Cluster headache (CR) is the most severe human headache and is chronic in 10%–20% of patients, and 10% can become refractory to all effective drugs. In this scenario, surgical procedures are indicated: radiofrequencies of the sphenopalatine ganglion ipsilateral to pain (RF-SPG), bilateral stimulation of the occipital nerves (NOM-S) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the ipsilateral posterior hypothalamus. The efficacy and safety of each of these procedures has been specifically analyzed, but the progress of a series of patients following this surgical route in order of aggressiveness has not been described.
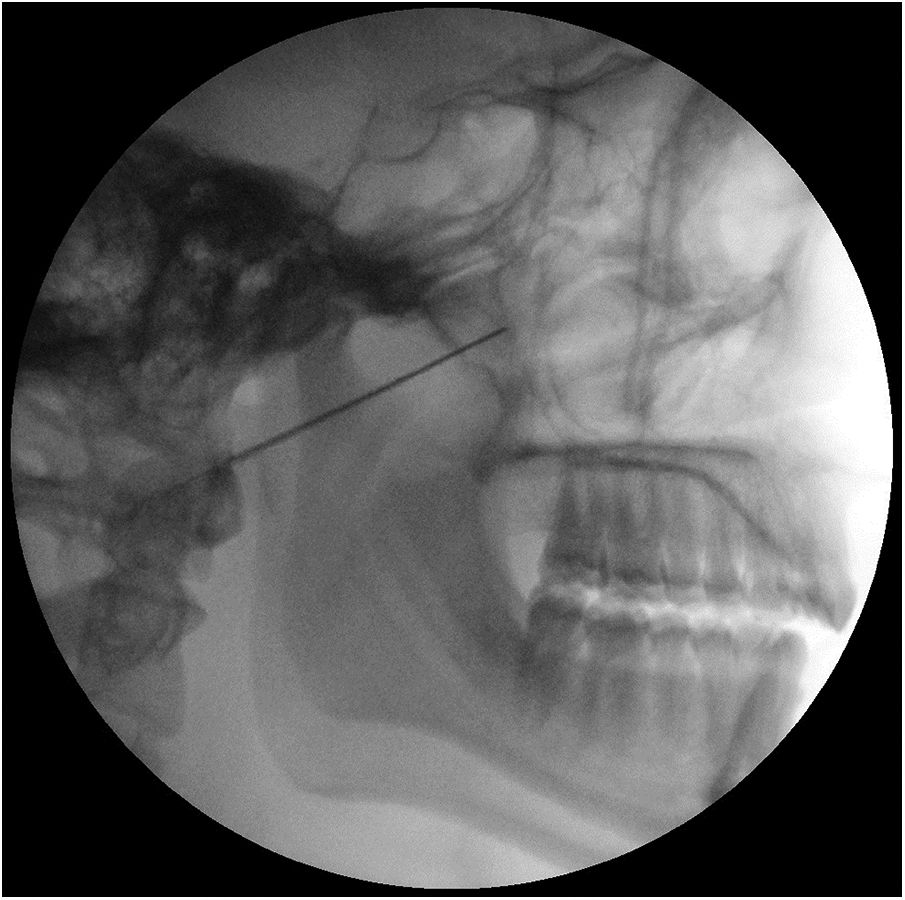
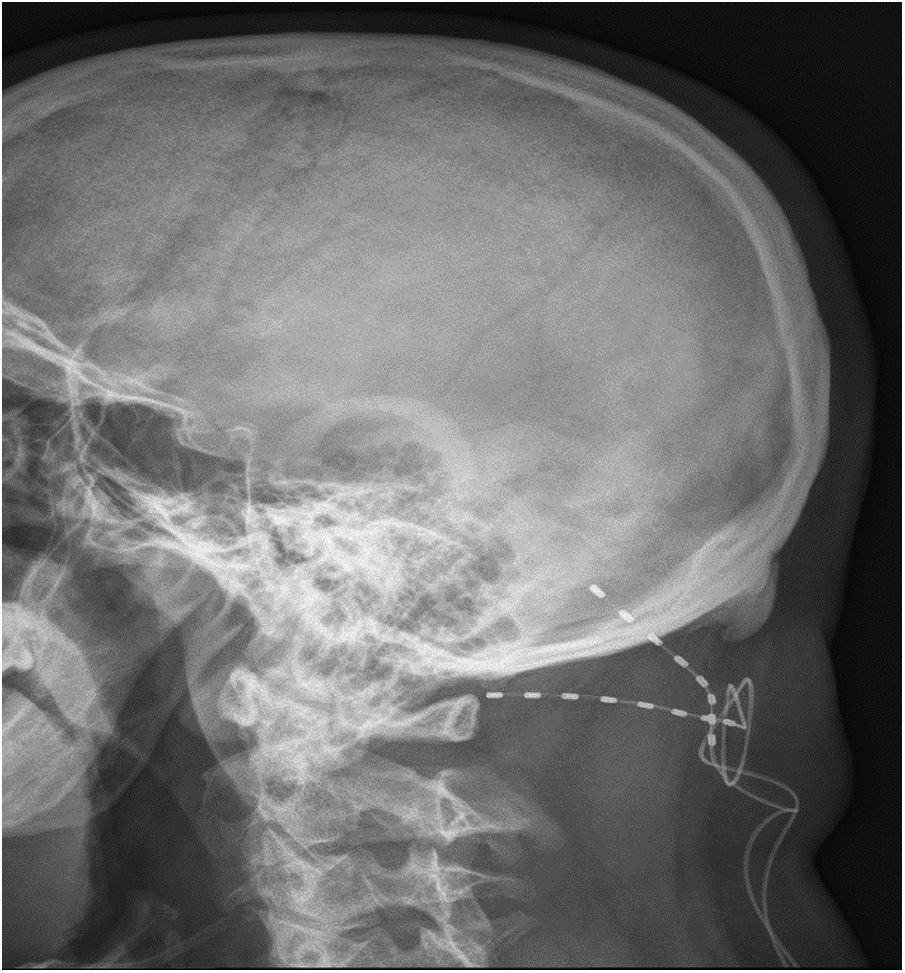
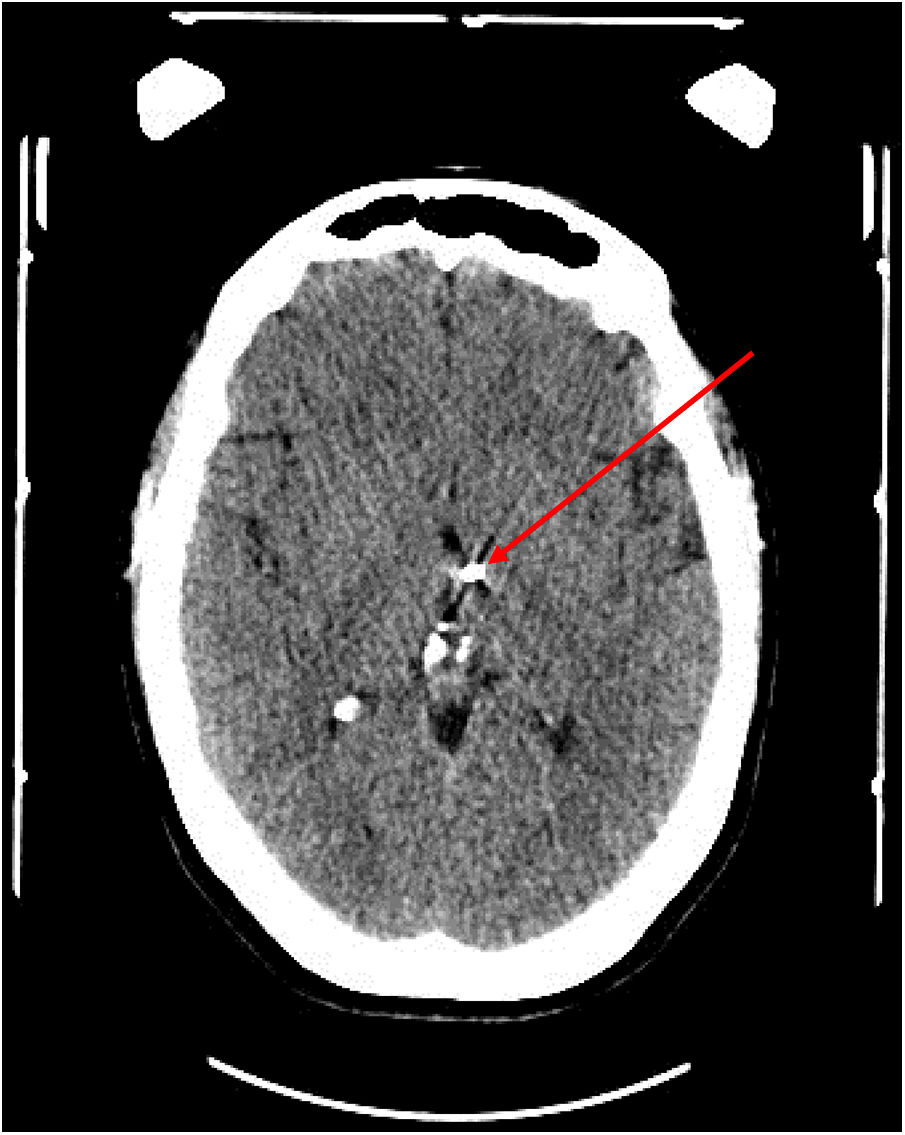
