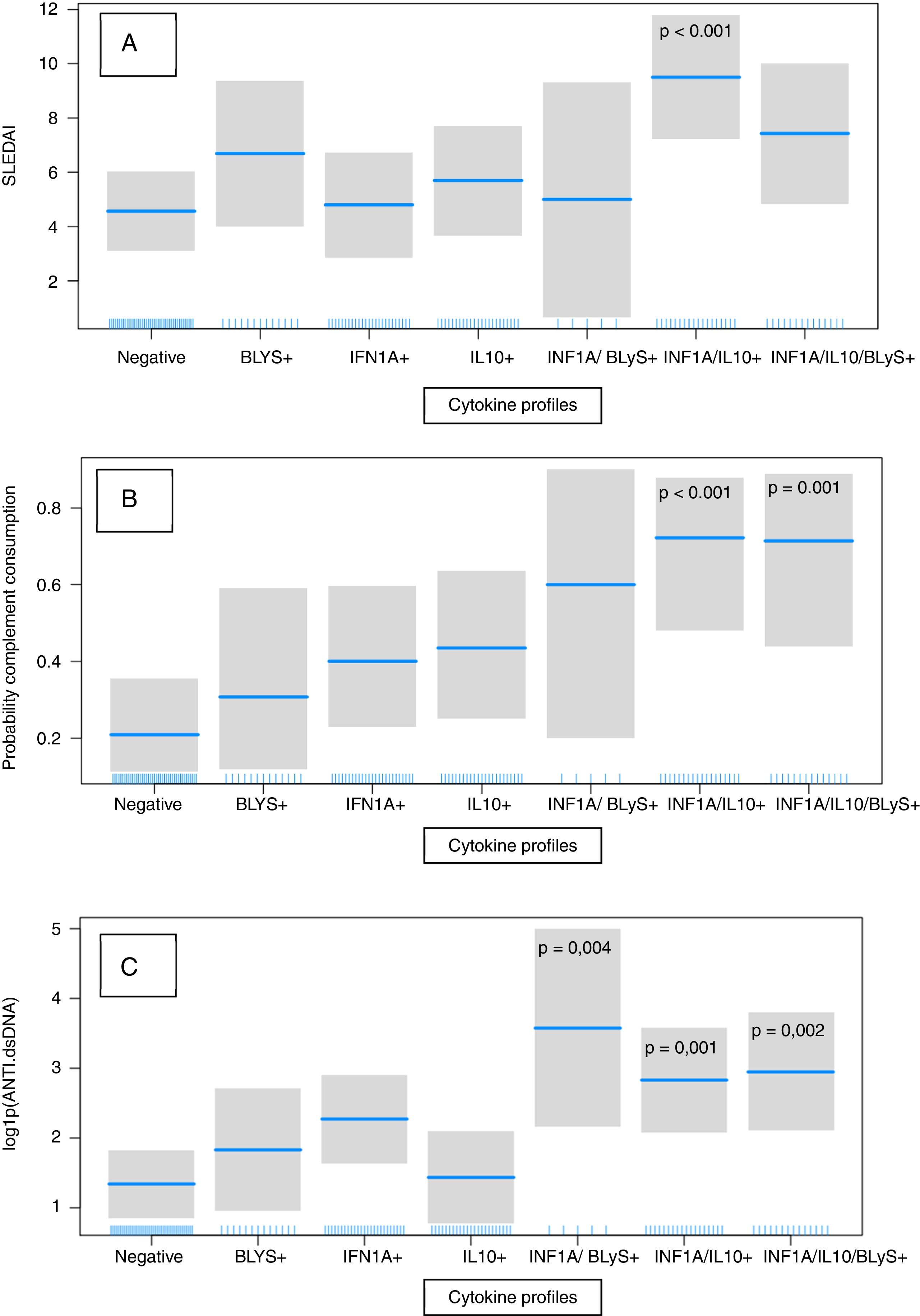
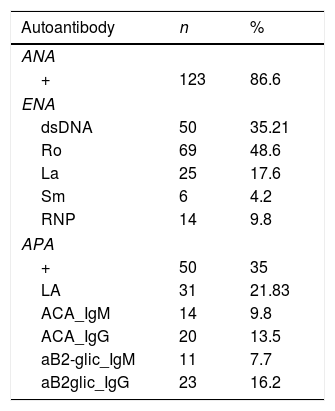
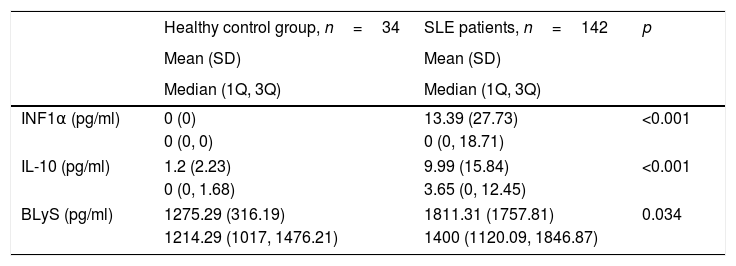
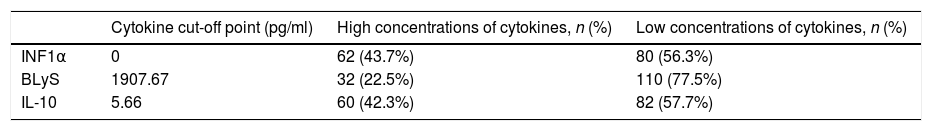
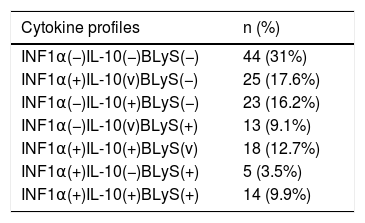
Results69% of our SLE patients showed at least one cytokine increased. INF1α, IL-10 and BLyS are higher in SLE patients than in healthy controls (p<0.001, p=0.005 and p=.043, respectively), being INF1α the most frequent. Patients were categorised according to low or high concentrations of the three cytokines. We found a significant association between increased IL-10/INF1α concentrations and a higher clinical activity measured by SELENA-SLEDAI (p<0.0001) and, to a lesser extent, an association with increased INF1α/IL-10/BLyS concentrations. Elevated levels of IL-10/INF1α and INF1α/IL-10/BLyS related to increased C3-C4 consumption (p<0.001 and p=0.001, respectively) and anti-dsDNA titres (p=0.001 and p=0.002, respectively). Elevated INF1α/BLyS related to higher anti-dsDNA titres (p=0.004) and ENA positivity (p<0.001). Increased levels of INF1α/IL-10/BLyS related to positivity of ANAs (p<0.001) and APL (p=0.004).
ConclusionsINF1α, IL-10 and BLyS are higher in SLE patients than in healthy controls. Increased IL-10 levels, regardless of whether or not there were also increased levels of BLyS and/or INF1α, was the cytokine that best fit with clinical activity in SLE measured with classic methods.
Analizar la asociación entre concentraciones de interferón-1α (INF1α), interleucina 10 (IL-10) y BLyS con la actividad clínica en el lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES).
