To describe the pattern of drug use among men who have sex with men (MSM) living in Spain and its association with sexual risk practices.
Material and methodThe European MSM Internet Survey was implemented in 2010 in 38 European countries on websites for MSM and collected data on sociodemographics, sexual behavior, and other sexual health variables. The association between unprotected anal intercourse (UAI) with casual partners and drug consumption was evaluated using multivariate logistic regression models.
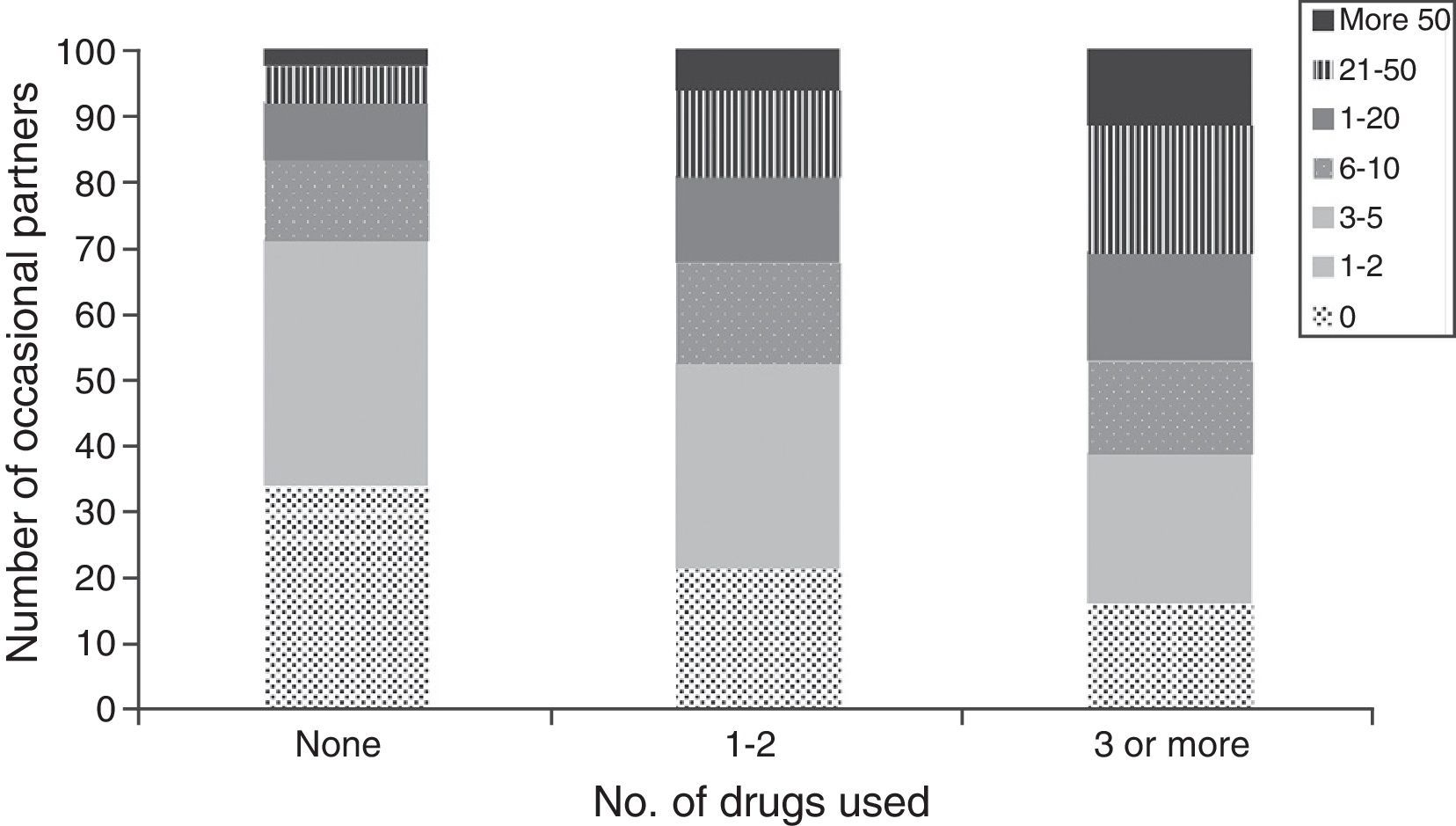
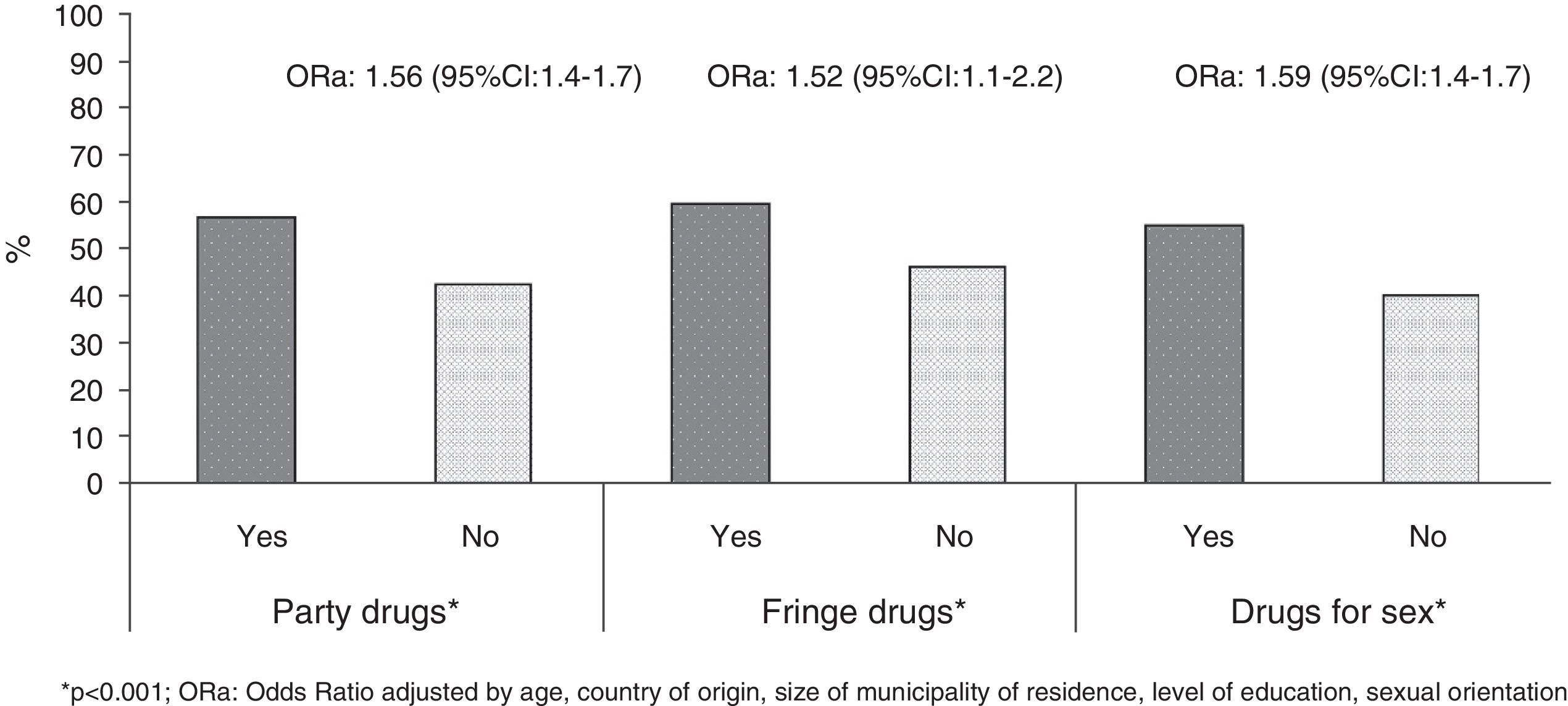
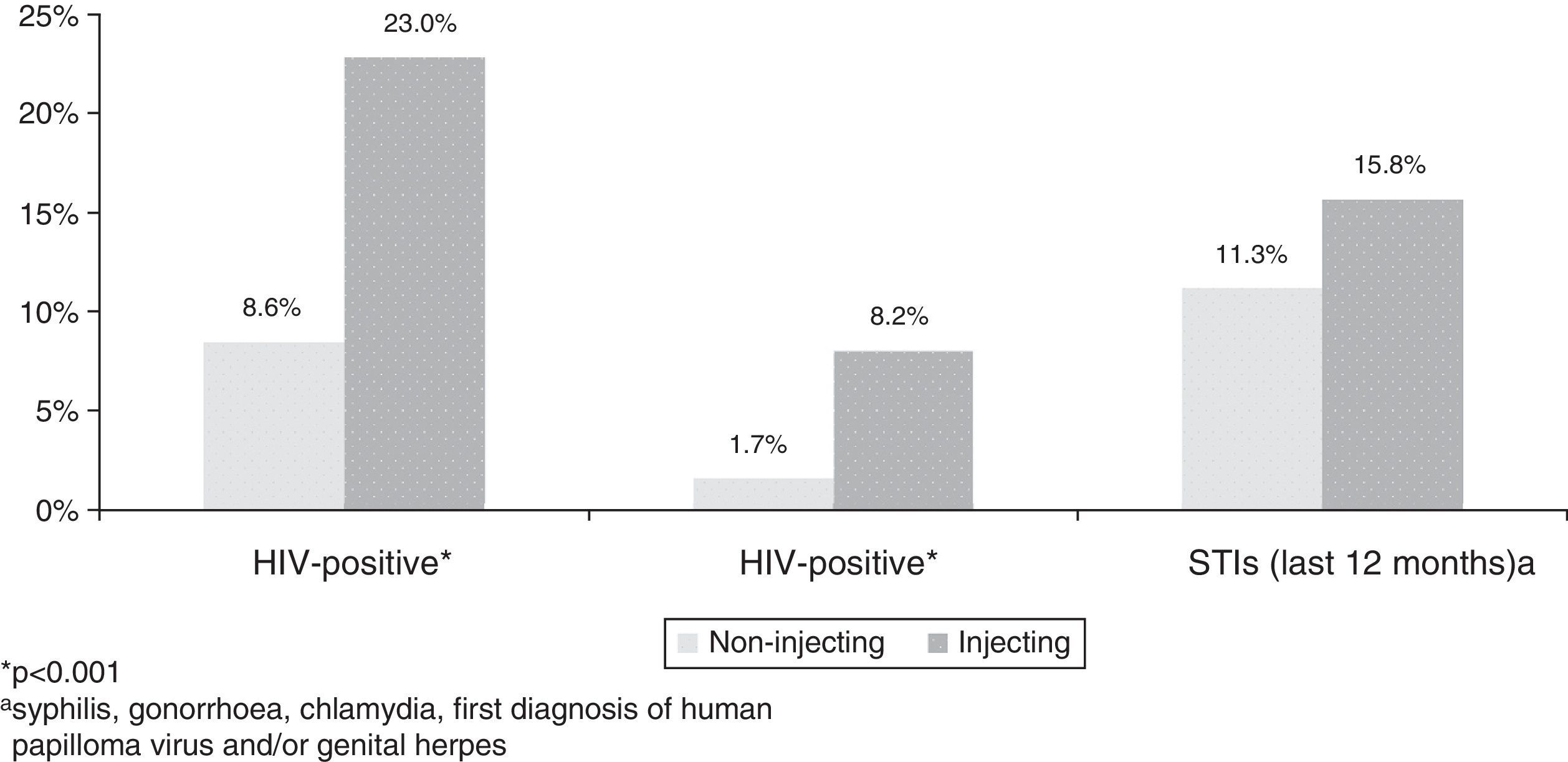
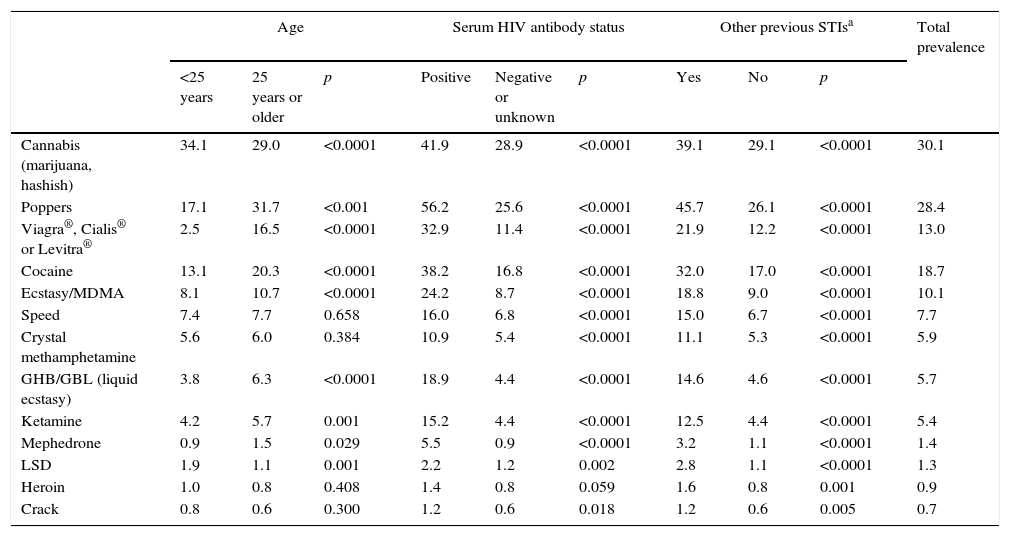
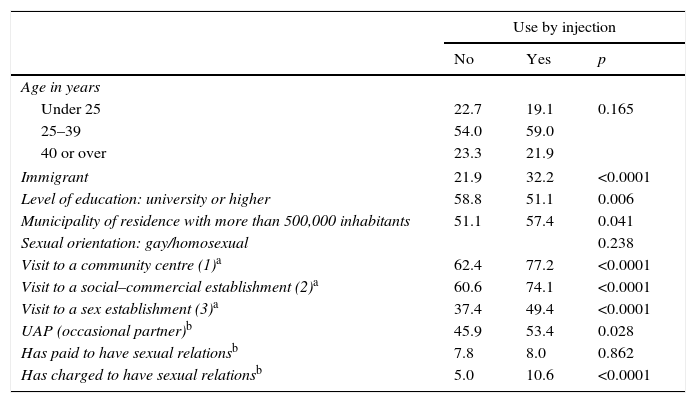