PatientsPatients with chronic and refractory CR according to the criteria of the European Headache Federation. The patients underwent RF-SPG, NOM-S sequentially if the previous procedure had been ineffective, and DBS if the previous procedure had been ineffective.
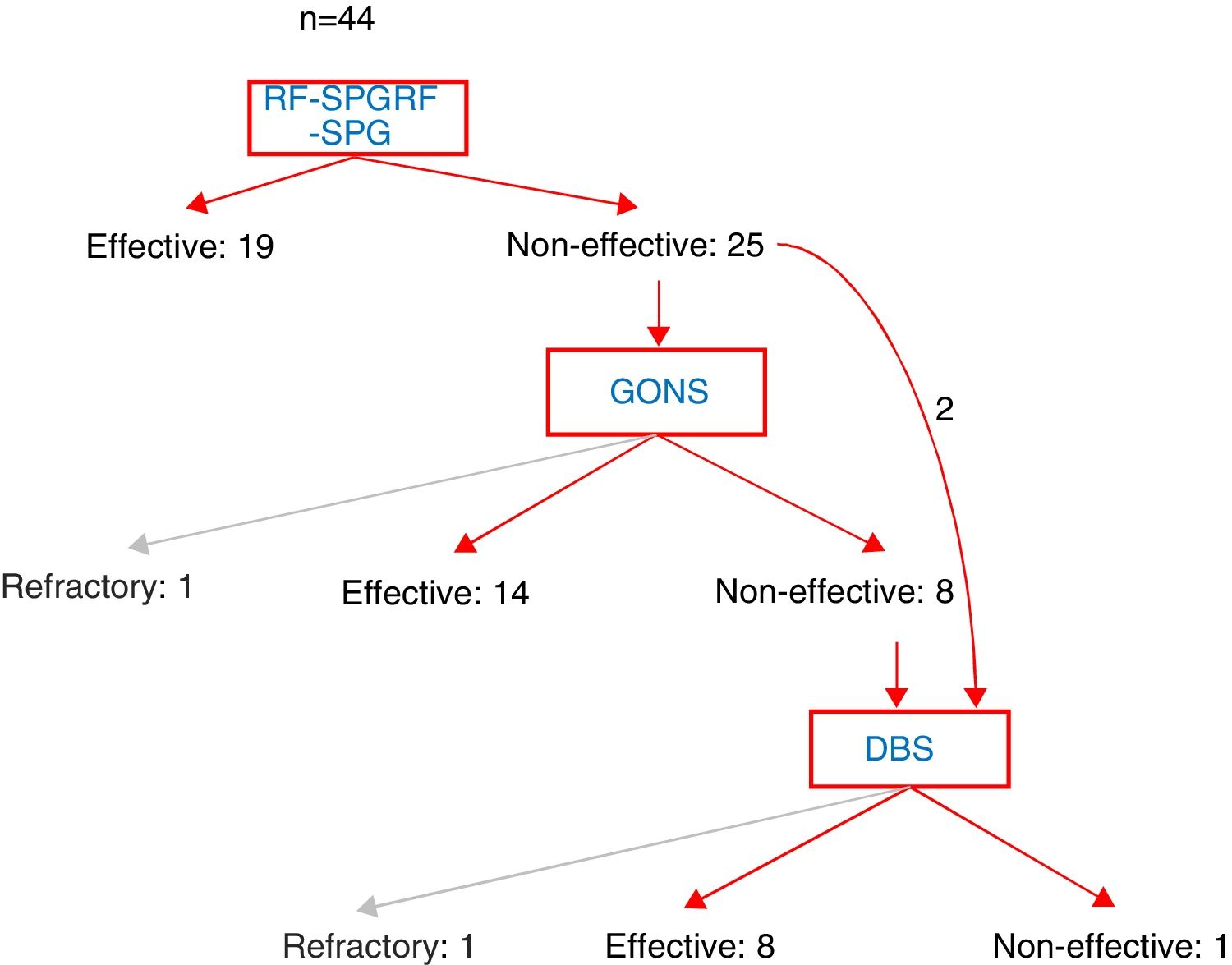
ResultsWe prospectively included 44 patients between November 2003 and June 2018 with an average age of 38.3 years; 70% were men. The mean follow-up was 87.4 months. Nineteen patients responded to 74 procedures of RF-SPG (33.3%). Of the remaining 25 patients, a NOM-S device was implanted in 22, showing an efficacy of 50%. Finally, 9 patients underwent ECP of the ipsilateral lower-posterior hypothalamus with an efficacy of 88.8%. No serious complications were found following any of these three procedures.
ConclusionsThe sequential application of these three surgical procedures succeeded in reversing the serious situation of chronic CR refractory to an episodic CR in 93% of patients with acceptable surgical morbidity.