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional transversal de 142 pacientes con LES y 34 controles sanos mediante analítica de sangre y orina y revisión de la historia clínica. La concentración sérica de citocinas se determinó mediante métodos colorimétricos. El análisis bioestadístico se realizó con R (3.3.2).
ResultadosEl 69% de pacientes mostraron al menos una citocina aumentada. Las tres citocinas están más elevadas en pacientes que en controles (p<0,001, p=0,005 y p=0,043), siendo INF1α el más frecuente. Los pacientes fueron categorizados según las concentraciones de las tres citocinas. Encontramos una asociación significativa entre concentraciones elevadas de IL-10/INF1α y una mayor actividad clínica según SELENA-SLEDAI (p<0,0001) y, en menor medida, con concentraciones aumentadas de INF1α/IL-10/BLyS. Concentraciones elevadas de IL-10/INF1α e INF1α/IL-10/BLyS se relacionaron con un mayor consumo de C3-C4 (p<0,001 y p=0,001) y títulos elevados de anti-dsDNA (p=0,001 y p=0,002). Concentraciones elevadas de INF1α/BLyS se relacionaron con títulos más altos de anti-dsDNA (p=0,004) y positividad ENA (p<0,001). Concentraciones altas de INF1α/IL-10/BLyS se relacionaron con la positividad de ANA (p<0,001) y anticuerpos antifosfolípidos (p=0,004).
ConclusionesINF1α, IL-10 y BLyS están más elevados en pacientes con LES que en controles sanos. El aumento de IL-10, asociado o no a aumento de BLyS y/o INF1α, es la citocina que mejor se ajusta a la actividad clínica del LES medida con métodos clásicos.