ResultsAmong the 13,111 participants, most consumed drugs were cannabis (30.1%), popper (28.4%) and cocaine (18.7%). The risk of UAI with casual partners was 1.5 among those who had used drugs in relation to the other participants. The proportion of MSM who had injected drugs at least once in life was 2.5%, and 1.4% in the last 12 months. The prevalence of UAI with casual partners (53.4%), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (23%), hepatitis C (8.2%) and sexually transmitted infections (STI) (15.8%) was higher in MSM injectors related to those who had not used injected drugs (p<.05).
ConclusionsThe results of this study confirm a high prevalence of drug use in MSM and their relationship to sexual risk behavior. Although the use of injected drugs in MSM is a minority, this group reported a higher level of sexual risk behaviors, self-reported HIV, hepatitis C and other STI.
Describir el patrón de uso de drogas en hombres que tienen relaciones sexuales con hombres (HSH) residentes en España y su asociación con las prácticas de riesgo sexual.
Material y métodoLa Encuesta Europea por Internet para HSH se implementó en 2010 en 38 países europeos y recogió información sociodemográfica y sobre conducta y salud sexual, entre otras. Mediante modelos de regresión logística multivariante se evaluó la asociación entre la variable penetración anal desprotegida (PANP) con parejas ocasionales y el consumo de drogas.
ResultadosEntre los 13.111 HSH encuestados, el cannabis fue la droga consumida con más frecuencia en los últimos 12 meses (30,1%), seguido del popper (28,4%) y la cocaína (18,7%). Los modelos de regresión logística ajustados mostraron un riesgo de PANP de 1,5 entre los consumidores de drogas en relación con los que no las habían consumido. El 2,5% de los HSH se había inyectado drogas alguna vez en la vida, y el 1,4%, en los últimos 12 meses. La prevalencia de PANP con parejas ocasionales (53,4%), de infección por el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH) (23%), de hepatitis C (8,2%) y de infecciones de transmisión sexual (ITS) (15,8%) fue superior en HSH inyectores con respecto al resto de los participantes (p<0,05).
ConclusionesSe confirma una elevada prevalencia de consumo de drogas en HSH y su asociación con las conductas sexuales de riesgo. Aunque el uso de la vía inyectada en HSH es minoritario, el subgrupo de HSH inyectores presenta una mayor prevalencia de conductas sexuales de riesgo, VIH, hepatitis C y otras ITS.