La cefalea en racimos (CR) es la cefalea humana más grave y se cronifica en un 10-20% de pacientes, pudiendo llegar a ser refractaria a todos los fármacos eficaces en un 10% de ellos. En este escenario se indican procedimientos quirúrgicos: radiofrecuencias del ganglio esfenopalatino ipsilateral al dolor (RF-GEFP), estimulación bilateral de los nervios occipitales (E-NOM) y estimulación cerebral profunda (ECP) del hipotálamo postero-inferior ipsilateral. Se ha analizado específicamente la eficacia y seguridad de cada uno de ellas, pero no se ha descrito la evolución de una serie de pacientes siguiendo este itinerario quirúrgico por orden de agresividad.
PacientesPacientes con CR crónica y refractaria según los criterios de la European Headache Federation. Fueron sometidos secuencialmente a RF-GEFP, E-NOM si ineficacia del anterior y ECP si ineficacia del anterior.
ResultadosIncluimos prospectivamente 44 pacientes entre Noviembre de 2003 y Junio de 2018 con una edad media de 38,3 años siendo el 70% hombres. El seguimiento medio fue de 87.4 meses. Respondieron a 74 procedimientos de RF-GEFP 19 pacientes (33.3%). De los 25 restantes, se implantó un dispositivo de E-NOM en 22 de ellos, mostrando una eficacia del 50%. Finalmente, se sometieron a ECP del hipotálamo postero-inferior ipsilateral 9 pacientes con una eficacia del 88.8%. No se constataron complicaciones graves en ninguno de los tres procedimientos.
ConclusionesLa aplicación secuencial de los tres procedimientos quirúrgicos logró revertir la grave situación de CR crónica y refractaria a CR episódica en el 93% de los pacientes con una morbilidad quirúrgica aceptable.